Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article details methods for achieving the Australian Cyber Security Centre (ACSC) Essential Eight Maturity Model for patching applications.
ISM controls and patch applications maturity levels
A mapping between Maturity Level 1 (ML1), Maturity Level 2 (ML2), and Maturity Level 3 (ML3) of the Patch Application Essential Eight Control to the ISM is outlined in the following table.
| ISM control Mar 2025 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISM-0304 | 3 | Applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Using Intune’s Application management method, unsupported applications are removed. |
| ISM-1690 | 1, 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in online services are applied within two weeks of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Intune service is updated and patched regularly by Microsoft to ensure no working exploit exist. |
| ISM-1691 | 1, 2 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within two weeks of release. | Using Windows Update for Business, and defined update rings, the patches are installed with 2 weeks of release. For install latest patch for email clients, PDF software and security product, Intune Application deployment method is used. |
| ISM-1692 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Microsoft Defender vulnerability method is used to identity vulnerabilities. Intune application deployment method is used to deploy the patches within 48 hours of release. |
| ISM-1693 | 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within one month of release. | Intune application deployment method is used to deploy the application patches within one month of release. |
| ISM-1698 | 1, 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least daily to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in online services. | Devices are onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management continuously monitors and detects risk across an organization’s devices. |
| ISM-1699 | 1, 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least weekly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products. | Devices are onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management continuously monitors and detects risk across an organization’s devices. |
| ISM-1700 | 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products. | Devices are onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management continuously monitors and detects risk across an organization’s devices. |
| ISM-17041 | 1, 2, 3 | Office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Intune Application deployment method is used to remove unsupported applications and extensions. |
| ISM-18071 | 1, 2, 3 | An automated method of asset discovery is used at least fortnightly to support the detection of assets for subsequent vulnerability scanning activities. | Use a scanner to perform asset discovery and maintain asset inventory. |
| ISM-18081 | 1, 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner with an up-to-date vulnerability database is used for vulnerability scanning activities. | DVM's vulnerability database is continuously updated as Microsoft and others discover vulnerabilities in software installed on your network |
| ISM-1876 | 1, 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in online services are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Intune service is updated and patched regularly by Microsoft to ensure no working exploit exist. |
| ISM-1901 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within two weeks of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Microsoft Defender vulnerability method is used to identity vulnerabilities. Intune application deployment method is used to deploy the patches within two weeks of release. |
| ISM-1905 | 1, 2, 3 | Online services that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | IT admin disables all the account and connectors that are associated with the online service that are no longer supported the vendor. |
Note
1 These controls cover both Patch Application and Patch OS within Essential 8.
Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management (DVM)
The discovery of new security vulnerabilities, and disruptions from adversaries, may occur at any time. As such, organizations should ensure that security vulnerabilities are addressed in a timely manner. When a vendor releases a patch, the patch should be applied with the following considerations:
- A timeframe, commensurate with an organization's exposure to the security vulnerability,
- The level of cyber threat the organization is aiming to protect themselves against; and
- The ML level they're wishing to achieve
One problem faced by many organizations is a lack of visibility of the true patch status of their environment. This lack of visibility can leave organizations unknowingly exposed to exploitation by adversaries. Organizations can incorrectly assume that patches were applied, or reported that they were applied, when they failed to be applied successfully. Using Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management (DVM) assists organizations to gather information on patches in their environment. In special cases where a vulnerability scanner can't be used, organizations should refer to vendor documentation on how to identify patching levels and conduct manual audits instead.
As the Essential 8 outlines a minimum set of preventative measures, organizations need to implement more measures if it's assessed as warranted by their environment. Further, while the Essential 8 can help to mitigate most of cyber threats, it doesn't mitigate all cyber threats. More mitigation strategies and security controls need to be considered, such as the Strategies to Mitigate Cyber Security Incidents and the Information Security Manual (ISM).
Implementation – patch applications
Control specific guidance
There are two main components to this control. One is technology to discover vulnerabilities and the other is the organization's process for vulnerability management.
- Technology: Technology such as vulnerability scanners and patch rollout systems can assist organizations. The vulnerability scanners assist to gather information on vulnerable applications and missing patches in the environment.
- Process: Organization process defining vulnerability management plan to discover, identify, classify, risk assess and remediate or mitigate vulnerabilities. The organization should also have a process that mandates either onboarding systems to automated vulnerability scanners or having equivalent workaround such as setting up email notifications from vendor. In cases where vulnerability scanners can't be used, organizations should refer to vendor documentation on how to identify patching levels and conduct manual audits instead. For the application patching control, the vulnerability management process and its mandate play a key role in achieving the maturity levels defined by ACSC. The timely rollout of patches is crucial to vulnerability management process. Therefore, organizations must have a patch rollout timeline defined as part of their Essential 8 ML level. Additionally they require defined responsibilities for teams using roles responsibility matrix or equivalent model.
Implementation with Microsoft platform
Effectively identifying, assessing, and remediating weaknesses in a system is crucial in running a healthy security program and reducing organizational risk. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management (DVM) serves as an infrastructure for reducing organizational exposure, hardening endpoint surface area, and increasing organizational resilience.
