Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this article, you learn how to connect to an Azure Data Lake Storage (ADLS) Gen 2 or Windows Azure Storage Blob (WASB) account through an instance of .NET for Apache Spark running locally on your Windows machine.
Warning
.NET for Apache Spark targets an out-of-support version of .NET (.NET Core 3.1). For more information, see the .NET Support Policy.
Set up the environment
Download the Apache Spark distribution built without Hadoop from official website (choose a version supported by .NET for Apache Spark), and extract it to a directory. Set the environment variable
SPARK_HOMEto this directory.Download the Apache Hadoop binary from here and extract to a folder, and set your
HADOOP_HOMEenvironment variable to this folder.Download the
winutils.exeandhadoop.dllfiles from this location (depending on the version of Hadoop installed in the previous step) and put them in the bin folder of your Hadoop. These binaries are needed on Windows in order to get everything setup correctly (this is explained in detail in the Apache wiki here).Configure your Hadoop installation by making the following changes to your
%HADOOP_HOME%\etc\hadoop\hadoop-env.cmdfile:- Set the
JAVA_HOMEproperty using the DOS path (since Hadoop doesn't like spaces inJAVA_HOME). This should look something like this:C:\Progra~1\Java\jdk1.8.0_241(Pointing to whatever version of Java you have installed on your local machine). - Append
%HADOOP_HOME%\share\hadoop\tools\lib\*toHADOOP_CLASSPATH. Your finalhadoop-env.cmdfile should look something like this:
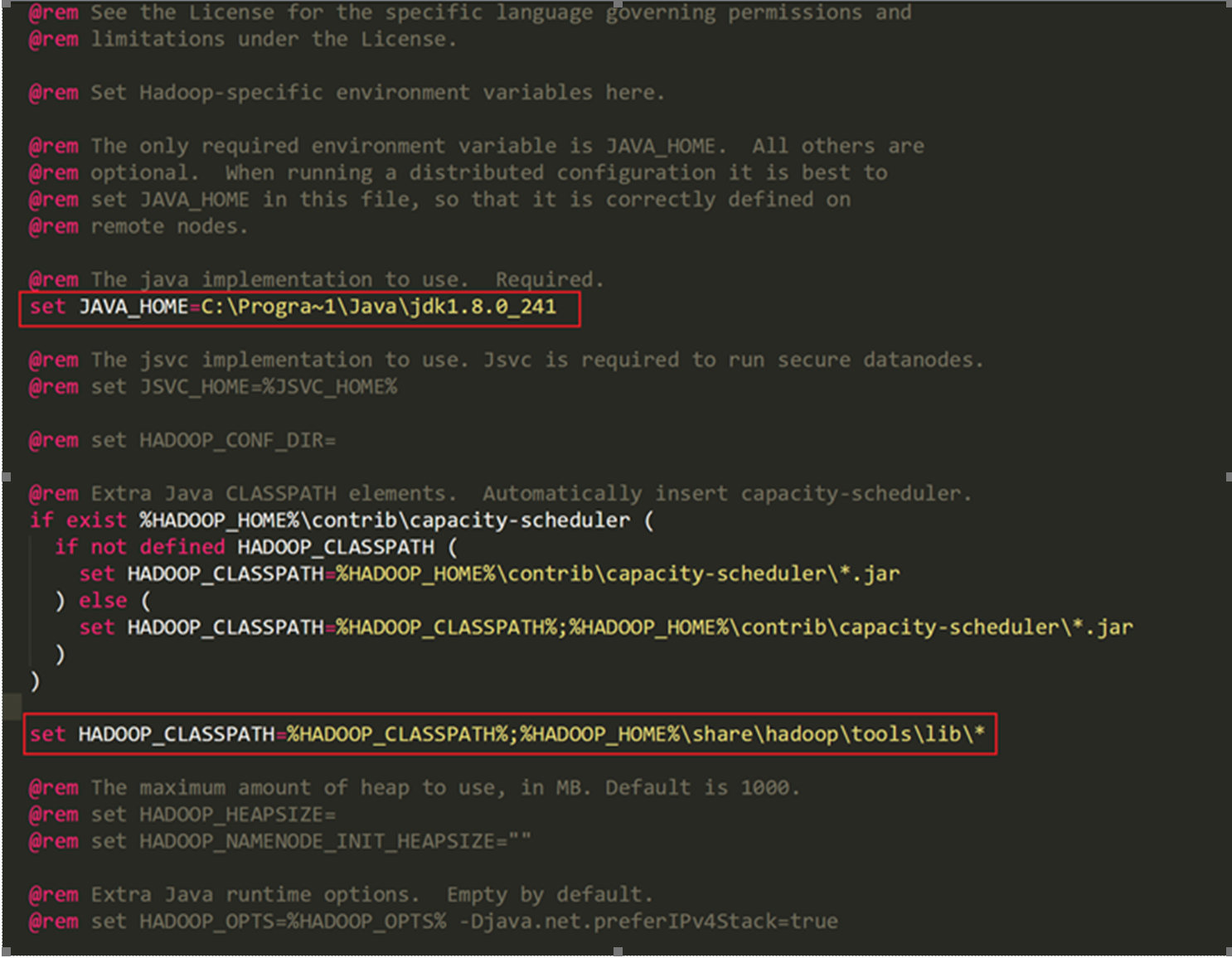
- Set the
Configure your storage account in Hadoop
Open the ADLS Gen 2 or WASB storage account you want to connect to through the Azure portal and open the Access keys panel under the Settings blade and copy the value of Key from under key1.
Now in order to configure Hadoop to access your ADLS Gen2 account you would have to edit your
