Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In Dynamics 365 Sales, assignment rules automatically distribute, or assign, new and updated leads, opportunities, and insights to your sales team. The automated process saves you time and effort and optimizes the workload across your sales team.
Assignment rules can distribute these records in either of two ways: round robin or load balancing.
- In round robin distribution, the primary consideration is when sellers were last assigned a record.
- In load balancing distribution, the primary consideration is their capacity, or how many active records they're working on.
Depending on its definition, a rule that prioritizes load balancing might still use round robin criteria to assign records to sellers.
It's important to understand both the differences between them and how other criteria—like your sellers' workload and schedules—affect how records are assigned.
Segments and assignment rules are part of the work assignment feature. Work assignment is available in sales accelerator version 9.1.23074.10021 and is rolling out in phases in different regions. Learn more about work assignment.
Round robin distribution
Round robin assignment distributes a new or updated record fairly among the sellers who meet the rule's criteria. It gives the record to the seller who's waited the longest for a new lead, opportunity, or insight, including records that were assigned manually or by an add-in. The order of round robin distribution is stored at the organization level, not at the rule level.
Let's look at some scenarios to understand round robin distribution.
Scenario 1
A lead comes into the system at 11:20 PM. Based on the selection criteria that are defined in the assignment rule, three sellers can potentially work on the lead:
| Seller | Last assigned record |
|---|---|
| Miriam | 10:02 AM |
| Sanjay | 10:31 AM |
| Susana | 11:17 AM |
Miriam's last assignment is earlier than Sanjay's and Susana's. Miriam has been waiting longest, so the lead is assigned to her.
An opportunity comes into the system at 1:50 PM, and a sales manager manually assigns it to Susana. When a record is assigned manually, the order of assignment changes from the last assignment for the rule that's associated with that record type. However, the order of assignment doesn't change for assignment rules that are associated with other entity types.
Another lead comes into the system at 2:30 PM. The assignment rule assigns it to Sanjay. The order now looks like this:
| Seller | Last assigned record | Entity type | Assignment source | Next assignment order when only lead rules are configured | Next assignment order when lead and opportunity rules are configured |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miriam | 11:20 PM | Lead | Assignment rule engine | Sanjay, Susana, Miriam | Sanjay, Susana, Miriam |
| Susana | 1:50 PM | Opportunity | Manual | Sanjay, Susana, Miriam | Sanjay, Miriam, Susana |
| Sanjay | 2:30 PM | Lead | Assignment rule engine | Susana, Miriam, Sanjay | Miriam, Susana, Sanjay |
A new lead comes into the system at 3:00 PM. A sales manager manually assigns it to Miriam. The new order of assignment looks like this:
| Seller | Last assigned record | Entity type | Assignment source | Next assignment order when only lead rules are configured | Next assignment order when lead and opportunity rules are configured |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Miriam | 3:00 PM | Lead | Manual | Susana, Sanjay, Miriam | Susana, Sanjay, Miriam |
Scenario 2
A set of rules is created for assigning records to three sellers, Miriam, Sanjay, and Susana, in that order.
- Rule 1 assigns an incoming lead to Miriam. The new order becomes Sanjay, Susana, Miriam.
- Rule 2 assigns the next incoming lead to Sanjay. The order is now Susana, Miriam, Sanjay.
- Rule 3 assigns the next lead to Susana. The order is now Miriam, Sanjay, Susana.
- Rule 1 assigns the next lead to Miriam.
Only Rule 1 assigns the record to Miriam twice consecutively. This is because the order of assigning records is stored at the organization level, not at the rule level.
Scenario 3
A rule is created for assigning records to two sellers, Miriam and Sanjay, in that order.
Miriam generates a lead and automatically becomes its owner. When the rule is executed, the lead is assigned to Sanjay, not Miriam, and the assignment order is now Miriam and Sanjay.
Why? When a seller creates a record, they become its owner and are automatically included in the distribution list. This affects the order in which future records are assigned.
