Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article helps you create an Azure VPN gateway using PowerShell. A VPN gateway is used when creating a VPN connection to your on-premises network. You can also use a VPN gateway to connect virtual networks. For more comprehensive information about some of the settings in this article, see Create a VPN gateway - portal.
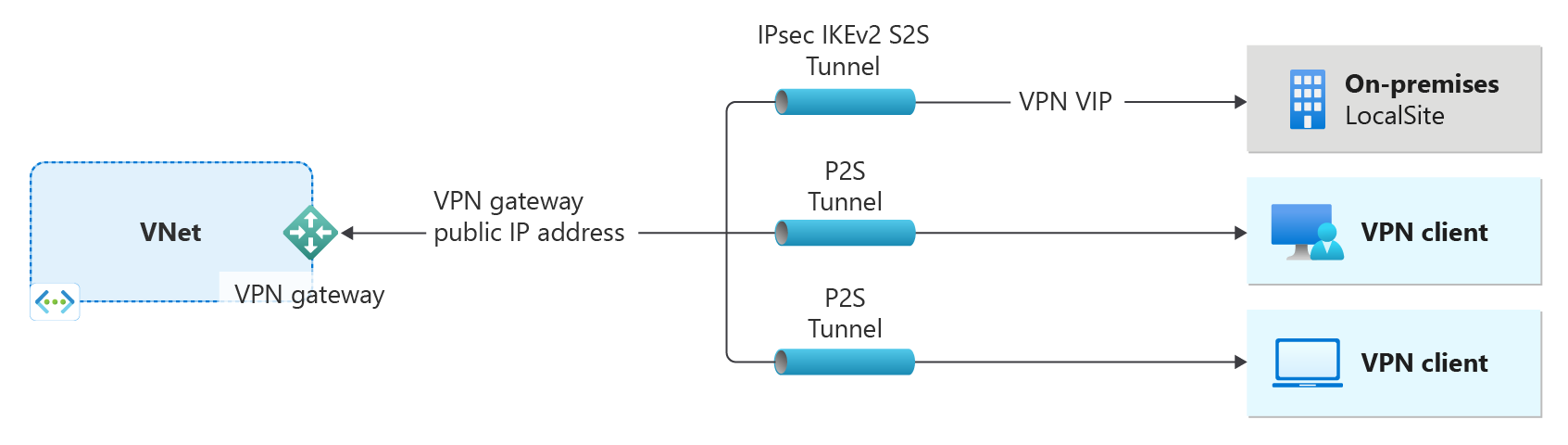
- The left side of the diagram shows the virtual network and the VPN gateway that you create by using the steps in this article.
- You can later add different types of connections, as shown on the right side of the diagram. For example, you can create site-to-site and point-to-site connections. To view different design architectures that you can build, see VPN gateway design.
The steps in this article create a virtual network, a subnet, a gateway subnet, and a route-based, zone-redundant active-active mode VPN gateway (virtual network gateway) using the Generation 2 VpnGw2AZ SKU. Once the gateway is created, you can configure connections.
- If you want to create a VPN gateway using the Basic SKU instead, see Create a Basic SKU VPN gateway.
- We recommend that you create an active-active mode VPN gateway when possible. Active-active mode VPN gateways provide better availability and performance than standard mode VPN gateways. For more information about active-active gateways, see About active-active mode gateways.
- For information about availability zones and zone redundant gateways, see What are availability zones?
Note
The steps in this article use the gateway SKU VpnGw2AZ, which is a SKU that supports Azure availability zones. Effective May 2025, all regions will accept an AZ SKU, regardless of whether availability zones are supported in that region. For more information about gateway SKUs, see About gateway SKUs.
Before you begin
These steps require an Azure subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
This article uses PowerShell cmdlets. To run the cmdlets, you can use Azure Cloud Shell. Cloud Shell is a free interactive shell that you can use to run the steps in this article. It has common Azure tools preinstalled and configured to use with your account.
To open Cloud Shell, just select Open Cloudshell from the upper-right corner of a code block. You can also open Cloud Shell on a separate browser tab by going to https://shell.azure.com/powershell. Select Copy to copy the blocks of code, paste them into Cloud Shell, and select the Enter key to run them.
You can also install and run the Azure PowerShell cmdlets locally on your computer. PowerShell cmdlets are updated frequently. If you haven't installed the latest version, the values specified in the instructions may fail. To find the versions of Azure PowerShell installed on your computer, use the Get-Module -ListAvailable Az cmdlet. To install or update, see Install the Azure PowerShell module.
Create a resource group
Create an Azure resource group using the New-AzResourceGroup command. A resource group is a logical container into which Azure resources are deployed and managed. If you're running PowerShell locally, open your PowerShell console with elevated privileges and connect to Azure using the Connect-AzAccount command.
New-AzResourceGroup -Name TestRG1 -Location EastUS
Create a virtual network
If you don't already have a virtual network, create one with New-AzVirtualNetwork. When you create a virtual network, make sure that the address spaces you specify don't overlap any of the address spaces that you have on your on-premises network. If a duplicate address range exists on both sides of the VPN connection, traffic doesn't route the way you might expect it to. Additionally, if you want to connect this virtual network to another virtual network, the address space can't overlap with other virtual network. Take care to plan your network configuration accordingly.