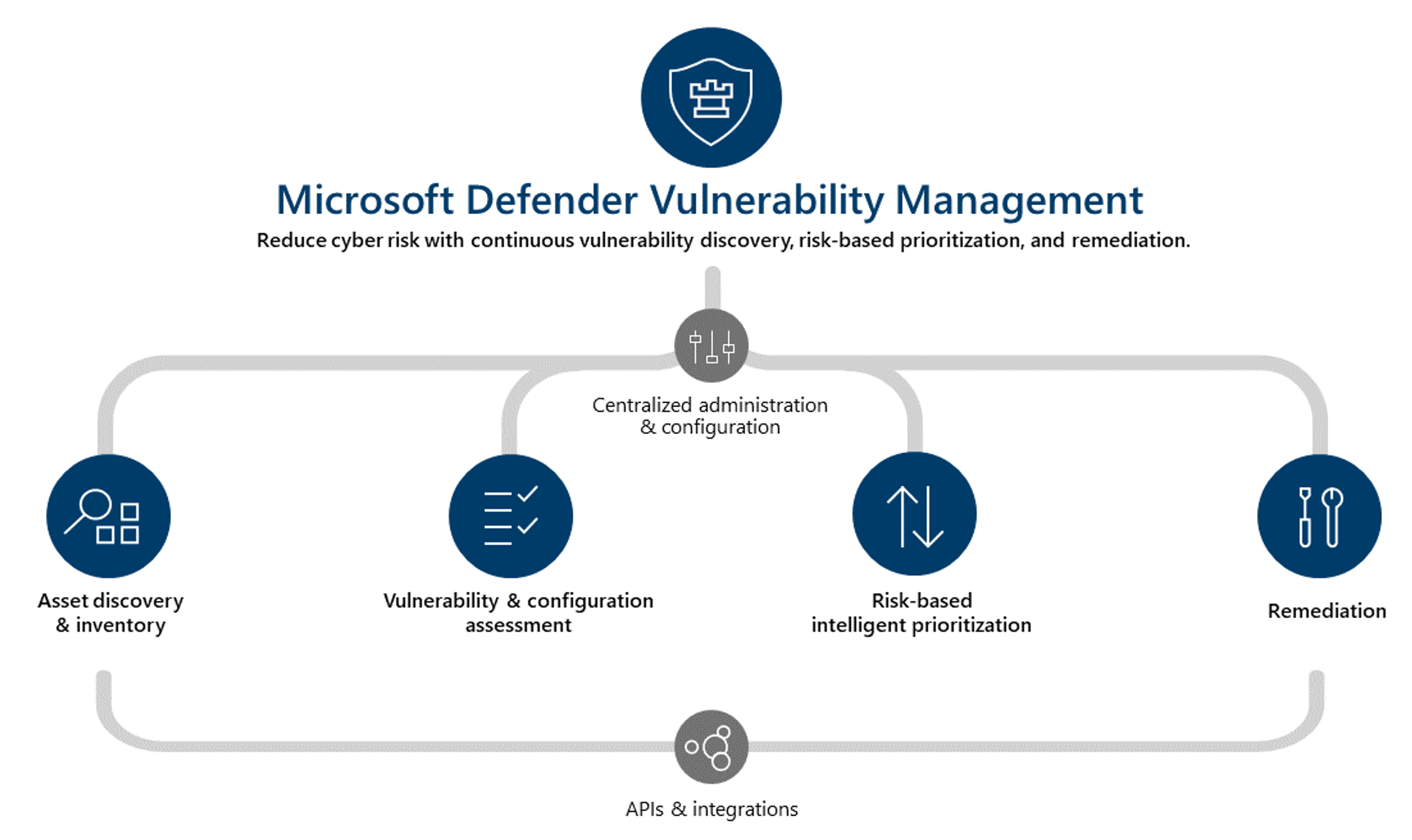
The DVM can be used for user endpoints and servers. For other cloud resources such as repositories, containers, etc., Defender for Cloud provides vulnerability management capabilities. Both these solutions are explained in the following sections.
For more information, see:
- Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management
- Configure Microsoft Defender for Cloud to automatically assess machines for vulnerabilities
Discovery of assets
Defender Vulnerability Management built-in and agentless scanners continuously monitor and detect risk in your organization even when devices aren't connected to the corporate network. A single inventory with a real-time consolidated view of your organization's software applications, digital certificates, network shares, and browser extensions helps you discover and assess all your organization's assets. View information on extension permissions and associated risk levels, identify certificates before they expire, detect potential vulnerabilities due to weak signature algorithms, and assess misconfigurations in internal network shares.
| ISM control Mar 2025 | Maturity level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1807 | 1, 2, 3 | An automated method of asset discovery is used at least fortnightly to support the detection of assets for subsequent vulnerability scanning activities. | Use a scanner to perform asset discovery and maintain asset inventory. |
Discovery of vulnerabilities
Defender Vulnerability Management (DVM) delivers asset visibility, intelligent assessments, and built-in remediation tools. DVM can be used for Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS, and network devices. When an organization uses Microsoft threat intelligence, breach likelihood predictions, business contexts, and devices assessments, Defender Vulnerability Management rapidly and continuously prioritizes the biggest vulnerabilities on your most critical assets and provides security recommendations to mitigate risk.
The software inventory in DVM provides a list of known software in your organization. The inventory view includes details such as the name of the vendor, number of weaknesses, threats, and number of exposed devices.