core-site.xml(located in%HADOOP_HOME%\etc\hadoop\) file which contains cluster-wide configuration. Add the following properties inside the<configuration>tags in this file:<configuration> <property> <name>fs.azure.account.auth.type.YOUR_ACCOUNT_NAME.dfs.core.windows.net</name> <value>SharedKey</value> <description></description> </property> <property> <name>fs.azure.account.key.YOUR_ACCOUNT_NAME.dfs.core.windows.net</name> <value>YOUR ACCESS KEY (copied from Step 1)</value> <description>The secret password. Never share these.</description> </property> </configuration>If you are trying to connect to a WASB account, replace
dfswithblobin the property names. For example,fs.azure.account.auth.type.YOUR_ACCOUNT_NAME.blob.core.windows.net.You can test the connectivity to your Storage Account from Hadoop by running the following command from your
%HADOOP_HOME%directory:bin\hdfs dfs -ls <URI to your account>
This should display a list of all files/folders in the path provided by your URI.
Note
The format to derive the URI to your Storage account is as follows:
For ADLS: abfs[s]://<file_system>@<account_name>.dfs.core.windows.net/<path>/<file_name>
For WASB: wasb[s]://<file_system>@<account_name>.blob.core.windows.net/<path>/<file_name>
Connect to your storage account
If the above command worked, you can now move on to accessing this storage account through Spark. First run the command
hadoop classpathfrom the commandline inside%HADOOP_HOME%and copy the output.Set the output of the command run in Step 1 to the value of environment variable
SPARK_DIST_CLASSPATH.Now you should be able to access your ADLS or WASB storage account through Spark .NET using the abfs URI as shown in the simple example below. (For this example we use the standard
people.jsonexample file provided with every Apache Spark installation.):SparkSession spark = SparkSession .Builder() .AppName("Connect to Azure Storage locally") .GetOrCreate(); DataFrame df = spark.Read().Json("wasbs://file_system@account_name.blob.core.windows.net/path/people.json"); //DataFrame df = spark.Read().Json("abfss://file_system@account_name.dfs.core.windows.net/path/file.json"); df.Show();The result as displayed is the DataFrame (
df) as shown below:+----+-------+ | age| name| +----+-------+ |null|Michael| | 30| Andy| | 19| Justin| +----+-------+