Create custom triggers in Customer Insights - Journeys
Custom triggers are a flexible way to capture important moments and interactions, allowing you to orchestrate uniquely engaging customer interactions.
A custom trigger is a user-defined signal that can contain and transport any type of information that a customer journey can act upon. Customer Insights - Journeys users are in full control of what custom triggers represent and what kind of information they convey.
Creating a custom trigger in Customer Insights - Journeys is straightforward. However, custom triggers require collaboration between marketing users and a developer team who will be responsible for integration of small snippets of code in systems that will ultimately allow the trigger to function.
Creating a custom trigger involves three steps: initial trigger creation, trigger integration, and finalization.
1. Initial trigger creation
This step is performed in the Triggers section of Customer Insights - Journeys. To create the custom trigger, select +New trigger from the top ribbon. On the following screen, you'll give the trigger a name and select that you want to trigger an action When a customer interacts with a website/app.
The other trigger option ("When a record related to a customer is created or updated") refers to triggers based on Dataverse record changes. Learn more: Trigger a journey based on a Dataverse record change
On the next screen, follow the on-screen instructions to define:
Title and Description
Give the trigger a short, descriptive title. Include a description to help other users find the right trigger in the catalog.
Attributes
Trigger attributes enrich the trigger and provide additional context for the journey to create branches or personalize content. For example, a Wi-Fi sign-up custom trigger might contain a Location attribute that represents the physical location where a customer has completed a sign-up. The value of the Location attribute could then be used in a journey to send a different message depending on whether the sign-up comes from the parking lot or the main lobby.
Attributes have a Name and a Data type. Choosing the correct data type (text, number, true or false, date/time, or entity reference) is important to ensure that customer journeys can provide appropriate comparators in conditions. For example, if an attribute is of data type Number, the journey provides a comparator such as less than or equal to. If an attribute is of type Date/time, the journey will provide comparators such as before, on, and after. An attribute of data type Entity reference points to a specific entity, saving you from having to define a complex list of attributes to trigger a journey based on changes to an entity.
You can stack attributes with different data types to create sophisticated triggers. If, for example, you want to trigger a journey when a customer purchases a product, you would add a Data/time attribute to activate the trigger when an action happens, then you would add an Entity reference attribute pointing to the Order entity to reference the items contained in the customer's order.
Special Attributes
Customer data is a special attribute present by default in every custom trigger. This attribute contains information about the customer that performs the trigger action. The data type can either be a Dynamics 365 contact or lead, or a Customer Insights - Data profile. In code, this attribute is referred to as authID.
contactpoint_email is a special attribute that is present in a custom trigger that is tied to a Customer Insights - Data profile. This attribute is used as a fallback in case the full Customer Insights - Data profile isn't available. Developers should include the customer's email in this attribute to ensure the customer can be reached by email even if their full profile information isn't available.
contactpoint_phone is a special attribute that is present in a custom trigger that is tied to a Customer Insights - Data profile. This attribute is used as a fallback in case the full Customer Insights - Data profile isn't available. Developers should include the customer's phone number in this attribute to ensure the customer can be reached by text messages even if their full profile information isn't available.
Entity references
Under the Data type drop-down, you'll find an Entity reference option. This option allows you to point to a specific entity, saving you from having to specify a list of attributes to capture
2. Trigger integration
Once the trigger is created, a code snippet is generated by the system. You can download the code snippet and share it with developers. Or, developers can access the snippet directly through the link provided by the app.
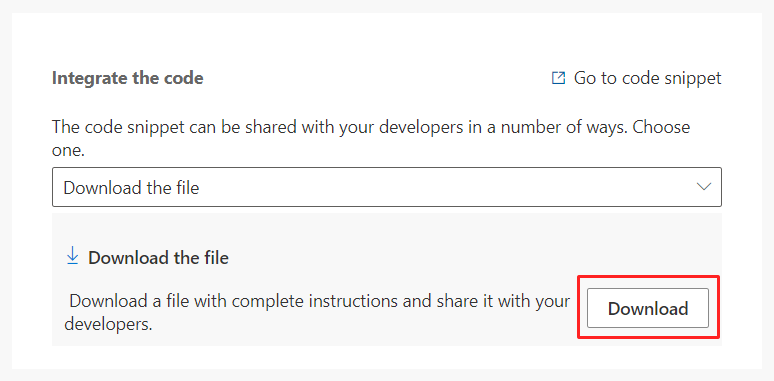
Note
To directly access the code snippet, developers will need access to the Dynamics 365 Customer Insights - Journeys app.
The code snippet enables a customer action on an external app or website to trigger a customer journey in Customer Insights - Journeys. For instance, when a customer clicks on the checkout button on an e-commerce website, the code kicks off an order confirmation customer journey using an “order confirmation” trigger that is invoked on the button click. By adding the code snippet, the developer simply connects the button click to the “order confirmation” trigger.
The code snippet contains instructions detailing how to integrate the trigger code on external systems. You can integrate the trigger using JavaScript (for web pages), C# or Python (for standalone systems), or through the iOS and Android SDKs.
Tip
Some integration of custom triggers can present security implications. The code snippet that is provided with the trigger contains an ingestion key that uniquely identifies the Customer Insights - Journeys instance. An attacker with access to the ingestion key could possibly send spurious triggers that can trigger unintended customer journeys. It's a good practice to:
- Protect the ingestion key wherever possible.
- Limit the use of attributes in custom triggers, especially when those attributes can be used to personalize content and act as potential attack vectors such as cross-site scripting.
3. Finalize the trigger
Once the integration has been completed, the Triggers page shows information to confirm that the custom trigger is working as expected. With the integration complete and verified, the trigger is marked as Ready to use, which makes the trigger visible and available in journeys.
Tip
When you're looking at the list of triggers, custom triggers have a plain lightning bolt icon  . Out-of-the-box triggers have a lightning bolt with a suitcase icon
. Out-of-the-box triggers have a lightning bolt with a suitcase icon  .
.