Device provisioning for iOS
While developing a .NET Multi-platform App UI (.NET MAUI) app it's essential to test it by deploying the app to a physical device, in addition to the simulator. Device-only bugs and performance issues can transpire when running on a device, due to hardware limitations such as memory or network connectivity. To test an app on a physical device, the device must be provisioned, and Apple must be informed that the device will be used for testing.
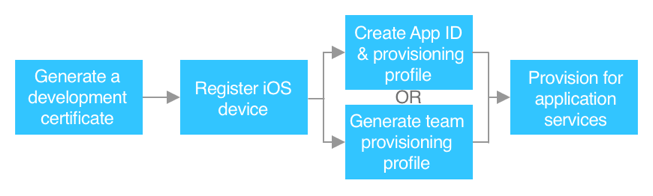
The following diagram shows the steps required to provision an app so that it can be deployed to a device:
Before attempting to deploy an app to a device, you must have an active subscription to Apple's Developer Program. Apple offers two program options:
- Apple Developer Program. Regardless of whether you are an individual or represent an organization, the Apple Developer Program enables you to develop, test, and distribute apps.
- Apple Developer Enterprise Program, which is most suited to organizations that want to develop and distribute apps in-house only. Members of the Apple Developer Enterprise Program do not have access to App Store Connect, and apps created cannot be published to the App Store.
To register for either of these programs, you must first have an Apple ID. Then you can visit the Apple Developer Program to register for a program.
To run an app on a device requires the app to include a thumbprint that contains information about the app and the developer. iOS uses this thumbprint to make sure that the app hasn't been tampered with. This is achieved by requiring app developers to register their Apple ID as a developer, generate a certificate, register the device on which the app will be deploying during the development process, and create an App ID and provisioning profile.
When deploying an app to a device, a provisioning profile is also installed on the device. The provisioning profile exists to verify the information that the app was signed with at build time and is cryptographically signed by Apple. Together, the provisioning profile and thumbprint checks determine if an app can be deployed to a device by checking the following:
- Certificate – has the app been signed with a private key that has a corresponding public key in the provisioning profile? The certificate also associates the developer with a development team.
- App ID – does the bundle identifier for the app match the App ID in the provisioning profile?
- Device – is the device contained in the provisioning profile?
Provisioning your device
There are two approaches to provisioning your iOS device:
- Automatically. Signing identities, App IDs, and provisioning profiles will be automatically created and managed by Visual Studio. This is the recommended approach for provisioning an iOS device. For more information, see Automatic provisioning.
- Manually. Signing identities, App IDs, and provisioning profiles will be created and managed in your Apple Developer Account. For more information, see Manual provisioning.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for
