Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
[This article is prerelease documentation and is subject to change.]
This article provides an overview of the architecture in Finance agents.
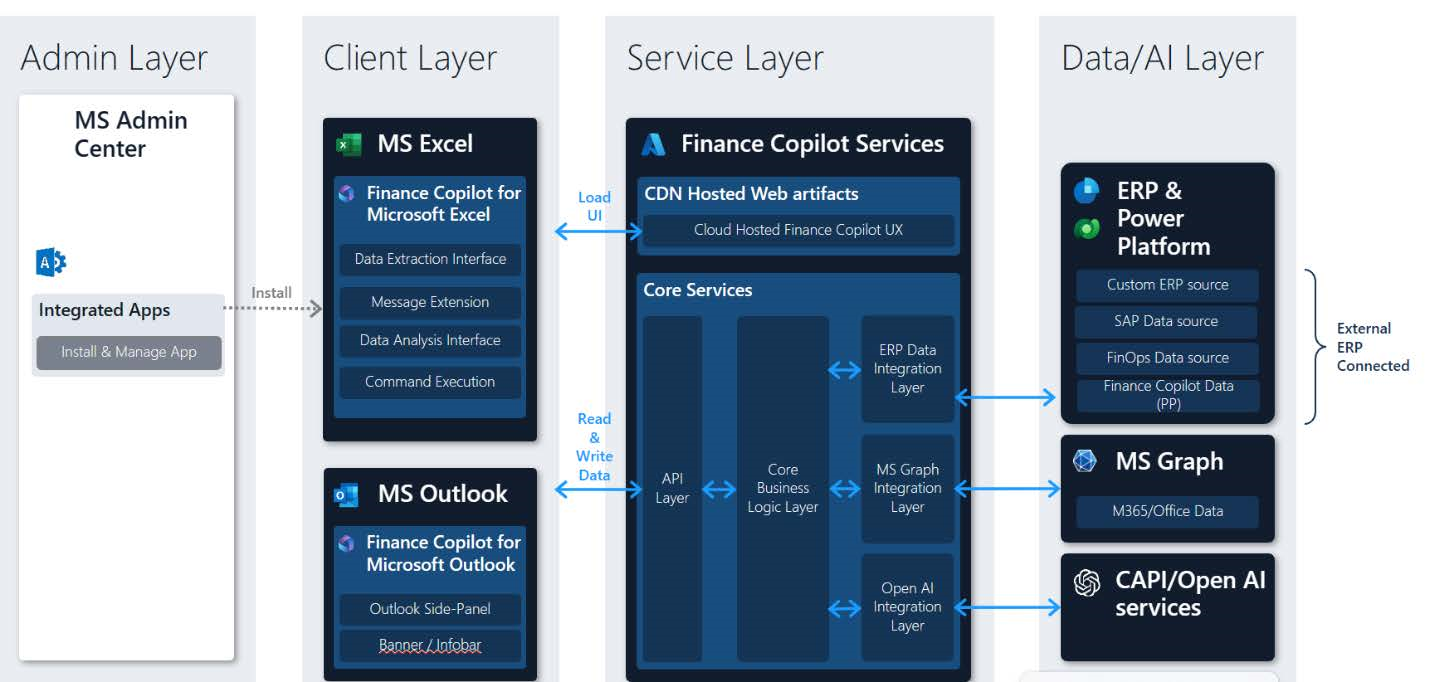
Architectural component layers
The architecture consists of the following component layers.
- Admin layer
- Client layer
- Service layer
- Storage and security layer
- Microsoft 365 and Microsoft Office data layer
- ERP data layer
Each layer is described in the following sections.
Admin layer
Finance agents are integrated as copilot extensions within Microsoft Office: Outlook and Excel. The administrative layer of Finance agents provides users with the ability to install and manage these Office add-ins.
Client layer
Finance agents consist of two distinct client experiences - Finance agents for Microsoft 365 Outlook and Finance agents for Microsoft 365 Excel. The Outlook experience is developed as a third-party Outlook add-in and the Excel experience is developed as a third-party Excel add-in.
Both consist of a manifest, which describes how the add-in and app integrate into Outlook and Excel, and JavaScript/HTML, which makes up the User Interface (UI) of the experience. The UI for both experiences is cloud-hosted and fully managed by Microsoft. None of the UI or business logic for Finance agents is shipped as client-side code in Excel or Outlook. Therefore, customers don't need to manage the application lifecycle for the Finance agents client or server-side components. For more information, see the Application Lifecycle Management section.
