Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
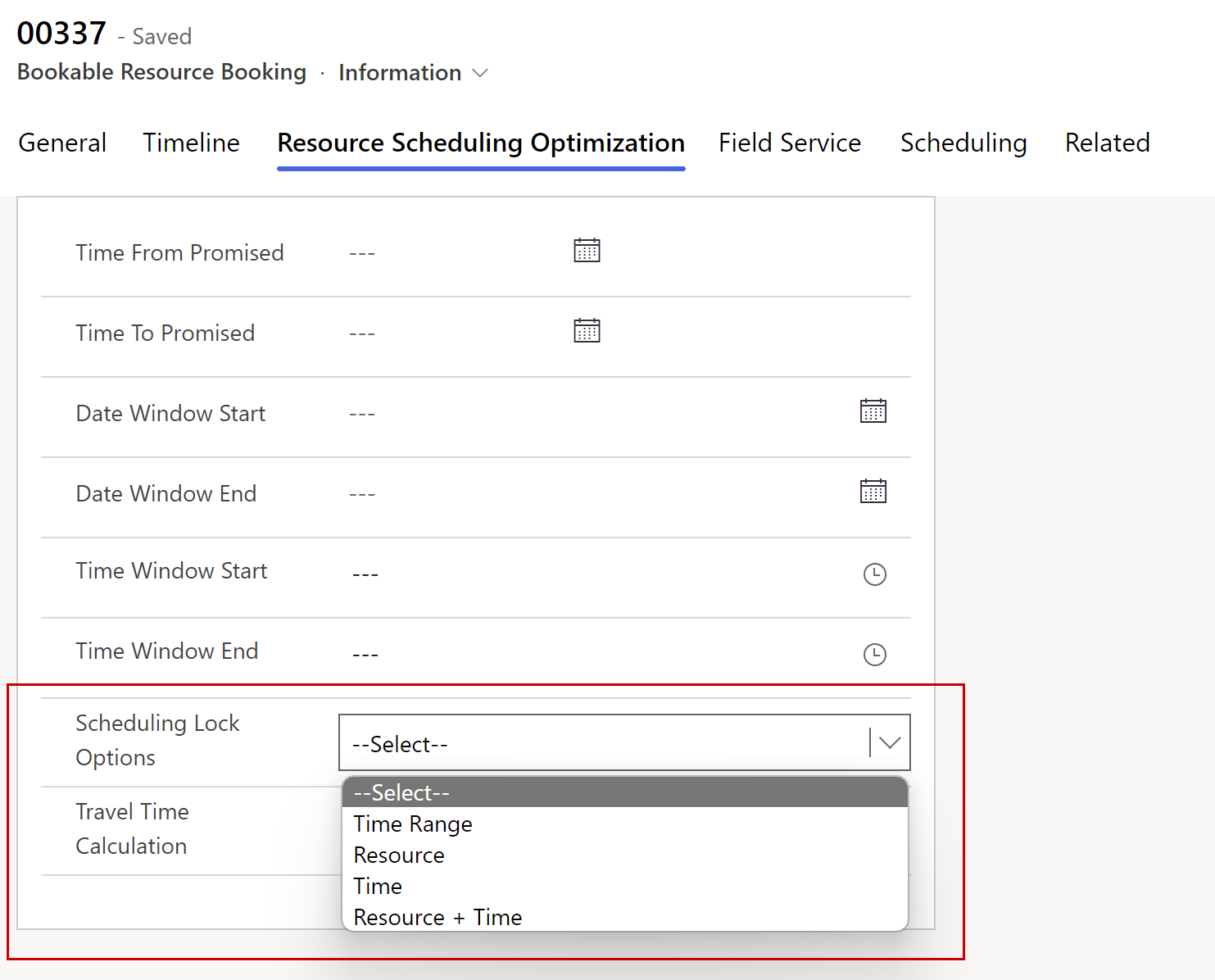
Once a booking is created, a lock can be set on the Scheduling Lock Options field in the Resource Scheduling Optimization tab of the Bookable Resource Booking record. Resource Scheduling Optimization always includes locked bookings as part of the optimized schedule.
