Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
If your Web Application Firewall (WAF) is blocking requests that should be allowed, there are a few steps you can take.
Start by reviewing the WAF overview and WAF configuration documentation, and ensure WAF monitoring is enabled. These articles explain how the WAF operates, how the rule sets work, and how to access WAF logs.
The OWASP rule sets are designed to be strict out of the box, and to be tuned to suit the specific needs of the application or organization using WAF. It's entirely normal, and expected in many cases, to create exclusions, custom rules, and even disable rules that may be causing issues or false positives. Per-site and per-URI policies allow for these changes to only affect specific sites/URIs. So changes shouldn’t have to affect other sites that may not be running into the same issues.
Understand WAF logs
The purpose of WAF logs is to show every request that WAF matches or blocks. It's a ledger of all evaluated requests that are matched or blocked. If you notice that the WAF blocks a request that it shouldn't (a false positive), you can do a few things. First, narrow down, and find the specific request. Look through the logs to find the specific URI, timestamp, or transaction ID of the request. When you find the associated log entries, you can begin to act on the false positives.
For example, say you have a legitimate traffic containing the string 1=1 that you want to pass through your WAF. If you try the request, the WAF blocks traffic that contains your 1=1 string in any parameter or field. This is a string often associated with a SQL injection attack. You can look through the logs and see the timestamp of the request and the rules that blocked/matched.
In the following example, you can see that four rules are triggered during the same request (using the TransactionId field). The first one says it matched because the user used a numeric/IP URL for the request, which increases the anomaly score by three since it's a warning. The next rule that matched is 942130, which is the one you’re looking for. You can see the 1=1 in the details.data field. This further increases the anomaly score by three again, as it's also a warning. Generally, every rule that has the action Matched increases the anomaly score, and at this point the anomaly score would be six. For more information, see Anomaly scoring mode.
The final two log entries show the request was blocked because the anomaly score was high enough. These entries have a different action than the other two. They show they actually blocked the request. These rules are mandatory and can’t be disabled. They shouldn’t be thought of as rules, but more as core infrastructure of the WAF internals.
{
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/RESOURCEGROUPS/MYRESOURCEGROUP/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/DEMOWAF-V2",
"operationName": "ApplicationGatewayFirewall",
"category": "ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog",
"properties": {
"instanceId": "appgw_3",
"clientIp": "203.0.113.139",
"clientPort": "",
"requestUri": "\/",
"ruleSetType": "OWASP_CRS",
"ruleSetVersion": "3.0.0",
"ruleId": "920350",
"message": "Host header is a numeric IP address",
"action": "Matched",
"site": "Global",
"details": {
"message": "Warning. Pattern match \\\"^[\\\\\\\\d.:]+$\\\" at REQUEST_HEADERS:Host. ",
"data": "40.90.218.160",
"file": "rules\/REQUEST-920-PROTOCOL-ENFORCEMENT.conf\\\"",
"line": "791"
},
"hostname": "vm000003",
"transactionId": "AcAcAcAcAKH@AcAcAcAcAyAt"
}
}
{
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/RESOURCEGROUPS/MYRESOURCEGROUP/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/DEMOWAF-V2",
"operationName": "ApplicationGatewayFirewall",
"category": "ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog",
"properties": {
"instanceId": "appgw_3",
"clientIp": "203.0.113.139",
"clientPort": "",
"requestUri": "\/",
"ruleSetType": "OWASP_CRS",
"ruleSetVersion": "3.0.0",
"ruleId": "942130",
"message": "SQL Injection Attack: SQL Tautology Detected.",
"action": "Matched",
"site": "Global",
"details": {
