Use group policies to manage Microsoft Edge extensions
This article describes the options and steps for managing extensions by using group policies. These options assume that you already have Microsoft Edge managed for your users. If you haven't already set up Microsoft Edge to be managed for your users follow the link below to do so now.
Note
The Microsoft Edge management service, a dedicated and simplified management tool in the Microsoft 365 admin center, is rolling out now. Learn more.
Block extensions based on their permissions
You can control what extensions your users can install based on permissions using the ExtensionSettings policy. If an installed extension needs a permission that's blocked, it just won't run. The extension isn't removed, just disabled.
Note
The blocked permissions setting can only be set within the extension settings policy.
Use the following steps as a guide for blocking an extension.
Open the group policy management editor and go to Administrative Templates > Microsoft Edge > Extensions and then select Configure extension management settings.
Enable the policy, then enter the permissions that you want allowed or blocked, by using a JSON string that gets compressed. The next screenshot shows how to block an extension that uses the permission "usb".
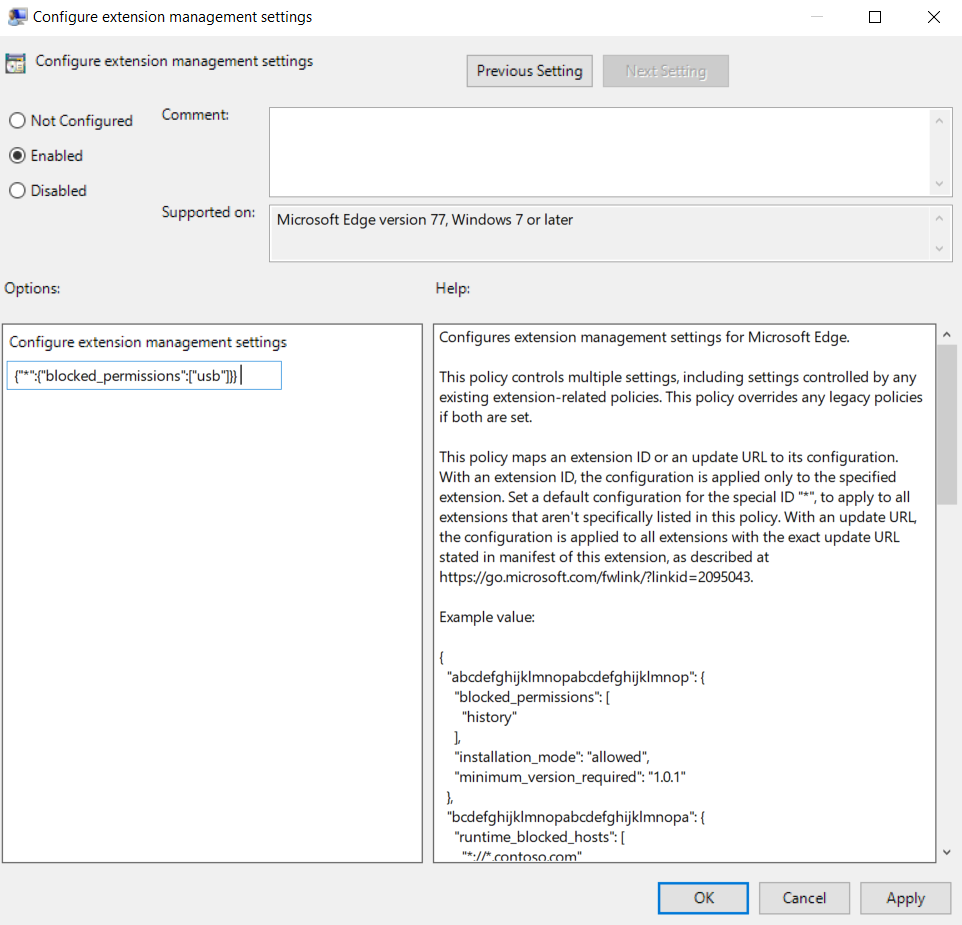
The following example shows the JSON to block any extension that needs the use of permission "usb" and its compressed string.
JSON example
{
"*": {
"blocked_permissions": ["usb"]
}
}
{"*":{"blocked_permissions":["usb"]}}
Note
To block all extensions that use the permission, use an asterisk for the extension ID, as shown in the previous example. If you specify one extension ID, the policy will only apply to that extension. You can block more than one, but they need to be separate entries.