For discovery, Microsoft uses the same set of signals that is responsible for detection and vulnerability assessment in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint detection and response capabilities. Since it's real time, in a matter of minutes, the vulnerability information is presented in the portal as they get discovered. Common Platform Enumerations (CPE) are used by vulnerability management to identify the software and any vulnerabilities associated with the software. The engine automatically grabs information from multiple security feeds. In fact, see if a particular software is connected to a live threat campaign. It also provides a link to a Threat Analytics report soon as it's available.
Note
For software products without a CPE, the software is shown in the inventory page. However, software without CPE aren't supported by vulnerability management and information such as exploits, number of exposed devices, and weaknesses aren't available for this software.
The following steps describe the onboarding process and vulnerability discovery using DVM:
Licensing requirements
- Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management (DVM), a new standalone offering provides the complete set of vulnerability tools and capabilities; or
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Plan 2 or E5 license provides subset of core vulnerability management capabilities. Full capabilities of DVM are available as an add-on
The comparison of features for the two licensing offerings is available on following link: Compare Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management offerings.
For server resources, Defender for Cloud plan enabled for servers or the servers onboarded to Defender for Endpoint.
For other cloud resources, specific Defender for Cloud plan must be enabled. For example, to scan container registries the Defender for Containers plan must be enabled within the cloud environment.
Accessing the DVM portal
The DVM information is available in Microsoft Defender portal. The portal is accessible through Microsoft Edge (recommended) or Google Chrome browser. To access the portal, at minimum you should be part of 'Security Reader' AD built-in role. More details on managing access to the portal are documented on this link: Use role-based access control to grant fine-grained access to Microsoft Defender portal.
Onboarding of devices to DVM
- For devices that are already onboarded to Defender for Endpoint (having P2 license), the DVM features are enabled and available in Microsoft Defender portal
- For devices not onboarded to Defender for Endpoint, at minimum, the DVM requires the Defender for Endpoint running in block mode that is, running in passive mode
Microsoft has created multiple means to onboard the devices to Defender for Endpoint such as group policy, endpoint manager, or local scripts. Detailed guidance is documented on Onboard devices and configure Microsoft Defender for Endpoint capabilities.
Supported operating systems are documented on the following link: Supported operating systems platforms and capabilities
Discovery of vulnerabilities using DVM
The Vulnerability Management section in Microsoft Defender portal provides a dashboard to view quick insights about vulnerability exposure and security recommendations, as shown in the following example screenshot.
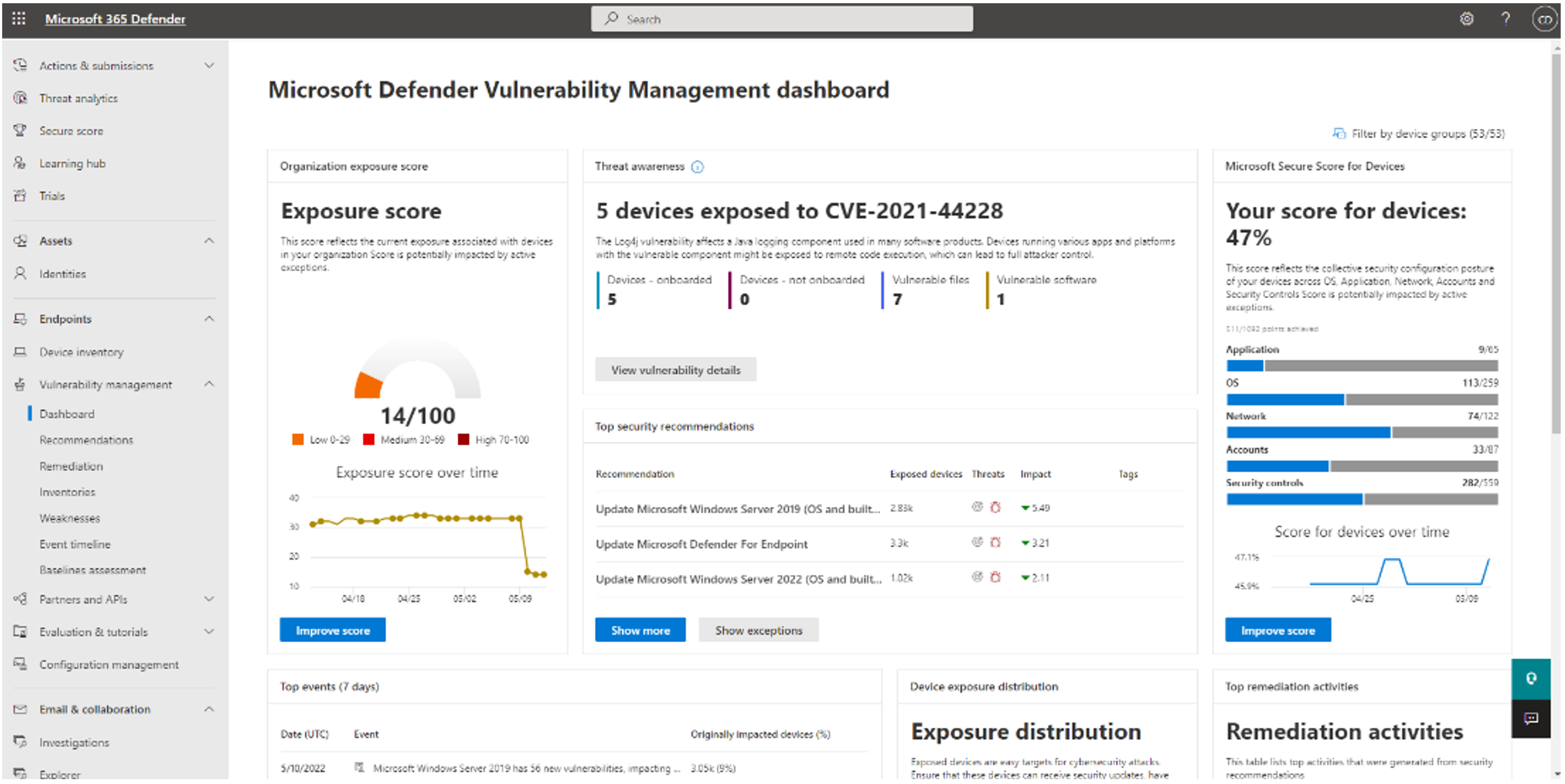
The Software inventory page contains a list of software installed in your network, including the vendor name, weaknesses found, threats associated with them, exposed devices, exposure score, and tags.