Booking lock options
There are four options:
Time Range: Resource Scheduling Optimization can move bookings within certain time ranges to ensure the Estimated Arrival Time falls into this time range but not the booking end time. Resource Scheduling Optimization can assign bookings to other resources by respecting the time range and the following time-related fields.
- Date Window Start and Date Window End are set to the same day: Resource Scheduling Optimization schedules the booking on that day but the time of day doesn't matter.
- Time Window Start and Time Window End define a time frame: Resource Scheduling Optimization schedules the booking in that time frame but the date doesn't matter.
- Time From Promised and Time To Promised are set to a date and a time frame: Resource Scheduling Optimization schedules a booking on the selected date in the selected time range.
- Date Window Start/End and Time Window Start/End are set to a time frame on the same day: Resource Scheduling Optimization schedules a booking on the selected date in the selected time range.
Note
If time and date fields contain conflicting information, Resource Scheduling Optimization uses Time From/To Promised first.
Resource: Resource Scheduling Optimization can move bookings to other time frames, but has to keep the same resource.
Time: Resource Scheduling Optimization can move bookings to other resources but has to keep the estimated arrival time.
Resource and Time: Resource Scheduling Optimization can’t move bookings to any other resource or any other time frame. The booking’s start time and estimated travel duration might be changed if Resource Scheduling Optimization schedules a booking in a new location before the booking becomes a locked booking.
Example
The resource Bernadette has a booking that starts at 9:15 AM. This booking is locked to time. When Resource Scheduling Optimization runs, the system detects a 15-minute idle time for Bernadette in the morning. No other requirement duration fits into that slot with the locked booking next to it.
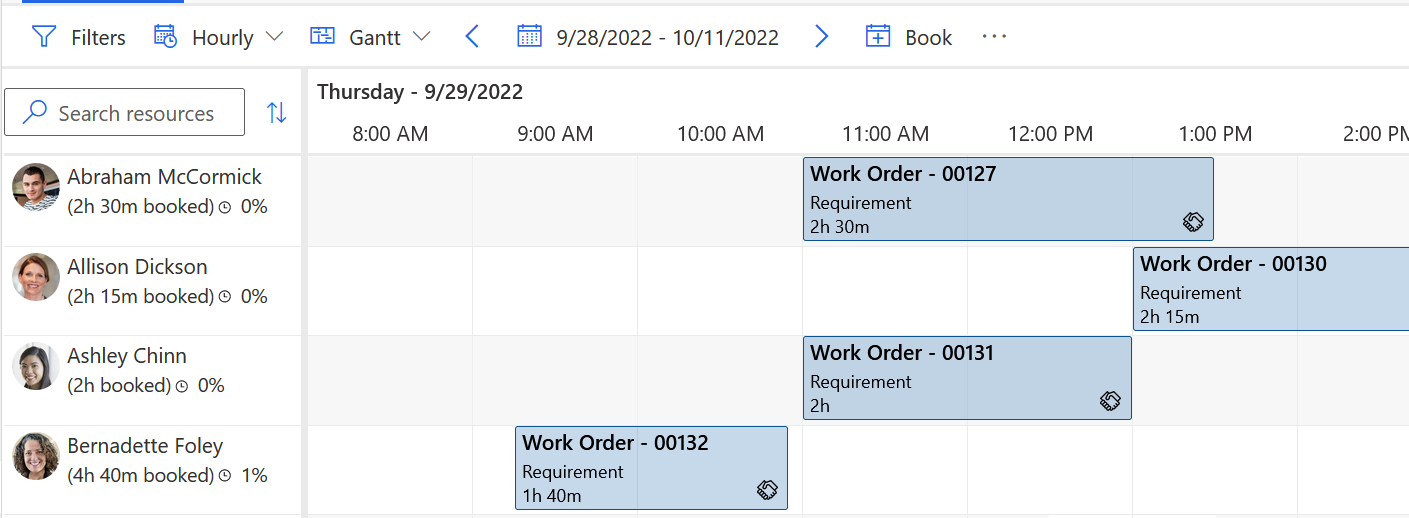
To respect the defined lock option, Resource Scheduling Optimization keeps the locked booking in the schedule. However, as part of the schedule optimization, the booking gets assigned to Ashley. This change frees up time for Bernadette to complete other jobs.
