Quickstart: Create a NAT gateway using Azure PowerShell
In this quickstart, learn how to create a NAT gateway by using PowerShell. The NAT Gateway service provides outbound connectivity for virtual machines in Azure.
Prerequisites
An Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
Azure Cloud Shell or Azure PowerShell.
The steps in this quickstart run the Azure PowerShell cmdlets interactively in Azure Cloud Shell. To run the commands in the Cloud Shell, select Open Cloudshell at the upper-right corner of a code block. Select Copy to copy the code and then paste it into Cloud Shell to run it. You can also run the Cloud Shell from within the Azure portal.
You can also install Azure PowerShell locally to run the cmdlets. The steps in this article require Azure PowerShell module version 5.4.1 or later. Run
Get-Module -ListAvailable Azto find your installed version. If you need to upgrade, see Update the Azure PowerShell module.
Create a resource group
Create a resource group with New-AzResourceGroup. An Azure resource group is a logical container into which Azure resources are deployed and managed.
The following example creates a resource group named test-rg in the eastus2 location:
$rsg = @{
Name = 'test-rg'
Location = 'eastus2'
}
New-AzResourceGroup @rsg
Create the NAT gateway
In this section we create the NAT gateway and supporting resources.
To access the Internet, you need one or more public IP addresses for the NAT gateway. Use New-AzPublicIpAddress to create a public IP address resource named public-ip-nat in test-rg.
Create a global Azure NAT gateway with New-AzNatGateway. The result of this command will create a gateway resource named nat-gateway that uses the public IP address public-ip-nat. The idle timeout is set to 10 minutes.
Create a virtual network named vnet-1 with a subnet named subnet-1 using New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig in the test-rg using New-AzVirtualNetwork. The IP address space for the virtual network is 10.0.0.0/16. The subnet within the virtual network is 10.0.0.0/24.
Create an Azure Bastion host named bastion to access the virtual machine. Use New-AzBastion to create the bastion host. Create a public IP address for the bastion host with New-AzPublicIpAddress.
## Create public IP address for NAT gateway ##
$ip = @{
Name = 'public-ip-nat'
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Location = 'eastus2'
Sku = 'Standard'
AllocationMethod = 'Static'
Zone = 1,2,3
}
$publicIP = New-AzPublicIpAddress @ip
## Create NAT gateway resource ##
$nat = @{
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Name = 'nat-gateway'
IdleTimeoutInMinutes = '10'
Sku = 'Standard'
Location = 'eastus2'
PublicIpAddress = $publicIP
}
$natGateway = New-AzNatGateway @nat
## Create subnet config and associate NAT gateway to subnet##
$subnet = @{
Name = 'subnet-1'
AddressPrefix = '10.0.0.0/24'
NatGateway = $natGateway
}
$subnetConfig = New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig @subnet
## Create Azure Bastion subnet. ##
$bastsubnet = @{
Name = 'AzureBastionSubnet'
AddressPrefix = '10.0.1.0/26'
}
$bastsubnetConfig = New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig @bastsubnet
## Create the virtual network ##
$net = @{
Name = 'vnet-1'
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Location = 'eastus2'
AddressPrefix = '10.0.0.0/16'
Subnet = $subnetConfig,$bastsubnetConfig
}
$vnet = New-AzVirtualNetwork @net
## Create public IP address for bastion host. ##
$ip = @{
Name = 'public-ip'
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Location = 'eastus2'
Sku = 'Standard'
AllocationMethod = 'Static'
Zone = 1,2,3
}
$publicip = New-AzPublicIpAddress @ip
## Create bastion host ##
$bastion = @{
Name = 'bastion'
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
PublicIpAddressRgName = 'test-rg'
PublicIpAddressName = 'public-ip'
VirtualNetworkRgName = 'test-rg'
VirtualNetworkName = 'vnet-1'
Sku = 'Basic'
}
New-AzBastion @bastion
The bastion host can take several minutes to deploy. Wait for the bastion host to deploy before moving on to the next section.
Virtual machine
In this section, you'll create a virtual machine to test the NAT gateway and verify the public IP address of the outbound connection.
Create a network interface with New-AzNetworkInterface.
Set an administrator username and password for the VM with Get-Credential.