The following example creates a virtual network named VNet1 in the EastUS location:
$virtualnetwork = New-AzVirtualNetwork `
-ResourceGroupName TestRG1 `
-Location EastUS `
-Name VNet1 `
-AddressPrefix 10.1.0.0/16
Create a subnet configuration using the New-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig cmdlet. The FrontEnd subnet isn't used in this exercise. You can substitute your own subnet name.
$subnetConfig = Add-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig `
-Name FrontEnd `
-AddressPrefix 10.1.0.0/24 `
-VirtualNetwork $virtualnetwork
Set the subnet configuration for the virtual network using the Set-AzVirtualNetwork cmdlet.
$virtualnetwork | Set-AzVirtualNetwork
Add a gateway subnet
Virtual network gateway resources are deployed to a specific subnet named GatewaySubnet. The gateway subnet is part of the virtual network IP address range that you specify when you configure your virtual network.
If you don't have a subnet named GatewaySubnet, when you create your VPN gateway, it fails. We recommend that you create a gateway subnet that uses a /27 (or larger). For example, /27 or /26. For more information about the gateway subnet, see VPN Gateway settings - Gateway Subnet.
Important
NSGs on the gateway subnet aren't supported. Associating a network security group to this subnet might cause your virtual network gateway (VPN and ExpressRoute gateways) to stop functioning as expected. For more information about network security groups, see What is a network security group?.
Set a variable for your virtual network.
$vnet = Get-AzVirtualNetwork -ResourceGroupName TestRG1 -Name VNet1
Create the gateway subnet using the Add-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig cmdlet.
Add-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig -Name 'GatewaySubnet' -AddressPrefix 10.1.255.0/27 -VirtualNetwork $vnet
Set the subnet configuration for the virtual network using the Set-AzVirtualNetwork cmdlet.
$vnet | Set-AzVirtualNetwork
Request public IP addresses
A VPN gateway must have a public IP address. When you create a connection to a VPN gateway, this is the IP address that you specify. For active-active mode gateways, each gateway instance has its own public IP address resource. You first request the IP address resource, and then refer to it when creating your virtual network gateway. Additionally, for any gateway SKU ending in AZ, you must also specify the Zone setting. This example specifies a zone-redundant configuration because it specifies all three regional zones.
The IP address is assigned to the resource when the VPN gateway is created. The only time the public IP address changes is when the gateway is deleted and re-created. It doesn't change across resizing, resetting, or other internal maintenance/upgrades of your VPN gateway.
Use the following examples to request a static public IP address for each gateway instance.
$gw1pip1 = New-AzPublicIpAddress -Name "VNet1GWpip1" -ResourceGroupName "TestRG1" -Location "EastUS" -AllocationMethod Static -Sku Standard -Zone 1,2,3
To create an active-active gateway (recommended), request a second public IP address:
$gw1pip2 = New-AzPublicIpAddress -Name "VNet1GWpip2" -ResourceGroupName "TestRG1" -Location "EastUS" -AllocationMethod Static -Sku Standard -Zone 1,2,3
Create the gateway IP address configuration
The gateway configuration defines the subnet and the public IP address to use. Use the following example to create your gateway configuration.
$vnet = Get-AzVirtualNetwork -Name VNet1 -ResourceGroupName TestRG1
$subnet = Get-AzVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig -Name 'GatewaySubnet' -VirtualNetwork $vnet
$gwipconfig1 = New-AzVirtualNetworkGatewayIpConfig -Name gwipconfig1 -SubnetId $subnet.Id -PublicIpAddressId $gw1pip1.Id
$gwipconfig2 = New-AzVirtualNetworkGatewayIpConfig -Name gwipconfig2 -SubnetId $subnet.Id -PublicIpAddressId $gw1pip2.Id
Create the VPN gateway
Creating a gateway can often take 45 minutes or more, depending on the selected gateway SKU. Once the gateway is created, you can create connection between your virtual network and your on-premises location. Or, create a connection between your virtual network and another virtual network.
Create a VPN gateway using the New-AzVirtualNetworkGateway cmdlet. Notice in the examples that both public IP addresses are referenced and the gateway is configured as active-active using the EnableActiveActiveFeature switch. In the example, we add the optional -Debug switch. If you want to create a gateway using a different SKU, see About Gateway SKUs to determine the SKU that best fits your configuration requirements.
New-AzVirtualNetworkGateway -Name VNet1GW -ResourceGroupName TestRG1 `
-Location "East US" -IpConfigurations $gwipconfig1,$gwipconfig2 -GatewayType "Vpn" -VpnType RouteBased `
-GatewaySku VpnGw2AZ -VpnGatewayGeneration Generation2 -EnableActiveActiveFeature -Debug
View the VPN gateway
You can view the VPN gateway using the Get-AzVirtualNetworkGateway cmdlet.
Get-AzVirtualNetworkGateway -Name Vnet1GW -ResourceGroup TestRG1
View gateway IP addresses
Each VPN gateway instance is assigned a public IP address resource. To view the IP address associated with the resource, use the Get-AzPublicIpAddress cmdlet. Repeat for each gateway instance. Active-active gateways have a different public IP address assigned to each instance.
Get-AzPublicIpAddress -Name VNet1GWpip1 -ResourceGroupName TestRG1
Clean up resources
When you no longer need the resources you created, use the Remove-AzResourceGroup command to delete the resource group. This deletes the resource group and all of the resources it contains.
Remove-AzResourceGroup -Name TestRG1
Next steps
Once the gateway is created, you can configure connections.