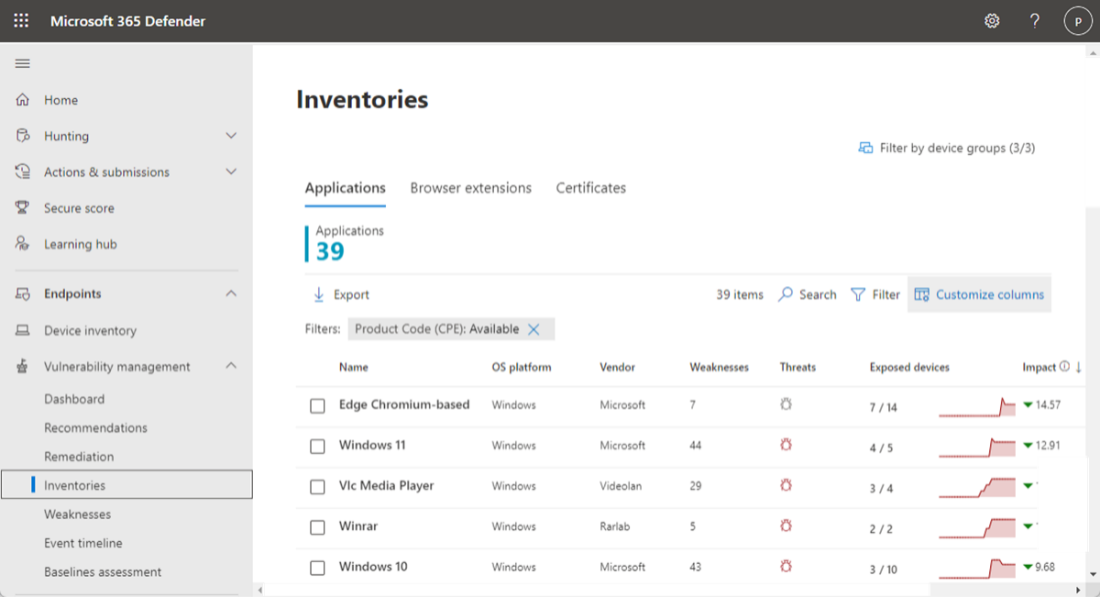
You can also look for software inventories on specific devices by navigating to the Device inventory page. Select the name of a device to open the device page (like Computer1), then select the Software inventory tab to see a list of all the known software present on the device. Select a specific software entry to open the flyout with more information.
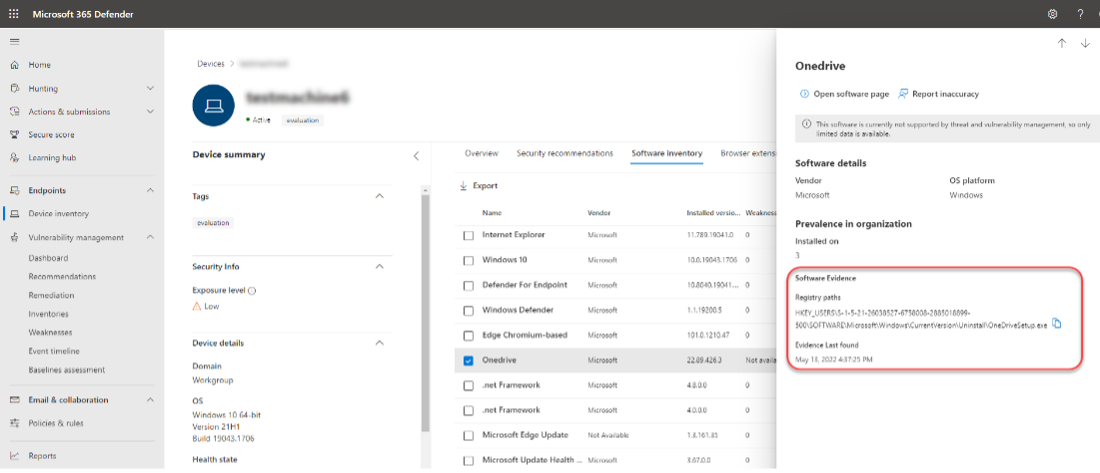
Opening the specific software page provides more details about the application as shown in the following screenshot:
- Corresponding security recommendations for the weaknesses and vulnerabilities identified
- Named CVEs of discovered vulnerabilities
- Devices that have the software installed (along with device name, domain, OS, and more)
- Software version list (including number of devices the version is installed on, the number of discovered vulnerabilities, and the names of the installed devices)
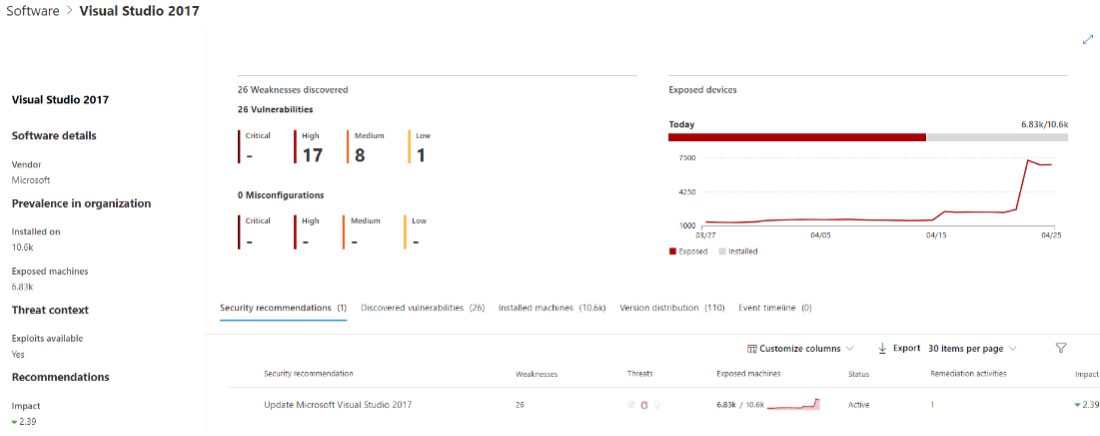
Similarly, you can view vulnerability assessment of browser extensions and certificates using DVM.
The vulnerability management features also extend to the server operating systems. The servers onboarded to Defender for Cloud (Defender for Servers Plan) and configured to use Defender Vulnerability Management appear in Microsoft Defender portal. The vulnerability management information also gets synchronized in Defender for Cloud portal for visibility.
For applications or software products not supported by CPE or vulnerability assessment solutions, security teams should have other means to identify the vulnerabilities. The other means include, having email subscriptions to the application vendor to receive notifications about the application updates and related vulnerabilities.
| ISM Control Mar 2025 | Maturity level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1808 | 1, 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner with an up-to-date vulnerability database is used for vulnerability scanning activities. | DVM's vulnerability database is continuously updated as Microsoft and others discover vulnerabilities in software installed on your network |
| 1698 | 1, 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least daily to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in online services. | Devices are onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management continuously monitors and detects risk across an organization’s devices |
| 1699 | 1, 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least weekly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products. | Devices are onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management continuously monitors and detects risk across an organization’s devices |
| 1700 | 2, 3 | A vulnerability scanner is used at least fortnightly to identify missing patches or updates for vulnerabilities in applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products. | Devices are onboarded to Defender for Endpoint. Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management continuously monitors and detects risk across an organization’s devices. |