"message": "Warning. Pattern match \\\"(?i:([\\\\\\\\s'\\\\\\\"`\\\\\\\\(\\\\\\\\)]*?)([\\\\\\\\d\\\\\\\\w]++)([\\\\\\\\s'\\\\\\\"`\\\\\\\\(\\\\\\\\)]*?)(?:(?:=|\\u003c=\\u003e|r?like|sounds\\\\\\\\s+like|regexp)([\\\\\\\\s'\\\\\\\"`\\\\\\\\(\\\\\\\\)]*?)\\\\\\\\2|(?:!=|\\u003c=|\\u003e=|\\u003c\\u003e|\\u003c|\\u003e|\\\\\\\\^|is\\\\\\\\s+not|not\\\\\\\\s+like|not\\\\\\\\s+regexp)([\\\\\\\\s'\\\\\\\"`\\\\\\\\(\\\\\\\\)]*?)(?!\\\\\\\\2)([\\\\\\\\d\\\\\\\\w]+)))\\\" at ARGS:text1. ",
"data": "Matched Data: 1=1 found within ARGS:text1: 1=1",
"file": "rules\/REQUEST-942-APPLICATION-ATTACK-SQLI.conf\\\"",
"line": "554"
},
"hostname": "vm000003",
"transactionId": "AcAcAcAcAKH@AcAcAcAcAyAt"
}
}
{
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/RESOURCEGROUPS/MYRESOURCEGROUP/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/DEMOWAF-V2",
"operationName": "ApplicationGatewayFirewall",
"category": "ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog",
"properties": {
"instanceId": "appgw_3",
"clientIp": "203.0.113.139",
"clientPort": "",
"requestUri": "\/",
"ruleSetType": "",
"ruleSetVersion": "",
"ruleId": "0",
"message": "Mandatory rule. Cannot be disabled. Inbound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Score: 8)",
"action": "Blocked",
"site": "Global",
"details": {
"message": "Access denied with code 403 (phase 2). Operator GE matched 5 at TX:anomaly_score. ",
"data": "",
"file": "rules\/REQUEST-949-BLOCKING-EVALUATION.conf\\\"",
"line": "57"
},
"hostname": "vm000003",
"transactionId": "AcAcAcAcAKH@AcAcAcAcAyAt"
}
}
{
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/RESOURCEGROUPS/MYRESOURCEGROUP/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/DEMOWAF-V2",
"operationName": "ApplicationGatewayFirewall",
"category": "ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog",
"properties": {
"instanceId": "appgw_3",
"clientIp": "203.0.113.139",
"clientPort": "",
"requestUri": "\/",
"ruleSetType": "",
"ruleSetVersion": "",
"ruleId": "0",
"message": "Mandatory rule. Cannot be disabled. Inbound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Inbound Score: 8 - SQLI=5,XSS=0,RFI=0,LFI=0,RCE=0,PHPI=0,HTTP=0,SESS=0): SQL Injection Attack: SQL Tautology Detected.",
"action": "Blocked",
"site": "Global",
"details": {
"message": "Warning. Operator GE matched 5 at TX:inbound_anomaly_score. ",
"data": "",
"file": "rules\/RESPONSE-980-CORRELATION.conf\\\"",
"line": "73"
},
"hostname": "vm000003",
"transactionId": "AcAcAcAcAKH@AcAcAcAcAyAt"
}
}
Fix false positives
With this information, and the knowledge that rule 942130 is the one that matched the 1=1 string, you can do a few things to stop this from blocking your traffic:
Use an exclusion list. For more information about exclusion lists, see WAF exclusion lists.
Disable the rule.
Use an exclusion list
To make an informed decision about handling a false positive, it’s important to familiarize yourself with the technologies your application uses. For example, say there isn't a SQL server in your technology stack, and you're getting false positives related to those rules. Disabling those rules doesn't necessarily weaken your security.
One benefit of using an exclusion list is that only a specific part of a request is being disabled. However, this means that a specific exclusion is applicable to all traffic passing through your WAF because it's a global setting. For example, this could lead to an issue if 1=1 is a valid request in the body for a certain app, but not for others. Another benefit is that you can choose between body, headers, and cookies to be excluded if a certain condition is met, as opposed to excluding the whole request.
Occasionally, there are cases where specific parameters get passed into the WAF in a manner that may not be intuitive. For example, there's a token that gets passed when authenticating using Microsoft Entra ID. __RequestVerificationToken is usually passed in as a request cookie. However, in some cases where cookies are disabled, this token is also passed as a request attribute or arg. If this happens, you need to ensure that __RequestVerificationToken is added to the exclusion list as a Request attribute name as well.
