Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Symptoms
Consider the following scenario:
You assign a renewed certificate to one or more Microsoft Exchange Server services.
You try to remove the old certificate in the Exchange admin center (EAC) or by using the Remove-ExchangeCertificate PowerShell cmdlet.
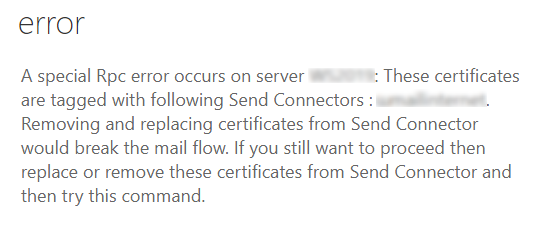
In this scenario, you receive the following error message:
"A special Rpc error occurs on server <server name>: These certificates are tagged with following Send Connectors : <Send connector names>. Removing and replacing certificates from Send Connector would break the mail flow. If you still want to proceed then replace or remove these certificates from Send Connector and then try this command."
The issue occurs if the new certificate has the same issuer name and subject name that are used by the old certificate.
Cause
To avoid disruptions to mail flow, Exchange Server prevents a certificate from being removed if the issuer name and subject name are specified in the TlsCertificateName property of any Send connector. The format of the TlsCertificateName property value is "<I>IssuerName<S>SubjectName". If the TlsCertificateName value matches both the old and the new certificate, Exchange Server will prevent both those certificates from being removed.
Resolution
To remove the old certificate, use the following steps. Unless noted otherwise, run the following PowerShell commands in the Exchange Management Shell (EMS).
Get the thumbprints of the new and old certificates. To do this, get a list of all Exchange Server certificates by running the following command. Then, identify the new and old certificates in the list.
Get-ExchangeCertificate | Format-List FriendlyName,Subject,Issuer,CertificateDomains,Thumbprint,NotBefore,NotAfterFor each Send connector that's reported in the error message, use the Get-SendConnector cmdlet to build an aggregated list of associated source transport servers:
Get-SendConnector -Identity <connector name> | Format-List SourceTransportServersOr, identify the source transport servers in the EAC as follows:
Navigate to Mail flow > Send connectors.
For each Send connector that's reported in the error message:
Double-click to open the connector.
Navigate to Scoping > Source server to see the servers associated with that connector.
To minimize mail flow issues during this procedure, stop the Microsoft Exchange Transport service by running the following command on each source transport server that you found in step 2. The command doesn't have to be run in the EMS, but it does require an elevated PowerShell session.
Stop-Service MSExchangeTransportOr, stop the Microsoft Exchange Transport service by using the Services.msc snap-in on each source transport server.
Note
After you stop the transport service, mail flow on each source transport server is stopped until you restart the Microsoft Exchange Transport service in the final step of this procedure. For more information about mail flow in Exchange Server, see Queues and messages in queues.
For each Send connector that's reported in the error message, use the Set-SendConnector cmdlet to clear its
TlsCertificateNameproperty:Set-SendConnector -Identity <connector name> -TlsCertificateName $NullNote
If you have a large environment that uses different sites, you might have to force AD replication to fully remove the
TlsCertificateNameproperty value on the affected source transport servers.For each source transport server that you found in step 2, remove the old certificate by running the following command:
Remove-ExchangeCertificate -Server <server name> -Thumbprint <old certificate thumbprint>Or you can remove the old certificate in the EAC as follows:
Navigate to Servers > Certificates.
For each source transport server that you found in step 2:
Select the server.
Select the old certificate, and then delete it.
Note
If you don't remove the old certificate from all applicable source transport servers before you reassign the
TlsCertificateNameproperty value, you will have to repeat the resolution procedure to remove the remaining instances of the old certificate.Generate the
TlsCertificateNameproperty value by running the following commands:$cert = Get-ExchangeCertificate -Thumbprint <new certificate thumbprint> $tlscertificatename = "<i>$($cert.Issuer)<s>$($cert.Subject)"For each Send connector reported in the error message, run the following command to assign the
TlsCertificateNameproperty value that you generated in step 6:Set-SendConnector -Identity <connector name> -TlsCertificateName $tlscertificatenameRestart the Microsoft Exchange Transport service by running the following command on each source transport server that you found in step 2. The command doesn't have to be run in the EMS, but it does require an elevated PowerShell session.
Start-Service MSExchangeTransportOr, you can start the Microsoft Exchange Transport service in the Services.msc snap-in on each source transport server.
More information
To determine which certificate a Send or Receive connector is using, follow these steps:
Enable protocol logging for the connector. For more information about protocol logging, see Protocol logging in Exchange Server.
Open the most recent protocol log file for the connector. You can determine the applicable log folder path by running the following command in EMS:
Get-TransportService | Format-List Identity,*ProtocolLogPathIn the protocol log file, find the certificate information for the connector by searching for an entry that starts with "Sending certificate" in the
contextcolumn. The certificate information is in thedatacolumn of the same row. The format of the certificate information is "<Subject> <Issuer> <SerialNumber> <Thumbprint> <NotBefore> <NotAfter> <CertificateDomains>".You can find the corresponding Exchange Server certificate by running the following command in EMS:
Get-ExchangeCertificate | Format-List Subject,Issuer,SerialNumber,Thumbprint,NotBefore,NotAfter,CertificateDomains
For more information about certificate management, see Certificate procedures in Exchange Server.