| 1901 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within two weeks of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Microsoft Defender vulnerability method is used to identity vulnerabilities. Intune application deployment method is used to deploy the patches within two weeks of release. |
Prioritize and remediate vulnerabilities using DVM and Intune integration
Cybersecurity weaknesses identified in your organization are mapped to actionable security recommendations and prioritized by their impact. Prioritized recommendations help shorten the time to mitigate or remediate vulnerabilities and drive compliance. We also suggest defining a device's value to differentiate between asset priorities. The device value is used to incorporate the risk appetite of an individual asset into the threat and vulnerability management exposure score calculation. Devices assigned as "high value" receive more weight.
Each security recommendation includes actionable remediation steps. To help with task management, the recommendation can also be sent using Microsoft Intune. When the threat landscape changes, the recommendation also changes as it continuously collects information from your environment.
Note
For software products without a CPE, the software is shown in the inventory page. However, software without CPE aren't supported by vulnerability management and information such as exploits, number of exposed devices, and weaknesses aren't available for this software.
For certain cases, the risk and prioritization provided by Microsoft's solution may not be sufficient as there could be system complexities. Therefore, it's advised in this case to perform other risk assessment for critical or zero-day vulnerabilities based on the system's context. In doing so, organizations should seek to minimize any exceptions and their scope. For example, by implementing compensating security controls and ensuring the number of systems or users impacted are minimized. Any exceptions or compensating controls implemented to address the vulnerability should be documented and approved through an appropriate process.
The DVM capabilities are designed to bridge the gap between Security and IT administrators through the remediation request workflow. The DVM remediation actions can use native integrations to generate remediation tasks in Microsoft Endpoint Manager. The DVM API can be used to orchestrate remediation processes and actions with non-Microsoft tools where required.
The following steps describe the remediation workflow using DVM and Endpoint Manager:
- To use the remediation workflow capability, enable your Microsoft Intune connections. In the Microsoft Defender portal, navigate to Settings > Endpoints > General > Advanced features.