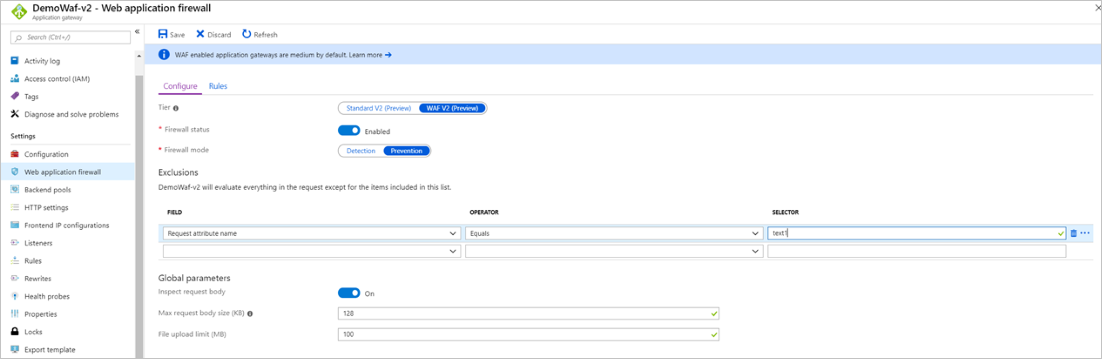
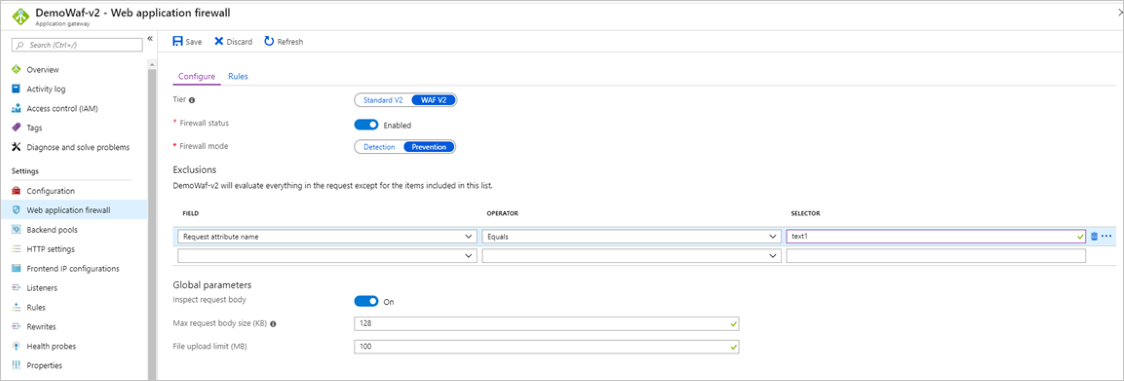
In this example, you want to exclude the Request attribute name that equals text1. This is apparent because you can see the attribute name in the firewall logs: data: Matched Data: 1=1 found within ARGS:text1: 1=1. The attribute is text1. You can also find this attribute name a few other ways, see Finding request attribute names.
You can create exclusions for WAF in Application Gateway at different scope levels. For more information, see Web Application Firewall exclusion lists.
Disable rules
Another way to get around a false positive is to disable the rule that matched on the input the WAF thought was malicious. Since you've parsed the WAF logs and have narrowed the rule down to 942130, you can disable it in the Azure portal. See Customize web application firewall rules through the Azure portal.
One benefit of disabling a rule is that if you know all traffic that contains a certain condition that is normally blocked is valid traffic, you can disable that rule for the entire WAF. However, if it’s only valid traffic in a specific use case, you open up a vulnerability by disabling that rule for the entire WAF since it's a global setting.
If you want to use Azure PowerShell, see Customize web application firewall rules through PowerShell. If you want to use Azure CLI, see Customize web application firewall rules through the Azure CLI.