The Finance agents client only stores minimal setup and settings data in the local browser-based application storage and no personal or other customer data outside of settings persists locally.
Service layer
The Finance agents service layer consists of the cloud-hosted Finance agents experiences, which are served to the Finance agents client experiences, and Core Business Logic Layer, which processes and combines ERP data, MS Graph data (for example, E-Mails, Meetings), Azure OpenAI generated data. All Finance agents services are hosted on the Microsoft Azure cloud to provide a resilient foundation to help meet organizational compliance, reliability, availability, and disaster recovery needs.
The Finance agents data layer consists of three distinct sets of data.
- MS Graph data: The end user’s existing Microsoft 365/Office Data (E-Mails, Meetings, etc.) are stored in Microsoft Graph.
- ERP data: The customer’s ERP data is only stored in the existing ERP system (SAP, Dynamics Finance, and operations, …), which serves as the system of record for all ERP entities.
- Non-ERP related data: Finance agents store some non-ERP related data in customer’s Power Platform Dataverse. For example, email summaries, emails, and notes.
- Finance agents data: The customer’s Finance agents data is generated through Finance agents feature flows and doesn't fall into the previous definition for Office Data or ERP Data, Dataverse data. For example, Finance agents settings or Finance agents generated insights data.
Storage and security layer
Finance agents always respect the data privacy, data security, data retention, and compliance boundaries of the underlying data store for data at rest and use Transport Layer Security (TLS) to protect data in transit and doesn't store data outside any of the data stores described previously.
Microsoft 365 and Office data layer
The end-user’s Microsoft 365 and Office data is always accessed in the end user’s authentication context and referenced in two distinct ways:
- Read in real-time to enable insights scenarios, for example Generative AI e-mail replies, AI generated e-mail summaries, etc. The Microsoft 365 / Office data is only read in these scenarios and discarded after it's processed.
- Read in real-time to enable value in the customer’s ERP system, for example when e-mail data is copied from the Microsoft Graph to the customer’s ERP as activities or meeting transcripts are copied to Dataverse to enable extensibility scenarios.
ERP data layer
All ERP data access (read and write access) in Finance agents is managed via real-time integrations with the underlying ERP system. Finance agents don't copy any ERP data to other systems except when unique identifiers are used for mapping ERP environment and entities to Finance agents specific data. For example, Finance agents customer identifiers are used to map customers to nonfinancial data stores in Dataverse. In these scenarios, Finance agents only store the unique identifiers from the ERP system being referenced. Finance agents fully respect the existing retention policies and compliance boundaries of the existing ERP system and Dataverse.
Finance agents are designed and intended to work with a single ERP connection at a time. Finance agents don't connect to multiple ERP or Dataverse instances at the same time, nor synchronize data between them. The data accessed and stored via Finance agents is always scoped to the ERP that the end user is currently connected to.
Application lifecycle management
This section describes the application lifecycle management for Finance agents.
Release cycle
There are two sets of release cycles for Finance agents.
- Bi-Monthly product releases, which include major product capabilities.
- Ongoing service updates, which include product hotfixes and minor product changes.
Component overview
There are two distinct components that are relevant to the Finance agents application lifecycle management.
- Finance agents client add-in / app manifests, which are deployed as third-party Outlook add-in and third-party Excel app and describe the behavior of the add-in / app.
- Finance agents service layer, which hosts the UI experiences for all Finance agents add-ins / apps and the core service layer, containing front-end APIs, core business logic, data integration layer, and AI services.
Updates
Finance agents client add-in and apps
The Finance agents manifest for the Microsoft Outlook add-In and the Microsoft Excel add-In require occasional updates when new capabilities are introduced. These updates are rolled out by Microsoft as part of the bi-monthly product releases and is automatically pushed to all users who have the add-in / app installed without the need for an admin or end-user to take any action. In rare circumstances, Microsoft introduces new permissions as part of a bi-monthly release, which requires explicit consent and update from the admin or end-user. In these circumstances, admins and users see that a new update is available via the Microsoft 365 Admin Center. Additionally, Microsoft informs admins via the What’s New section of the Finance agents documentation, and via the Microsoft Viva Blog. Customers aren't able to take advantage of the latest Finance agents capabilities if they haven't applied the latest updates to the add-in / app.