Prevent extensions from altering web pages
This setting prevents extensions from reading and changing data from sensitive websites and domains. Blocking unwanted actions is done by blocking actions such as script injection into your websites, reading the cookies, or making web-request modifications. This setting doesn't prevent your users from installing or removing extensions, it only prevents extensions from altering the specified websites.
Note
The Runtime allowed/blocked hosts setting can only be set within the extension settings policy.
You can configure the following settings in the ExtensionSettings policy to prevent (or allow) alterations of websites or domains:
Runtime_blocked_hosts. This setting blocks extensions from making changes or reading data from the websites you specify.
Runtime_allowed_hosts. This setting allows extensions to make changes or read data from the websites you specify. The following format is used for specifying your site(s) in the JSON string in the policy:
[http|https|ftp|*]://[subdomain|*].[hostname|*].[eTLD|*] [http|https|ftp|*],Note
[hostname|*], and [eTLD|*]sections are required, but[subdomain|*]section is optional.
The following table shows examples of valid host patterns and matching patterns.
| Valid host patterns | Matches | Doesn't match |
|---|---|---|
*://*.example.* |
http://example.comhttps://test.example.co.uk |
https://example.microsoft.comhttp://example.microsoft.co.uk |
http://example.* |
http://example.comhttp://example.ly |
https://example.comhttp://test.example.com |
http://example.com |
http://example.com |
https://example.comhttp://test.example.co.uk |
*://* |
All URLs |
Use the following steps as a guide to block or allow extensions to access a website or domain.
- Open the group policy management editor and go to Administrative Templates > Microsoft Edge > Extensions, and then select Configure extension management settings.
- Enable the policy, then enter the permissions that you want allowed or blocked, compressing the permissions to a single JSON string.
The following examples show how to block extensions on a hostname and how to block extensions on the same domain.
JSON example to block hostname
This example shows the JSON and compressed JSON string to block any extension from accessing the www.microsoft.com hostname.
{
"*":{
"runtime_blocked_hosts":["www.microsoft.com"]
}
}
{"*":{"runtime_blocked_hosts":["www.microsoft.com"]}}
Note
To block all extensions from accessing a webpage, use an asterisk for the extension ID, as shown in the previous example. If you specify one extension ID instead of an asterisk, the policy will only apply to that extension. You can block more than one extension, but they need to be separate entries.
JSON example to block extensions on same domain
This example shows the JSON and compressed JSON string to block specific extensions from running on the same domain, "importantwebsite".
{
"aapbdbdomjkkjkaonfhkkikfgjllcleb": {
"runtime_blocked_hosts": ["*://*.importantwebsite"]
},
"bfbmjmiodbnnpllbbbfblcplfjjepjdn": {
"runtime_blocked_hosts": ["*://*.importantwebsite"]
}
}
{"aapbdbdomjkkjkaonfhkkikfgjllcleb": {"runtime_blocked_hosts": ["*://,*.importantwebsite"]},"bfbmjmiodbnnpllbbbfblcplfjjepjdn": {"runtime_blocked_hosts": ["*://*.importantwebsite"]}}
Allow or block extensions in group policy
You can use the ExtensionInstallBlocklist and ExtensionInstallAllowlist policies to control which extensions are blocked or allowed. Use the following steps as a guide to allow all extensions except those you want to block.