- Scroll down and look for Microsoft Intune connection. By default, the toggle is turned off. Turn your Microsoft Intune connection toggle On.
Note
If you have Intune connection enabled, you get an option to create an Intune security task when creating a remediation request. This option doesn't appear if the connection isn't set.
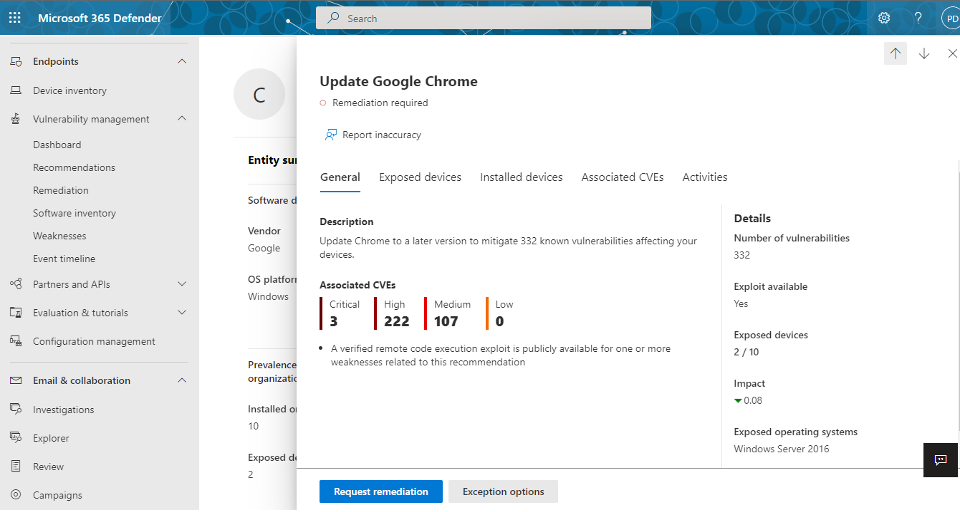
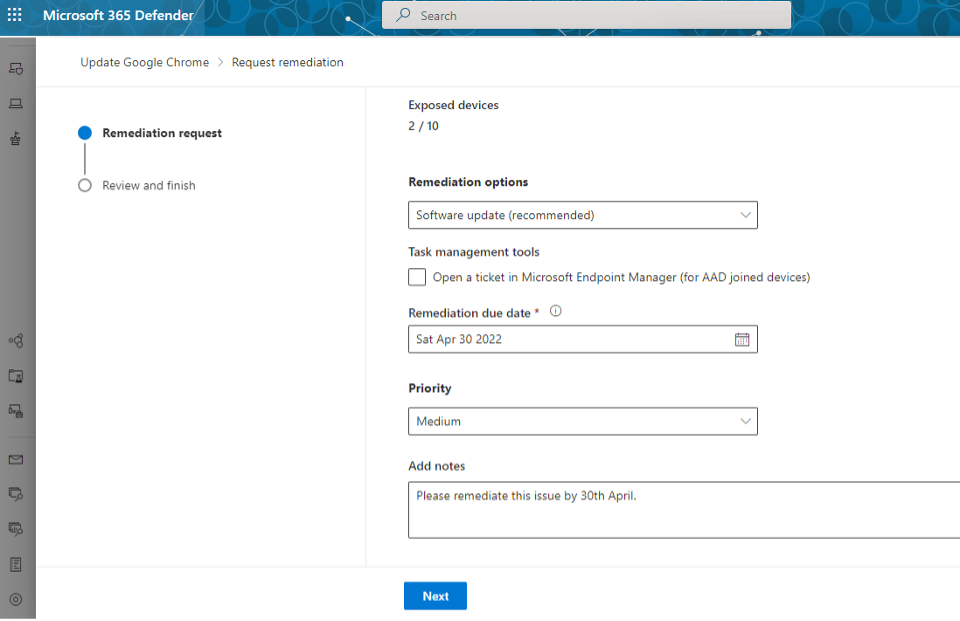
Go to the Vulnerability management navigation menu in the Microsoft Defender portal and select Recommendations. Select a security recommendation you would like to request remediation for, and then select Remediation options. Fill out the form, including what you are requesting remediation for, applicable device groups, priority, due date, and optional notes. Following screenshots provides reference to these steps:
Request remediation for selected vulnerability
Select remediation options and priority
Submitting a remediation request creates a remediation activity item within vulnerability management, which can be used for monitoring the remediation progress for this recommendation. When you submit a remediation request from the Security recommendations page, it kicks-off a remediation activity. A security task is created that can be tracked on a Remediation page, and a remediation ticket is created in Microsoft Intune. This won't trigger remediation or apply any changes to devices. The following image shows a security task created in Intune:
Security task created in Intune for remediation request
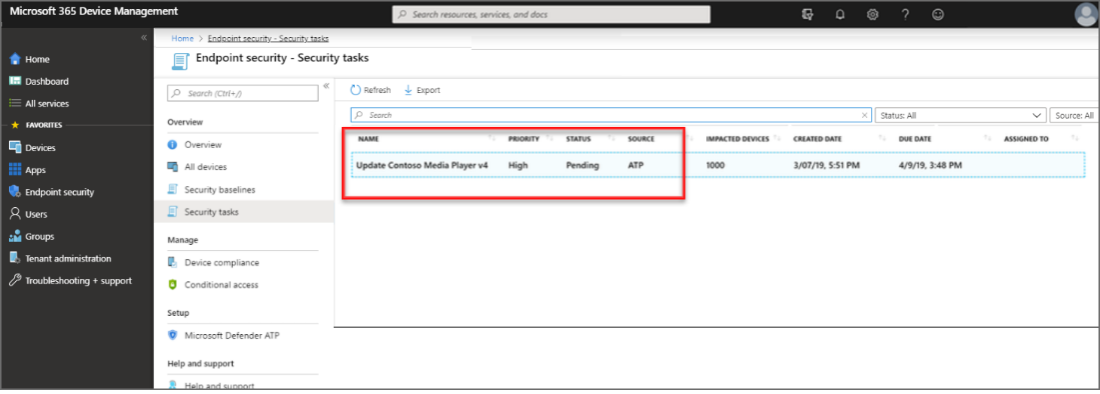
The Intune admin selects the security task to view details about the task. The admin then selects Accept, which updates the status in Intune, and in Defender for Endpoint to be Accepted.