Record HAR files
You can use your browser or an external tool like Fiddler to record HTTP Archive (HAR) files. HAR files contain information about the requests and responses that your browser makes when loading a web page. This information can be useful for troubleshooting WAF issues.
Tip
It's a good practice to have the HAR file ready when you contact support. The support team can use the HAR file to help diagnose the issue.
To record and save a HAR file in Microsoft Edge, follow these steps
Press F12 or Ctrl+Shift+I to launch Edge Developer tools. You can also launch the tools from the toolbar menu under More tools > Developer tools.
In the Console tab, select Clear console or press Ctrl+L.

Select the Network tab.
Select Clear network log or press Ctrl+L, and then select the Record network log if it's not recording.

Load the webpage that's protected by your WAF for which you want to troubleshoot.
Stop recording by selecting the Stop recording network log.
Select Export HAR (sanitized)... and save the HAR file.

Find request attribute names
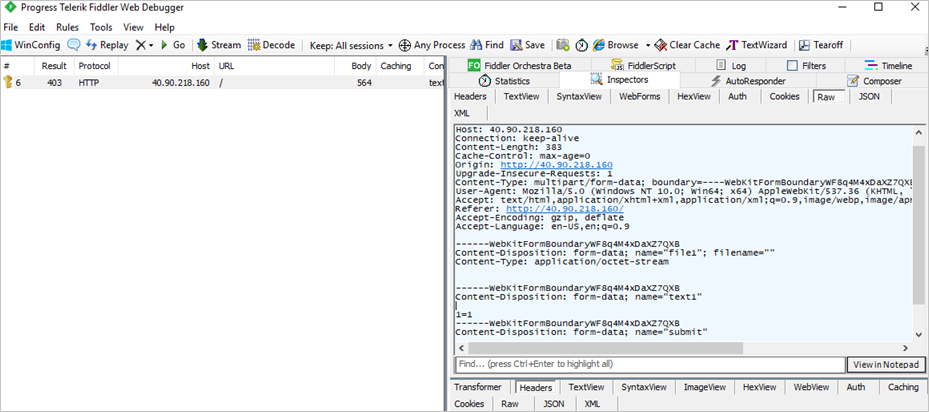
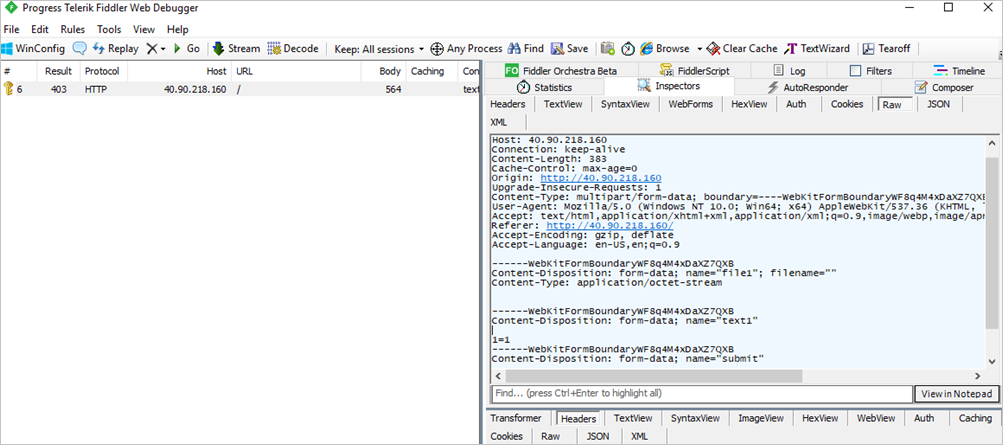
You can use Fiddler to inspect individual requests and determine what specific fields of a web page are called. Using this information helps to exclude certain fields from inspection using Exclusion Lists.
In this example, you can see that the field where the 1=1 string was entered is called text1.
This is a field you can exclude. To learn more about exclusion lists, See Web application firewall exclusion lists. You can exclude the evaluation in this case by configuring the following exclusion:
You can also examine the firewall logs to get the information to see what you need to add to the exclusion list. To enable logging, see Back-end health, resource logs, and metrics for Application Gateway.