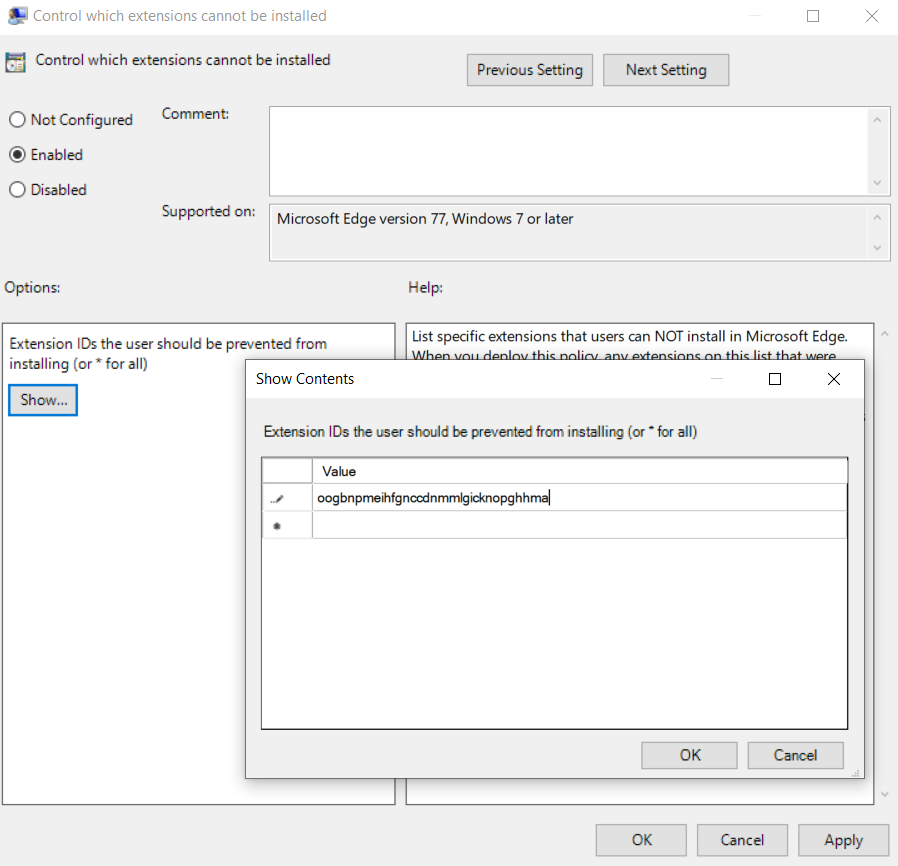
Open the group policy management editor and go to Administrative Templates > Microsoft Edge > Extensions > and then select Control which extensions cannot be installed.
Select Enabled.
Click Show.
Enter the app ID of the extensions that you want to block. When adding multiple app IDs, use a separate row for each ID.
To block all extensions, type * into the policy to prevent any extensions from being installed. You can use this command with the "Allow specific extensions to be installed" policy to only allow certain extensions to be installed. The next screenshot shows an extension that will be blocked based on the app ID that's provided.
Tip
If you can't find the app ID of an extension, look at the extension in the Microsoft Edge Add-ons website. Find the specific extension and you will see the app ID at the end of the URL in the omnibox.
Note
You can add an extension to the blocklist that's already installed on a user's computer. This will disable the extension and prevent the user from re-enabling it. It won't be uninstalled, just disabled.
Force-install an extension
Use the ExtensionInstallForcelist policy to control which extensions are blocked or allowed. Use the following steps as a guide to force-install an extension.
- In the Group Policy Editor, go to Administrative Templates> Microsoft Edge > Extensions > and then select Control which extensions are installed silently.
- Select Enabled.
- Click Show.
- Enter the app ID or IDs of the extension or extensions you want to force-install.
The extension is installed silently without user interaction. Also, the user won't be able to uninstall or disable the extension. This setting overwrites over any blocklist policy that's enabled.
Note
For extensions hosted in the Chrome web store use a string such as: pckdojakecnhhplcgfflhndiffaohfah;https://clients2.google.com/service/update2/crx.
For self-hosted extensions use the pattern extension_id;update_url where update_url points to the location of the update manifest XML file. For example,
mfjlfjaknfckffgjgmdfeheeealceoak;https://file_location.azurewebsites.net/picture_of_the_day.xml.
Block extensions from a specific store or update URL
To block extensions from a particular store or URL, you only need to block the update_url for that store using the ExtensionSettings policy.
Use the following steps as a guide to block extensions from an particular store or URL.
- Open the group policy management editor and go to Administrative Templates > Microsoft Edge > Extensions > and then select Configure extension management settings.
- Enable the policy, then enter the permissions that you want allowed or blocked, compressing it to a single JSON string.
The next example shows the JSON and compressed JSON string to block from the Chrome Web Store using its update URL (https://clients2.google.com/service/update2/crx).
JSON example for blocking on update URL
{
"update_url:https://clients2.google.com/service/update2/crx":{
" installation_mode":"blocked"
}
}
{"update_url:https://clients2.google.com/service/update2/crx":{"installation_mode":"blocked"}}
Note
You can still use ExtensionInstallForceList and ExtensionInstallAllowList to allow/force install specific extensions even if the store is blocked using the JSON in the previous example.