Create the virtual machine with:
# Set the administrator and password for the VMs. ##
$cred = Get-Credential
## Place the virtual network into a variable. ##
$vnet = Get-AzVirtualNetwork -Name 'vnet-1' -ResourceGroupName 'test-rg'
## Create network interface for virtual machine. ##
$nic = @{
Name = "nic-1"
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Location = 'eastus2'
Subnet = $vnet.Subnets[0]
}
$nicVM = New-AzNetworkInterface @nic
## Create a virtual machine configuration for VMs ##
$vmsz = @{
VMName = 'vm-1'
VMSize = 'Standard_DS1_v2'
}
$vmos = @{
ComputerName = 'vm-1'
Credential = $cred
}
$vmimage = @{
PublisherName = 'Canonical'
Offer = '0001-com-ubuntu-server-jammy'
Skus = '22_04-lts-gen2'
Version = 'latest'
}
$vmConfig = New-AzVMConfig @vmsz `
| Set-AzVMOperatingSystem @vmos -Linux `
| Set-AzVMSourceImage @vmimage `
| Add-AzVMNetworkInterface -Id $nicVM.Id
## Create the virtual machine for VMs ##
$vm = @{
ResourceGroupName = 'test-rg'
Location = 'eastus2'
VM = $vmConfig
}
New-AzVM @vm
Wait for the virtual machine creation to complete before moving on to the next section.
Test NAT gateway
In this section, you test the NAT gateway. You first discover the public IP of the NAT gateway. You then connect to the test virtual machine and verify the outbound connection through the NAT gateway.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Public IP. Select Public IP addresses in the search results.
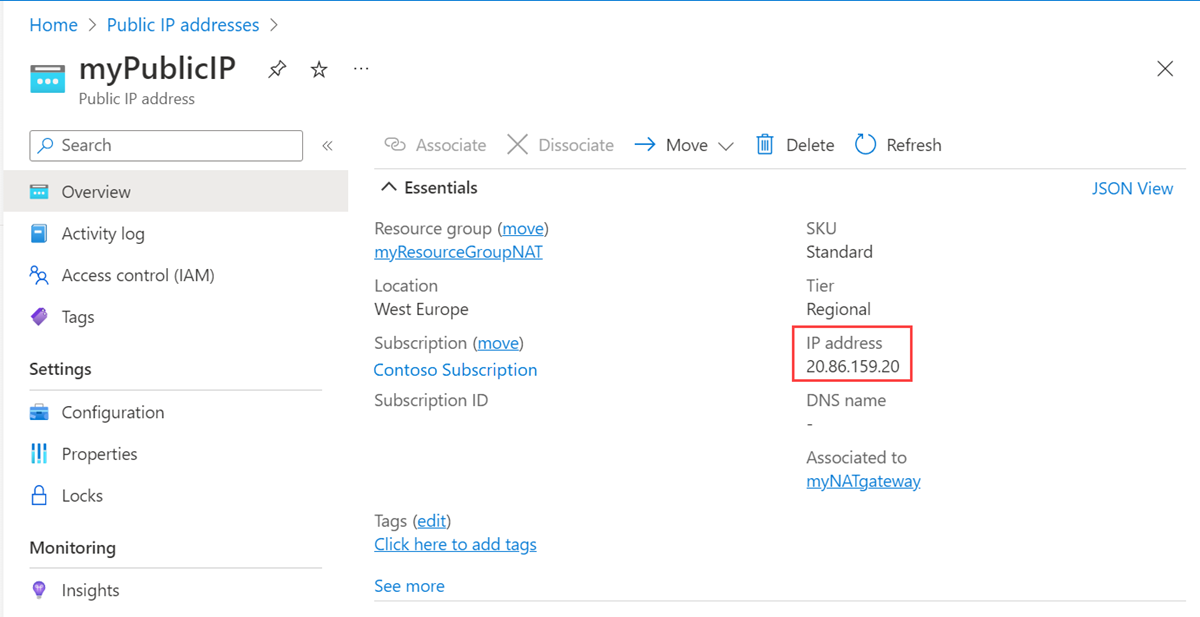
Select public-ip-nat.
Make note of the public IP address:
In the search box at the top of the portal, enter Virtual machine. Select Virtual machines in the search results.
Select vm-1.
On the Overview page, select Connect, then select the Bastion tab.
Select Use Bastion.
Enter the username and password entered during VM creation. Select Connect.
In the bash prompt, enter the following command:
curl ifconfig.meVerify the IP address returned by the command matches the public IP address of the NAT gateway.
azureuser@vm-1:~$ curl ifconfig.me 20.7.200.36
Clean up resources
If you're not going to continue to use this application, delete the virtual network, virtual machine, and NAT gateway with the following steps:
Remove-AzResourceGroup -Name 'test-rg' -Force
Next steps
For more information on Azure NAT Gateway, see:
