Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Note
Community interest groups have now moved from Yammer to Microsoft Viva Engage. To join a Viva Engage community and take part in the latest discussions, fill out the Request access to Finance and Operations Viva Engage Community form and choose the community you want to join.
This article provides an overview of the security architecture of finance and operations.
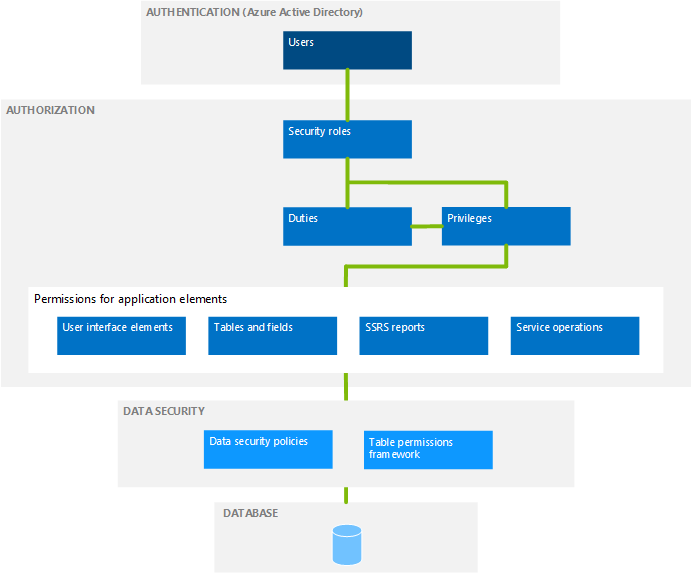
When you understand the security architecture, you can more easily customize security to fit the requirements of your business. The following diagram provides a high-level overview of the security architecture.
Authentication
By default, only authenticated users who have user rights can establish a connection.
Microsoft Entra ID is a primary identity provider. To access the system, users must be provisioned into a finance and operations instance and should have a valid Microsoft Entra account in an authorized tenant.
Authorization
Authorization is the control of access to finance and operations applications. Security permissions are used to control access to individual elements of the program: menus, menu items, action and command buttons, reports, service operations, web URL menu items, web controls, and fields in the finance and operations client.
Individual security permissions are combined into privileges, and privileges are combined into duties. The administrator grants security roles access to the program by assigning duties and privileges to those roles.
Context-based security controls access to securable objects. When a privilege is associated with an entry point (such as a menu item or a service operation), a level of access, such as Read or Delete, is specified. The authorization subsystem detects the access at run time when that entry point is accessed, and applies the specified level of access to the securable object that the entry point leads to. This functionality helps to ensure that there isn't any over-permissioning, and the developer gets the access that was intended.
For more information, see Role-based security.
Data security
Authorization is used to grant access to elements of the program. By contrast, data security is used to deny access to tables, fields, and rows in the database.
Use the extensible data security framework to supplement role-based security by restricting access to table records based on security policies. A security permission, as part of a user role, increases the access a user has to data, while a security policy decreases access to data.
For more information, see Extensible data security policies.
Additionally, the Table Permissions Framework helps protect some data. Data security for specific tables is enforced by Application Object Server (AOS).
Auditing user logins
A system administrator or security administrator can access the user logins logs. For more information, see Track user sign-ins.