Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Autotune automatically adjusts Apache Spark configuration to speed up workload execution and to optimize overall performance. Autotune saves time and resources compared to manual tuning which, requires extensive effort, resources, time, and experimentation. Autotune uses historical execution data from your workloads to iteratively discover and apply the most effective configurations for a specific workload.
Important
This feature is in preview.
Note
The autotune query tuning feature in Microsoft Fabric is currently in preview. Autotune is available across all production regions but is disabled by default. You can activate it through the Spark configuration setting within the environment or within a single session by including the respective Spark setting in your Spark notebook or Spark Job Definition code.
Query tuning
Autotune configures three Apache Spark settings for each of your queries separately:
spark.sql.shuffle.partitions- Sets the partition count for data shuffling during joins or aggregations. The default value is 200.spark.sql.autoBroadcastJoinThreshold- Sets the maximum table size in bytes that is broadcasted to all worker nodes when join operation is executed. The default value is 10 MB.spark.sql.files.maxPartitionBytes- Defines the maximum number of bytes to pack into a single partition when reading files. Works for Parquet, JSON, and ORC file-based sources. Default is 128 MB.
Tip
Autotune query tuning examines individual queries and builds a distinct ML model for each query. It specifically targets:
- Repetitive queries
- Long-running queries (with more than 15 seconds of execution)
- Apache Spark SQL API queries (excluding queries written in the RDD API, which are rare), but we optimize all queries regardless the language (Scala, PySpark, R, Spark SQL) This feature is compatible with notebooks, Apache Spark job definitions, and pipelines. The benefits vary based on the complexity of the query, the methods used, and the structure. Extensive testing has shown that the greatest advantages are realized with queries related to exploratory data analysis, such as reading data, running joins, aggregations, and sorting.
AI-based intuition behind the autotune
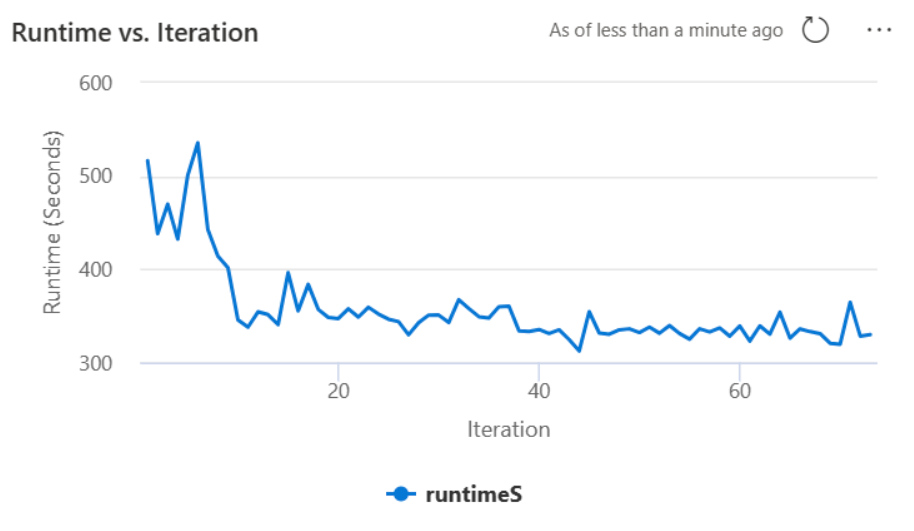
The autotune feature utilizes an iterative process to optimize query performance. It begins with a default configuration and employs a machine learning model to evaluate effectiveness. When a user submits a query, the system retrieves the stored models based on the previous interactions. It generates potential configurations around a default setting named centroid. The best candidate predicted by the model, is applied. After query execution, the performance data is sent back to the system to refine the model.
The feedback loop gradually shifts the centroid towards optimal settings. It refines performance over time while minimizing the risk of regression. Continuous updates based on user queries enable refinement of performance benchmarks. Moreover, the process updates the centroid configurations to ensure the model moves towards more efficient settings incrementally. This is achieved by evaluating past performances and using them to guide future adjustments. It uses all the data points to mitigate the impact of anomalies.