Load balancing distribution
Load balancing assignment also distributes a new or updated record fairly among the sellers who meet the rule's criteria. It gives the record to the seller who can take on more work. This method makes sure that all salespeople have a fair share of work and reduces uneven workloads.
Let's look at an example to understand load balancing distribution.
A lead comes into the system. Based on the selection criteria that are defined in the assignment rule, three sellers can potentially work on the lead:
| Seller | Available capacity |
|---|---|
| Miriam | 10 |
| Sanjay | 12 |
| Susana | 15 |
Susana can handle more work right now than Miriam or Sanjay. Susana gets the lead, and her available capacity is now 14.
Let's assume that Miriam, Sanjay, and Susana can all potentially work on the next few incoming leads.
Two new leads come into the system. Susana still has the most available capacity, so the leads are assigned to her. Afterward, their available capacity looks like this:
| Seller | Available capacity |
|---|---|
| Miriam | 10 |
| Sanjay | 12 |
| Susana | 12 |
One more lead comes into the system. Sanjay and Susana are equally available. Susana got a lead more recently, so the new one is assigned to Sanjay based on round robin criteria. Now their available capacity looks like this:
| Seller | Available capacity |
|---|---|
| Miriam | 10 |
| Sanjay | 11 |
| Susana | 12 |
Miriam closes three leads, increasing her available capacity to 13. A new lead comes into the system. Miriam now has the most capacity, so it's assigned to her.
Other distribution criteria
Assignment rules prioritize fairness in different ways depending on whether you select round robin or load balancing distribution. But fairness isn't the only consideration when records need to be assigned. They can also consider whether sellers are available to take on more work—that is, sellers' workload and work schedule.
Consider seller workload
In your assignment rule definitions, you can select Assign record type based on seller capacity. This option distributes records only to sellers who have the capacity to work on them. If no one does, the records are left unassigned.
Let's look again at our sales team, a little later on the same day.
A new lead comes into the system. Based on the selection criteria that are defined in the assignment rule, four sellers can potentially work on it:
| Seller | Last assignment | Available capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Sanjay | 2:37 PM | 0 |
| Susana | 2:57 PM | 4 |
| David | 3:02 PM | 1 |
| Miriam | 2:35 PM | –2 |
With round robin distribution alone, Miriam, who's been waiting longer for an assignment than the others, would get the lead. However, you told the rule to Assign leads based on seller capacity, and Miriam's available capacity right now is –2. Sanjay has been waiting next longest, but Sanjay's available capacity is 0. The lead goes to Susana.
If no seller who met the criteria had available capacity greater than zero, the lead would be left unassigned.
Consider seller work schedule
In your assignment rule definitions, you can select Assign if a seller is available within N hours, where N is a whole number from 1 to 120. This option distributes records only to sellers whose work schedule shows they're available within the time you select. If no one is, the records are left unassigned. Learn how to set sellers' availability.
The rule considers matched sellers first by assignment priority (load balancing or round robin) and then by who is available, from now up to the maximum time allowed.
As shown in the following diagram, matched sellers are divided into six buckets of 24 hours each based on their work schedules. If no sellers fall in the first bucket, round robin distribution supersedes load balancing even if load balancing distribution is prioritized. The rule continues to evaluate the buckets from top to bottom. When it encounters a nonempty bucket, the rule assigns the lead to the sellers in the bucket based on round robin criteria.
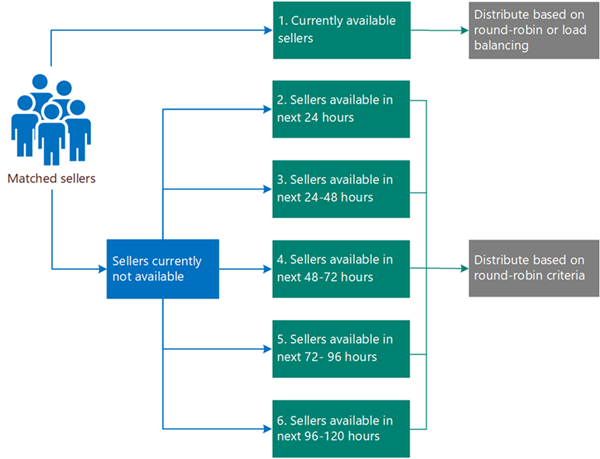
Let's look at an example to understand how sellers' work schedules affect the assignment of records.
