Globalization – enhanced configurability
Important
This content is archived and is not being updated. For the latest documentation, see Microsoft Dynamics 365 product documentation. For the latest release plans, see Dynamics 365 and Microsoft Power Platform release plans.
Note
These release notes describe functionality that may not have been released yet. To see when this functionality is planned to release, please review Summary of what’s new. Delivery timelines and projected functionality may change or may not ship (see Microsoft policy). For detailed information about our products, visit the Finance and Operations documentation.
Configurability of features lets partners and customers do extensions and customizations without coding. We continue to extend both the depth and the breadth of configurability and added the following new capabilities in this area:
- Static validations and dynamic performance rules for configuration - This feature prevents performance degradation when partners or customers customize configurations and guide users while doing such customizations.
- Automatic comparison of electronic reporting format executions with baselines defined in task guides - This feature provides us and our partners and customers with automatic test capabilities. These tests focus on business users rather than engineers.
- Relative paths in electronic reporting formulas - This feature allows quick remapping of the format if you need to switch to another data entity or XML node with a similar structure.
- Out-of-the-box configurable free text invoice templates - These templates are for customers and partners around the globe so they can easily modify them to meet their local requirements.
- Configuration-specific parameters for format configurations - This feature allows you to configure any electronic reporting (ER) format to be dependable at the execution stage on master data and settings of the current application. User interface is updated to associate format artifacts and the data of the current application is configured as part of the ER format. Using this user interface, the business user can specify required associations as business data lookups and can store completed lookups separately from the ER format configuration, which does not require knowledge of ER from this kind of business user. These lookups can be migrated from one application instance to another and used at run-time to generate application-specific business documents.
- Support of user defined arguments for calculated fields of ER expressions - This feature allows you to configure ER expressions for any calculated field in the ER format to be dependable on certain parameters. It allows you to reuse this expression many times by calling it with different arguments. Using this feature, the number of expressions in format mapping can be significantly reduced, which simplifies the maintenance of ER configurations.
- Batch import of data - Using this feature, locations of incoming files can be specified as SharePoint folders for ER formats that were designed to parse incoming documents for data import. Such ER formats can now be executed in batch mode. If included in a batch, the ER format takes appropriate files from configured source of files and repeats the data import in the background. Results of exactions are logged for each ER format. Processed files can be moved to different SharePoint folders depending on the results of data import.
- Separated model mapping from taxable documents - This feature allows you to share a set of taxable documents between different Finance and Operations versions.
- Linear equations solver for tax calculation - This requires users to create tax calculation formulas with linear equations. The result will be performance improvements in tax calculation.
- Improving tax configuration usability with reduced number of lookups - While configuring tax in Global Tax Engine (GTE), users can define multiple tables to look up for tax rates, non-deductible percentages, tax components, tax periods, and more. In the real business practice, users want to reduce the number of lookup tables by combining them. For example, data model properties such as Country/Region of Origin, Consumption of Country/Region and Product type determine the nature of the tax transaction, which can be reused in multiple places. In this release, users can add a string-type measure at the line level that can be a lookup, and this measure can be further used in other lookups. It can dramatically reduce the number of lookups users need to maintain and can improve the tax configuration usability. This line-level string-type measure will also be shown in the tax document user interface.
- Simplifying tax setup maintenance with Excel integration - Maintaining tax setup parameters (tax rates, non-deductible percentages, and so on) for tax configurations can be a very effort-intensive task for some countries and types of businesses. Now users can maintain these parameters in Excel files automatically generated based on tax lookup tables and integrated with the tax setup.
- Enabling tax configuration with tax currency and sales tax codes - Companies with multiple tax entities need to maintain different tax currency for tax components used in different tax entities. With the release of this feature, users can define the tax currency for tax components in lookup tables. Users can also maintain the sales tax code in tax setup, map the tax component to the sales tax code in lookup tables, and maintain periods and reporting codes of these sales tax codes.