Examine the firewall log and view the PT1H.json file for the hour that the request you want to inspect occurred.
In this example, you can see that you have four rules with the same TransactionID, and that they all occurred at the exact same time:
{
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/RESOURCEGROUPS/MYRESOURCEGROUP/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/DEMOWAF-V2",
"operationName": "ApplicationGatewayFirewall",
"category": "ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog",
"properties": {
"instanceId": "appgw_3",
"clientIp": "203.0.113.139",
"clientPort": "",
"requestUri": "\/",
"ruleSetType": "OWASP_CRS",
"ruleSetVersion": "3.0.0",
"ruleId": "920350",
"message": "Host header is a numeric IP address",
"action": "Matched",
"site": "Global",
"details": {
"message": "Warning. Pattern match \\\"^[\\\\\\\\d.:]+$\\\" at REQUEST_HEADERS:Host. ",
"data": "40.90.218.160",
"file": "rules\/REQUEST-920-PROTOCOL-ENFORCEMENT.conf\\\"",
"line": "791"
},
"hostname": "vm000003",
"transactionId": "AcAcAcAcAKH@AcAcAcAcAyAt"
}
}
{
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/RESOURCEGROUPS/MYRESOURCEGROUP/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/DEMOWAF-V2",
"operationName": "ApplicationGatewayFirewall",
"category": "ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog",
"properties": {
"instanceId": "appgw_3",
"clientIp": "203.0.113.139",
"clientPort": "",
"requestUri": "\/",
"ruleSetType": "OWASP_CRS",
"ruleSetVersion": "3.0.0",
"ruleId": "942130",
"message": "SQL Injection Attack: SQL Tautology Detected.",
"action": "Matched",
"site": "Global",
"details": {
"message": "Warning. Pattern match \\\"(?i:([\\\\\\\\s'\\\\\\\"`\\\\\\\\(\\\\\\\\)]*?)([\\\\\\\\d\\\\\\\\w]++)([\\\\\\\\s'\\\\\\\"`\\\\\\\\(\\\\\\\\)]*?)(?:(?:=|\\u003c=\\u003e|r?like|sounds\\\\\\\\s+like|regexp)([\\\\\\\\s'\\\\\\\"`\\\\\\\\(\\\\\\\\)]*?)\\\\\\\\2|(?:!=|\\u003c=|\\u003e=|\\u003c\\u003e|\\u003c|\\u003e|\\\\\\\\^|is\\\\\\\\s+not|not\\\\\\\\s+like|not\\\\\\\\s+regexp)([\\\\\\\\s'\\\\\\\"`\\\\\\\\(\\\\\\\\)]*?)(?!\\\\\\\\2)([\\\\\\\\d\\\\\\\\w]+)))\\\" at ARGS:text1. ",
"data": "Matched Data: 1=1 found within ARGS:text1: 1=1",
"file": "rules\/REQUEST-942-APPLICATION-ATTACK-SQLI.conf\\\"",
"line": "554"
},
"hostname": "vm000003",
"transactionId": "AcAcAcAcAKH@AcAcAcAcAyAt"
}
}
{
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/RESOURCEGROUPS/MYRESOURCEGROUP/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/DEMOWAF-V2",
"operationName": "ApplicationGatewayFirewall",
"category": "ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog",
"properties": {
"instanceId": "appgw_3",
"clientIp": "203.0.113.139",
"clientPort": "",
"requestUri": "\/",
"ruleSetType": "",
"ruleSetVersion": "",
"ruleId": "0",
"message": "Mandatory rule. Cannot be disabled. Inbound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Score: 8)",
"action": "Blocked",
"site": "Global",
"details": {
"message": "Access denied with code 403 (phase 2). Operator GE matched 5 at TX:anomaly_score. ",
"data": "",
"file": "rules\/REQUEST-949-BLOCKING-EVALUATION.conf\\\"",
"line": "57"
},
"hostname": "vm000003",
"transactionId": "AcAcAcAcAKH@AcAcAcAcAyAt"
}
}
{
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/RESOURCEGROUPS/MYRESOURCEGROUP/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.NETWORK/APPLICATIONGATEWAYS/DEMOWAF-V2",
"operationName": "ApplicationGatewayFirewall",
"category": "ApplicationGatewayFirewallLog",
"properties": {
"instanceId": "appgw_3",
"clientIp": "203.0.113.139",
"clientPort": "",
"requestUri": "\/",
"ruleSetType": "",
"ruleSetVersion": "",
"ruleId": "0",
"message": "Mandatory rule. Cannot be disabled. Inbound Anomaly Score Exceeded (Total Inbound Score: 8 - SQLI=5,XSS=0,RFI=0,LFI=0,RCE=0,PHPI=0,HTTP=0,SESS=0): SQL Injection Attack: SQL Tautology Detected.",
"action": "Blocked",
"site": "Global",
"details": {
"message": "Warning. Operator GE matched 5 at TX:inbound_anomaly_score. ",