The admin then remediates the task based on the guidance provided. The guidance varies depending on the type of remediation that's needed. When available, remediation guidance includes links that open relevant panes for configurations in Intune.
| ISM control Mar 2025 | Maturity level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1690 | 1, 2, 3 | Patches, updates, or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in online services are applied within two weeks of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Intune service is updated and patched regularly by Microsoft to ensure no working exploit exist. |
| 1691 | 1, 2 | Patches, updates, or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within two weeks of release. | Using Windows Update for Business, and defined update rings, the patches are installed with 2 weeks of release. For install latest patch for email clients, PDF software and security product, Intune Application deployment method is used. |
| 1692 | 3 | Patches, updates, or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Microsoft Defender vulnerability method is used to identity vulnerabilities. Intune application deployment method is used to deploy the patches within 48 hours of release. |
| 1693 | 2, 3 | Patches, updates, or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within one month of release. | Intune application deployment method is used to deploy the application patches within one month of release. |
| 1704 | 1, 2, 3 | Office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Intune Application deployment method is used to remove unsupported applications and extensions. |
| 0304 | 3 | Applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Using Intune’s Application management method, unsupported applications are removed. |
| 1876 | 1, 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in online services are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Intune service is updated and patched regularly by Microsoft to ensure no working exploit exist. |
Discover and remediate vulnerabilities for cloud and on-premises resources
Defender for Cloud provides vulnerability assessment capabilities for many services. These services include servers, Azure Container Registry, Amazon Elastic Container Registry, Azure SQL databases, SQL database servers, and DevOps. To provide the vulnerability assessment for specific cloud resources, the Defender for Cloud plan with the Azure Subscription or Amazon Account must be turned on.
Defender for Cloud collects data from your Azure virtual machines (VMs), Virtual Machine Scale Sets, IaaS containers, and non-Azure (including on-premises) machines to monitor for security vulnerabilities and threats. Some Defender plans require monitoring components to collect data from your workloads. Data collection is required to provide visibility into missing updates, misconfigured OS security settings, endpoint protection status, and health and threat protection. Data collection is only needed for compute resources such as VMs, Virtual Machine Scale Sets, IaaS containers, and non-Azure computers.
Patch Online services for vulnerabilities
New feature releases for Intune typically have a six to eight week cadence, from planning to release. This cadence is called a sprint. Intune releases use a YYMM naming convention. For example, 2301 is the January 2023 release.
The monthly release process involves many different environments and is deployed to multiple Azure services. After it's deployed to Azure, the release updates are deployed to the Intune admin center, which makes the release features available for you to use.
An internal environment called Self Host is the first environment to receive the release. Self Host is used only by the Intune engineering teams. After Self Host, the service release is deployed to the Microsoft tenant that manages many devices. Once it's validated that there are no key issues with the service release, the release begins deploying to customer environments in a phased approach. Once all tenants are successfully updated, the Microsoft Intune admin center is updated. This phased approach helps identify issues before they affect the service or our customers.
Updating the Company Portal app is a different process. Microsoft is subject to the release requirements and processes of the Apple App Store, Google Play, and sometimes mobile carriers. It isn't always possible to align the Intune release updates with updates to the Company Portal app. For more information on the Company Portal app updates, see UI updates for Intune end-user apps.
Patch applications
Applications can be segmented in two categories:
- Applications that have the capability to autoupdate (recommended).
- Applications for which updates have to be packaged and deployed manually.
Specific app types are supported based on the version of Windows 10/11 that your users are running. For specific supported apps, see Supported Windows app types.
Office C2R and Microsoft Edge get updated when Windows Update for Business or Autopatch is configured to update Windows OS and Microsoft products.
Microsoft Store app has the ability to self-update. If applications are deployed as .IntuneWin (that is, Win32 apps), you can use Intune to create one or more supersedence relationships between apps. In general, supersedence is where you update or replace something. In Intune, supersedence enables you to update and replace existing Win32 apps with newer versions of the same app or an entirely different Win32 app.
Applications that have the capability to autoupdate
Microsoft Store app
Admins can browse, deploy, and monitor Microsoft Store applications inside Intune. Upon deployment, Intune automatically keeps the apps up to date when a new version becomes available. The Microsoft Store supports Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps, desktop apps packaged in .msix, and now Win32 apps packaged in .exe or .msi installers.