- Enable configuring the visibility of tax measures in tax documents - Tax formulas may use some intermediate tax measures that do not need to be shown on the Tax document page in Dynamics 365 Finance and Operations, so it is possible to hide these tax measures.
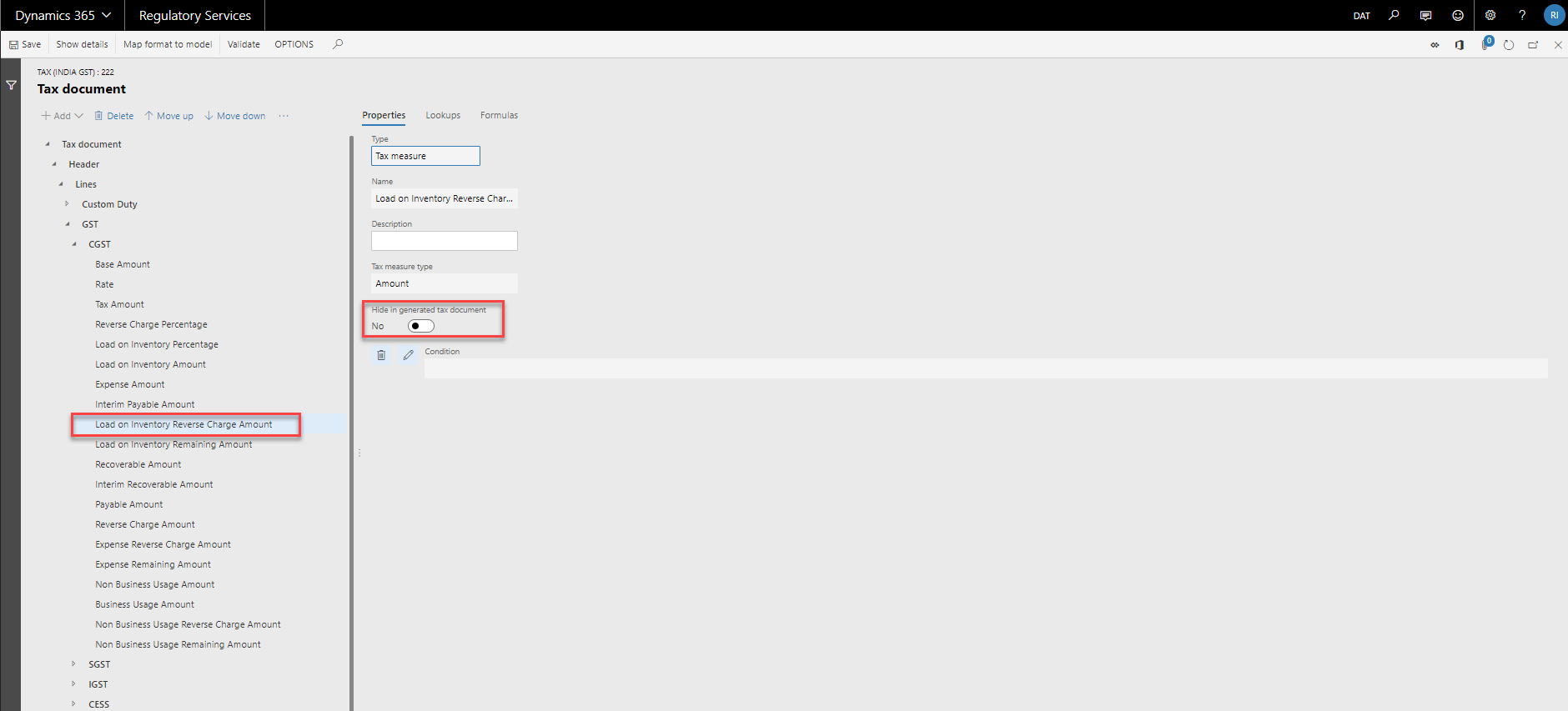
Configure the visibility of tax measures in tax documents
For more information, see Electronic reporting and Tax engine overview.