"data": "",
"file": "rules\/RESPONSE-980-CORRELATION.conf\\\"",
"line": "73"
},
"hostname": "vm000003",
"transactionId": "AcAcAcAcAKH@AcAcAcAcAyAt"
}
}
With your knowledge of how the CRS rule sets work, and that the CRS ruleset 3.0 works with an anomaly scoring system (see Web Application Firewall for Azure Application Gateway) you know that the bottom two rules with the action: Blocked property are blocking based on the total anomaly score. The rules to focus on are the top two.
The first entry is logged because the user used a numeric IP address to navigate to the Application Gateway, which can be ignored in this case.
The second one (rule 942130) is the interesting one. You can see in the details that it matched a pattern (1=1), and the field is named text1. Follow the same previous steps to exclude the Request Attribute Name that equals 1=1.
Find request header names
You can use Fiddler to find request header names. In the following screenshot, you can see the headers for this GET request, which include Content-Type, User-Agent, and so on.
Another way to view request and response headers is to use the developer tools of Microsoft Edge or Google Chrome. For more information, see Record HAR files.
Find request cookie names
If the request contains cookies, the Cookies tab can be selected to view them in Fiddler.
Restrict global parameters to eliminate false positives
Disable request body inspection
By setting Inspect request body to off, the request bodies of your traffic aren't evaluated by your WAF. This may be useful if you know that the request bodies aren’t malicious to your application.
When you disable this option, only the request body bypasses inspection. The headers and cookies are still inspected, unless individual ones are excluded using the exclusion list functionality.
Disable maximum request body limit
By disabling max request body limit, WAF can process large request bodies without rejecting them for exceeding the size limit. This setting is useful if you regularly have large requests.
When you disable this option, the request body will only be inspected up to the maximum request body inspection limit. If there's malicious content in the request beyond the max request body inspection limit, the WAF won't detect it.
Disable maximum file size limits
By disabling the file size limits for your WAF, large files can be uploaded without your WAF rejecting these file uploads. By allowing large files to be uploaded, the risk of your backend being overwhelmed increases. If you know the maximum size a file upload can be, you can set a size limit for file uploads slightly above your expected max size. Limiting the file size to a normal use case for your application is another way to prevent attacks. However, if your file uploads are regularly beyond the maximum enforceable file upload size limit you may need to disable file upload size limits entirely to avoid false positives.
Note
If you know that your app will never need any file upload above a given size, you can restrict that by setting a limit.
Warning
When assigning a new managed ruleset to a WAF policy, all the previous customizations from the existing managed rulesets such as rule state, rule actions, and rule level exclusions will be reset to the new managed ruleset's defaults. However, any custom rules, policy settings, and global exclusions will remain unaffected during the new ruleset assignment.
Firewall Metrics (WAF v1 only)
For v1 Web Application Firewalls, the following metrics are now available in the portal:
- Web Application Firewall Blocked Request Count The number of requests that were blocked
- Web Application Firewall Blocked Rule Count All rules that were matched and the request was blocked
- Web Application Firewall Total Rule Distribution All rules that were matched during evaluation
To enable metrics, select the Metrics tab in the portal, and select one of the three metrics.