Comply with privacy laws and regulations
Introduction
The European Union (EU) General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) gives significant rights to individuals regarding their data. Refer to the Microsoft Learn General Data Protection Regulation Summary for an overview of GDPR, including terminology, an action plan, and readiness checklists to help you meet your obligations under GDPR when using Microsoft products and services.
You can learn more about GDPR and how Microsoft helps support it and our customers who are affected by it.
- The Microsoft Trust Center provides general information, compliance best practices, and documentation helpful to GDPR accountability, such as Data Protection Impact Assessments, Data Subject Requests, and data breach notification.
- The Service Trust portal provides information about how Microsoft services help support compliance with GDPR.
Shared responsibility model
Your compliance with the privacy laws and regulations is an ongoing process and involves your role as a controller and, in some cases, Microsoft as a processor. Depending on which model-driven app your organization uses, you may find that you are both controller and processor or that you have a shared responsibility with Microsoft.
Unified Service Desk client application runs on-premises, so you hold both the controller and processor roles:
Controller. The natural or legal person, public authority, agency, or other body which, alone or jointly with others, determines the purposes and means of the processing of personal data. A controller doesn't have to be located within the EU for the privacy laws and regulations to apply.
Processor. The natural or legal person, public authority, agency, or other body which processes personal data on behalf of the controller.
Data definitions
Any information related to an identified or identifiable natural person is considered as personal data. This includes both direct identification (such as your legal name) and indirect identification (such as specific information that makes it clear that it's you the data references). Personal data also includes online identifiers (such as IP addresses and mobile device IDs) and location data.
Stages of privacy laws and regulations
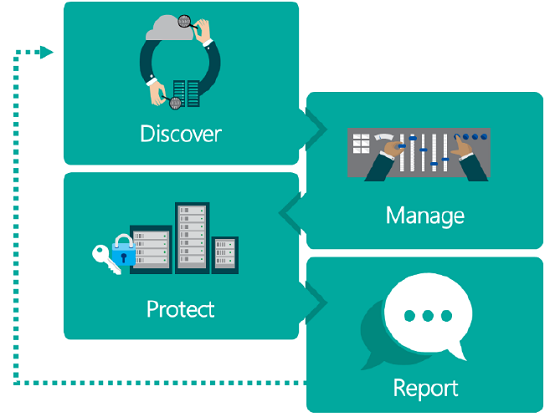
| Stages | Description |
|---|---|
| Discover | Identify what data under your control is subject to the privacy laws and regulations. This analysis includes understanding what data you have and where it exists. |
| Manage | The privacy laws provide more control over your data. You can manage access and control how data is used. |
| Protect | The privacy laws require you to establish security controls to prevent, detect, and respond to the vulnerabilities and data breaches. |
| Report | The privacy laws and regulations set new standards in transparency, accountability, execution, data requests, and report data breaches. |
See also
Unified Service Desk data compliance under privacy laws and regulations