For more information, see Microsoft Store app to Microsoft Intune..
| ISM control Mar 2025 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISM-0304 | 3 | Applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Using Intune’s Application management method, unsupported applications are removed. |
| ISM-1693 | 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within one month of release. | Intune application deployment method is used to deploy the application patches within one month of release. |
Microsoft Intune Enterprise Application Management
Enterprise App Management enables IT and security operation teams to simplify the lifecycle of managing first party and non-Microsoft applications by offering a secure, prepackaged catalog of apps. This reduces the time and effort IT administrators spend on packaging apps and tracking updates. With this solution, IT teams can efficiently deploy fixes to vulnerable apps and ensure that all apps are kept up to date from the Intune admin center. The introduction of the new catalog starts with Windows applications.
Enterprise App Management streamlines and consolidates the application update process by providing a comprehensive view of all apps that need an update from a single, easy-to-use screen. A list of apps in the catalog with available updates shows both current and new versions. The work traditionally required to monitor updates and gather application-related data and packaging is reduced, allowing admins to focus on more strategic tasks.
Note
Microsoft Intune Application Management is part of Intune Suite requires an additional license.
For more information, see Microsoft Intune Application Management, which is part of Intune Suite.
| ISM control Mar 2025 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISM-0304 | 3 | Applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Using Intune’s Application management method, unsupported applications are removed. |
| ISM-1693 | 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within one month of release. | Intune application deployment method is used to deploy the application patches within one month of release. |
Applications which updates have to be packaged and deployed manually
This section covers manual deployment of .MSI, LOB: APPX/MSIX, Web Apps, Store Link.
Tip
Consider using Microsoft Store App for continuous compliance as it supports Universal Windows Platform (UWP) apps, desktop apps packaged in .msix, and Win32 apps packaged in .exe or .msi installers.
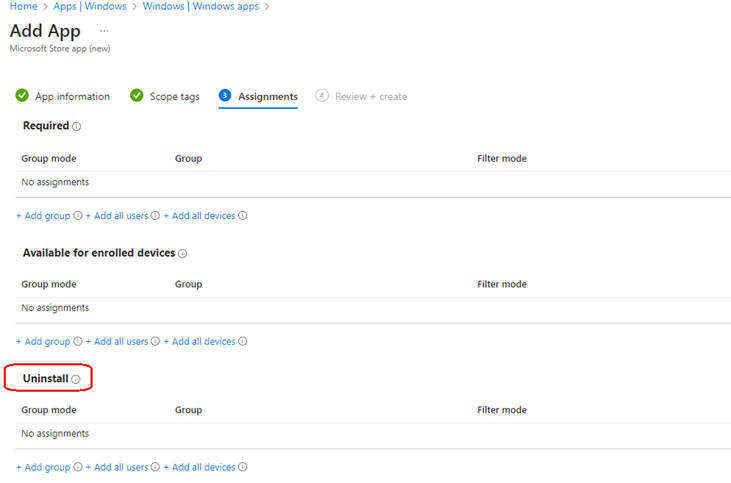
The admin must manually upload and deploy updates of LOB apps. These updates are automatically installed on user devices that have installed the application. No user intervention is required, and the user has no control over the updates. Older version of application must be uninstalled by changing the assignment type to uninstall.
| ISM control Mar 2025 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISM-0304 | 3 | Applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Using Intune’s Application management method, unsupported applications are removed. |
| ISM-1691 | 1, 2 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within two weeks of release. | Using Windows Update for Business, and defined update rings, the patches are installed with 2 weeks of release. For install latest patch for email clients, PDF software and security product, Intune Application deployment method is used. |
| ISM-1692 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within 48 hours of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as critical by vendors or when working exploits exist. | Microsoft Defender vulnerability method is used to identity vulnerabilities. Intune application deployment method is used to deploy the patches within 48 hours of release. |
| ISM-1693 | 2, 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in applications other than office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within one month of release. | Intune application deployment method is used to deploy the application patches within one month of release. |
| ISM-1704 | 1, 2, 3 | Office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, Adobe Flash Player, and security products that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | Intune Application deployment method is used to remove unsupported applications and extensions. |
| ISM-1901 | 3 | Patches, updates or other vendor mitigations for vulnerabilities in office productivity suites, web browsers and their extensions, email clients, PDF software, and security products are applied within two weeks of release when vulnerabilities are assessed as noncritical by vendors and no working exploits exist. | Microsoft Defender vulnerability method is used to identity vulnerabilities. Intune application deployment method is used to deploy the patches within two weeks of release. |
Removal of unsupported online services
Remove obsolete online services by completing the following steps:
- If an enterprise app was registered, the IT admin logs in to Microsoft Entra ID portal and delete the application.
Note
As an interim step, sign-in for relevant Service accounts for the online services can be disabled.
- If a connector was created, it's deleted using the Intune console, under Cross Platform connectors.
- The IT admin disables service account and revoke certificates created for the authentication of the (unused) online services.
| ISM control Mar 2025 | Maturity Level | Control | Measure |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISM-1905 | 1, 2, 3 | Online services that are no longer supported by vendors are removed. | The IT admin disables all the account and connectors that are associated with the online service that are no longer supported the vendor. |