Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article describes how to create calculations for attributes in a product configuration model.
Prerequisites
Calculations are used in a product configuration model to calculate the configuration values for a product. Before you can start to set up calculations, the related product configuration model must exist. For an overview of the setup process for configuration models and the related tasks, see Set up a product configuration model.
Create a calculation
A calculation consists of an expression and a target attribute. Learn more in Calculations for product configuration models FAQ.
To create a calculation for an existing product model, follow these steps.
Go to Product information management > Common > Product configuration models.
Open a product configuration model, and then select Edit.
On the Calculations FastTab, select Add to add a calculation, and then set the following fields:
- Name – Enter a name for the calculation.
- Description – Enter a description of the calculation.
- Target attribute – Select the attribute that you're making the calculation for.
Select Edit expression.
In the Enter a calculation dialog box, add the required attributes, operators, and values to the expression. For more information about how to work with these elements, see Expression constraints and table constraints in product configuration models.
When your expression is ready, select OK.
Calculation examples
This section provides a few examples that show how calculations work.
Example 1
The target attribute is Boolean, and the calculation uses the following conditional expression:
If[(decimalAttribute1 / decimalAttribute2) < 1, True, False]
This expression returns a value of True to the target attribute if decimalAttribute2 is greater than or equal to decimalAttribute1. Otherwise, it returns a value of False.
Example 2
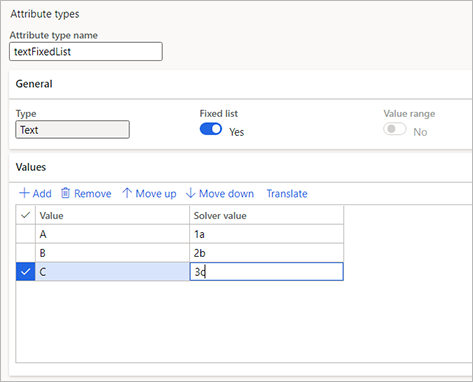
This example uses the text attribute textFixedList as the target attribute. This attribute contains the following fixed list.
| Value | Solver value |
|---|---|
| A | 1a |
| B | 2b |
| C | 2c |
The following screenshot shows how the settings for this attribute might look in your system.
The attribute is used in the following conditional statement:
If[integerAttribute < 150, 0, 2]
If integerAttribute is less than 150, this statement returns the text value of the first record in the fixed list, A. Otherwise, it returns the text value of the third record in the fixed list, C.
Note
The fixed list is equivalent to a zero-based enumeration (enum), and its values are accessed by the appropriate integer value. Therefore, the first fixed list value (A) is matched to 0, the second value (B) is matched to 1, and the third value (C) is matched to 2.
Example 3
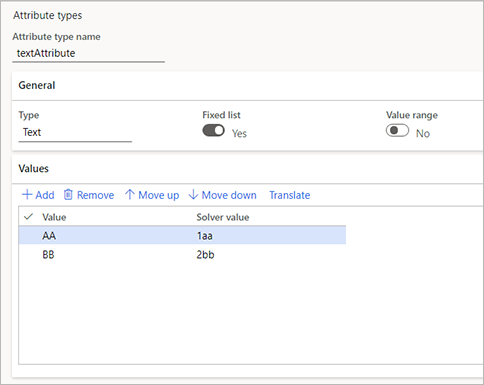
This example uses the textFixedList target attribute from the previous example. It also uses another text attribute, textAttribute, that contains the following fixed list.
| Value | Solver value |
|---|---|
| AA | 1aa |
| BB | 2bb |
The following screenshot shows how the settings for this attribute might look in your system.
The value for the textFixedList attribute is calculated by using the following conditional statement:
If[textAttribute == "1aa", 0, 2]
If the textAttribute value has a solver value that equals 1aa, this expression returns the text value of the first record in the textFixedList fixed list, A. Otherwise, it returns the text value of the third record in the textFixedList fixed list, C.
Note
- The conditional statement must use the solver value of the attribute.
- Only fixed-list text attributes can be used in calculations.