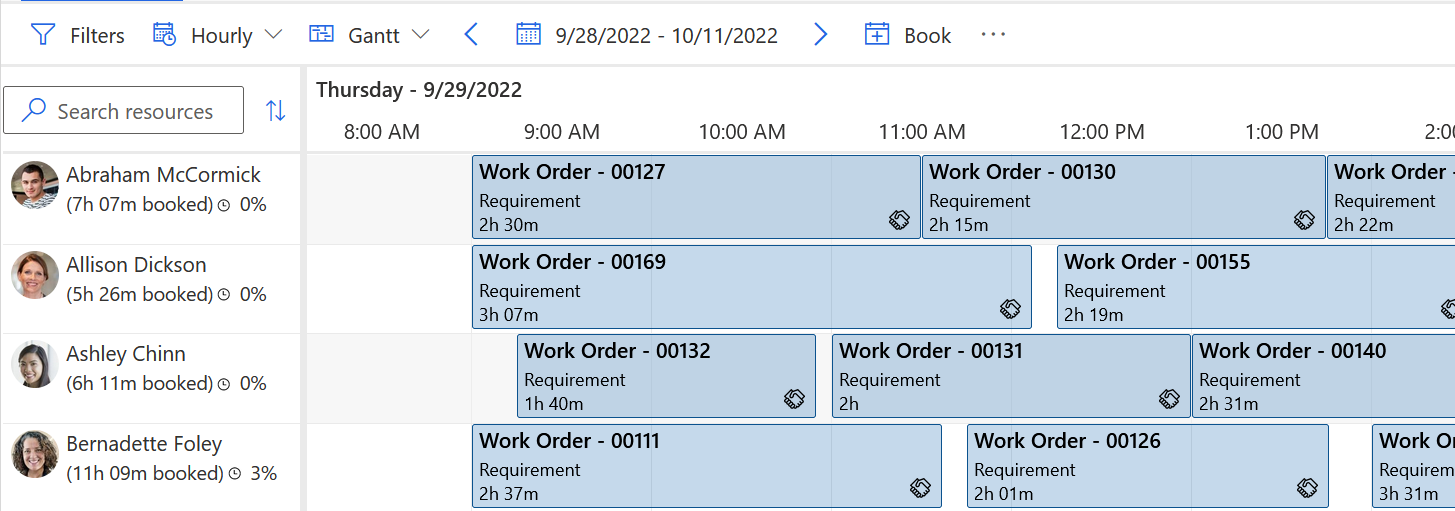
Excessive use of lock constraints
Excessive use of lock constraints might result in poor optimization of the final schedule. Booking lock options should be used wisely to maximize Resource Scheduling Optimization results and minimize interference with other Resource Scheduling Optimization objectives.
For example, there are two requirements, A (one hour) and B (eight hours). We have one resource (Jeff) that works eight hours per day. When Resource Scheduling Optimization is run with the objective to maximize total working hours, requirement B (8 hours) should be assigned to the resource Jeff.
If you book requirement A (1 hour) to the resource Jeff and lock that booking to the resource, Resource Scheduling Optimization makes sure that requirement A remains on the schedule. But, it doesn't schedule the requirement B (eight hours) on the same day and leaves Jeff with only one hour of scheduled work.