Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Automated machine learning (AutoML) automates the process of applying machine learning to data. Given a dataset, you can run AutoML to iterate over different data transformations, machine learning algorithms, and hyperparameters to select the best model.
Note
This article refers to the ML.NET AutoML API, which is currently in preview. Material is subject to change.
How does AutoML work?
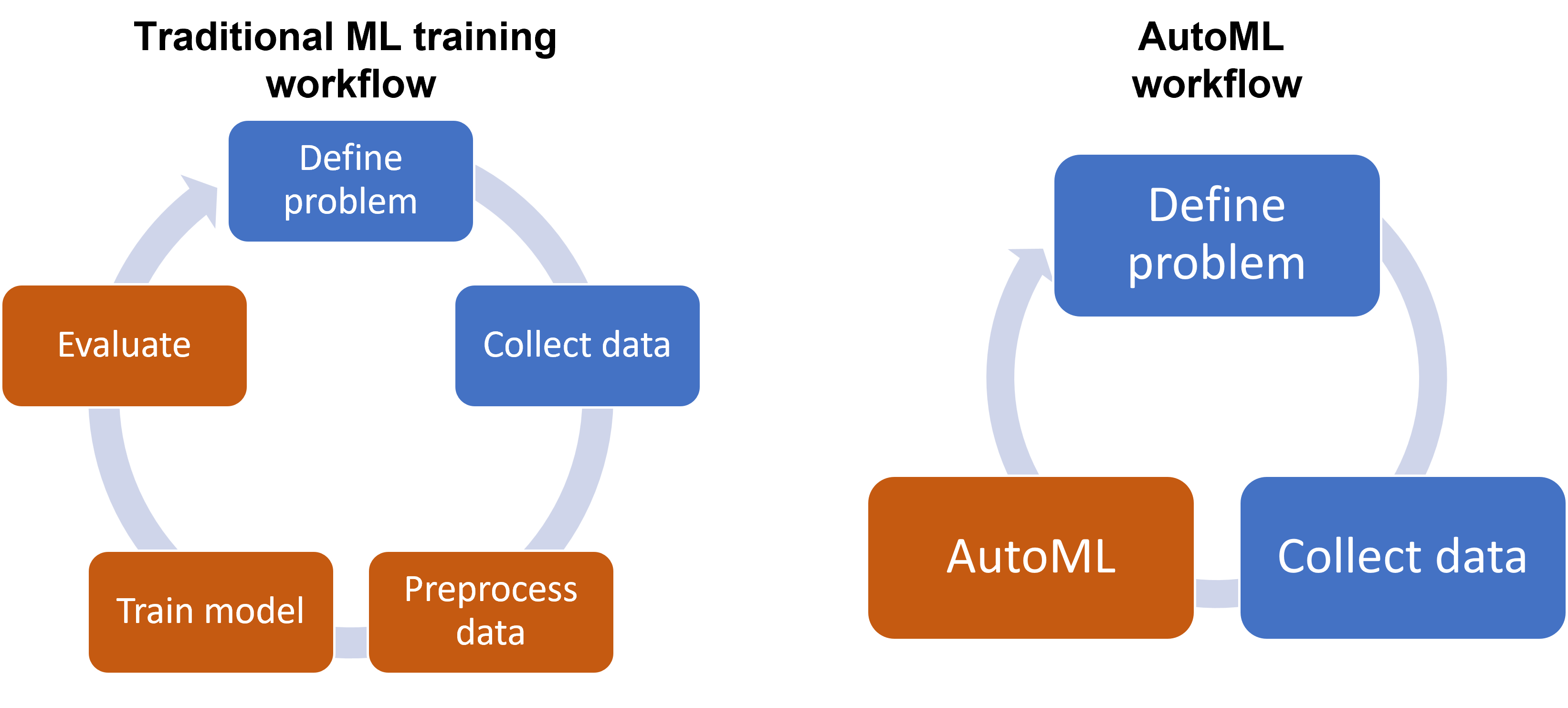
In general, the workflow to train machine learning models is as follows:
- Define a problem
- Collect data
- Preprocess data
- Train a model
- Evaluate the model
Preprocessing, training, and evaluation are an experimental and iterative process that requires multiple trials until you achieve satisfactory results. Because these tasks tend to be repetitive, AutoML can help automate these steps. In addition to automation, optimization techniques are used during the training and evaluation process to find and select algorithms and hyperparameters.
When should I use AutoML?
Whether you're just getting started with machine learning or you're an experienced user, AutoML provides solutions for automating the model development process.
- Beginners - If you're new to machine learning, AutoML simplifies the model development process by providing a set of defaults that reduces the number of decisions you have to make when training your model. In doing so, you can focus on your data and the problem you're trying to solve and let AutoML do the rest.
- Experienced users - If you have some experience with machine learning, you can customize, configure, and extend the defaults provided by AutoML based on your needs while still leveraging its automation capabilities.
AutoML in ML.NET
- Featurizer - Convenience API to automate data preprocessing.
- Trial - A single hyperparameters optimization run.
- Experiment - A collection of AutoML trials. ML.NET provides a high-level API for creating experiments which sets defaults for the individual Sweepable Pipeline, Search Space, and Tuner components.
- Search Space - The range of available options to choose hyperparameters from.
- Tuner - The algorithms used to optimize hyperparameters. ML.NET supports the following tuners:
- Cost Frugal Tuner - Implementation of Frugal Optimization for Cost-related Hyperparameters, which takes training cost into consideration
- Eci Cost Frugal Tuner - Implementation of Cost Frugal Tuner for hierarchical search spaces. Default tuner used by AutoML.
- SMAC - Tuner that uses random forests to apply Bayesian optimization.
- Grid Search - Tuner that works best for small search spaces.
- Random Search
- Sweepable Estimator - An ML.NET estimator that contains a search space.
- Sweepable Pipeline - An ML.NET pipeline that contains one or more Sweepable Estimators.
- Trial Runner - AutoML component that uses sweepable pipelines and trial settings to generate trial results from model training and evaluation.
It's recommended for beginners to start with the defaults provided by the high-level experiment API. For more experienced users looking for customization options, use the sweepable estimator, sweepable pipeline, search space, trial runner, and tuner components.
For more information on getting started with the AutoML API, see the How to use the ML.NET Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) API guide.
Supported tasks
AutoML provides preconfigured defaults for the following tasks:
- Binary classification
- Multiclass classification
- Regression
For other tasks, you can build your own trial runner to enable those scenarios. For more information, see the How to use the ML.NET Automated Machine Learning (AutoML) API guide.