In your assignment rules, you prioritize round robin distribution and set a time limit of 48 hours.
A new lead comes into the system on a Friday evening from an inquiry form on your website. Several sellers meet the criteria of an assignment rule, but none of them are working now. Next, the rule considers matching sellers who are available within the next 24 hours. That day is Saturday. Ordinarily, Sanjay would be working, but Sanjay's calendar says he's on vacation. No other sellers are available, so the rule looks at the next 24 hours. No one is working on Sunday either. The rule has reached the limit of 48 hours, so the lead is left unassigned. If the time limit had been 60 hours, the lead would have been assigned to the first seller who was available on Monday morning.
Examples
Let's look at a few more examples in detail to understand how seller availability and workload affect round robin and load balancing distribution. Let's use the following notation for a seller's availability at the time of routing:
- 0D - Currently available
- 1D - Earliest available within 24 hours
- 2D - Earliest available from 24 to 48 hours
- 3D - Earliest available from 48 to 72 hours
- 4D - Earliest available from 72 to 96 hours
- 5D - Earliest available from 96 to 120 hours
Example 1: Round robin, consider seller availability only
The rule matched the following sellers:
| Seller | Availability | Last assigned a lead |
|---|---|---|
| Burt | 1D | 2:37 PM |
| Maya | 1D | 2:15 PM |
| Vivek | 0D | 3:02 PM |
| Maria | 2D | 3:10 PM |
| Sal | 0D | 2:29 PM |
Two sellers, Vivek and Sal, are available first. Vivek got a lead more recently than Sal, so the rule distributes the lead to Sal.
The next leads to come in are assigned to Vivek, then to Sal, and so on, until the availability of the matched sellers changes. The sellers' capacity isn't a consideration.
Example 2: Load balancing, consider seller availability only
Again, the rule matched the following sellers:
| Seller | Availability | Available capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Burt | 1D | 14 |
| Maya | 1D | 20 |
| Vivek | 0D | 5 |
| Maria | 2D | 10 |
| Sal | 0D | 2 |
Again, Vivek and Sal are available first. This time, Vivek has the higher capacity, so the rule distributes the lead to him.
The next leads to come in are assigned to Vivek until Vivek's capacity falls below Sal's. Following leads go to Sal until Sal's capacity falls below Vivek's, and so on, until the availability of the matched sellers changes. In this scenario, the sellers' capacity isn't a consideration. Vivek's and Sal's capacity can fall below zero as long as they're available before the others.
Example 3: Load balancing, consider seller availability and capacity
Once again, the rule matched the following sellers:
| Seller | Availability | Available capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Burt | 1D | 14 |
| Maya | 1D | 20 |
| Vivek | 0D | –1 |
| Maria | 2D | 10 |
| Sal | 0D | 0 |
Because Assign leads based on seller capacity has been selected in the assignment rule definition, the rule ignores Vivek and Sal even though they're available first. That leaves Burt, Maya, and Maria:
| Seller | Availability | Available capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Burt | 1D | 14 |
| Maya | 1D | 20 |
| Maria | 2D | 10 |
Burt and Maya are available before Maria, so Maria is dropped from consideration:
| Seller | Availability | Available capacity |
|---|---|---|
| Burt | 1D | 14 |
| Maya | 1D | 20 |
The rule is configured to prioritize load balancing. However, load balancing distribution only works with sellers who are available at the time of routing. Because Burt and Maya aren't available now, the rule uses round robin criteria instead.
With capacity no longer a consideration, the rule considers who's been waiting for a lead longer:
| Seller | Last assigned a lead |
|---|---|
| Burt | 2:37 PM |
| Maya | 2:15 PM |
The rule assigns the lead to Maya. The next leads to come in are assigned to Burt, then to Maya, and so on, until the availability of the matched sellers changes.