From a responsible AI perspective, the autotune feature includes transparency mechanisms designed to keep you informed about your data usage and benefits. The security and privacy align with Microsoft's standards. Ongoing monitoring maintains performance and system integrity post-launch.
Enable autotune
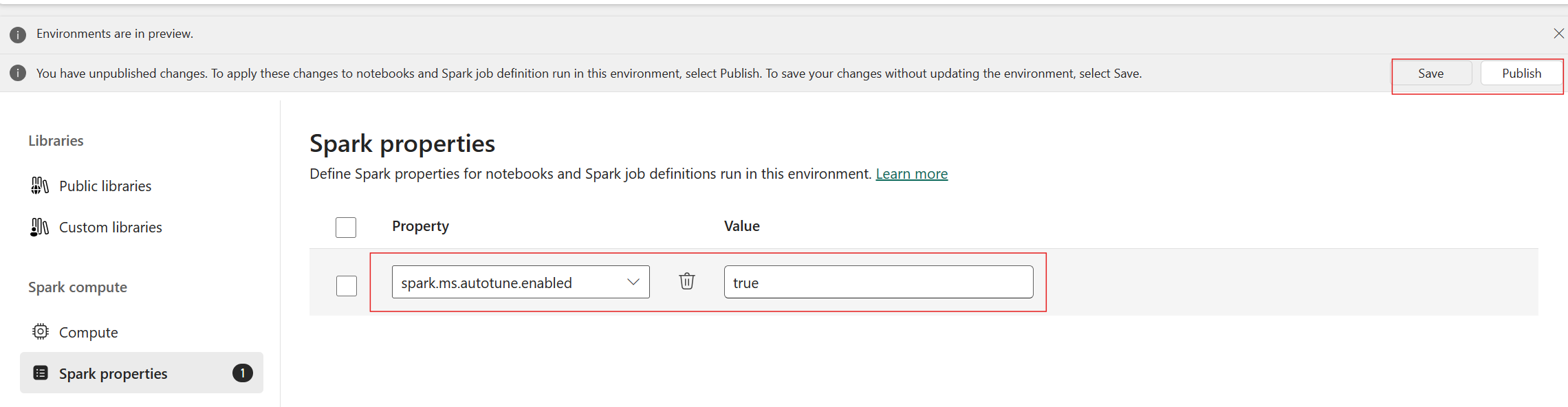
Autotune is available across all production regions but is disabled by default. You can activate it through the Spark configuration setting within the environment. To enable autotune, either create a new environment or, for the existing environment, set the Spark property 'spark.ms.autotune.enabled = true' as shown in the screenshot below. This setting is then inherited by all notebooks and jobs running in that environment, automatically tuning them.
Autotune includes a built-in mechanism for monitoring performance and detecting performance regressions. For instance, if a query processes an unusually large amount of data, autotune automatically deactivates. It typically requires 20 to 25 iterations to learn and identify the optimal configuration.
Note
The autotune is compatible with Fabric Runtime 1.1 and Runtime 1.2. Autotune doesn't function when the high concurrency mode or when the private endpoint is enabled. However, autotune seamlessly integrates with autoscaling, regardless of its configuration.
You can enable autotune within a single session by including the respective Spark setting in your Spark notebook or Spark Job Definition code.
%%sql
SET spark.ms.autotune.enabled=TRUE
You can control autotune through Spark settings for your respective Spark notebook or Spark job definition code. To disable autotune, execute the following commands as the first cell (notebook) or line of the code (SJD).
%%sql
SET spark.ms.autotune.enabled=FALSE
Case study
When you execute an Apache Spark query, autotune creates a customized ML model dedicated to optimizing the query's execution. It analyzes query patterns and resource needs. Consider an initial query filtering a dataset based on a specific attribute, such as a country. While this example uses geographic filtering, the principle applies universally to any attribute or operation within the query:
%%pyspark
df.filter(df.country == "country-A")
Autotune learns from this query, optimizing subsequent executions. When the query changes, for instance, by altering the filter value or applying a different data transformation, the structural essence of the query often remains consistent:
%%pyspark
df.filter(df.country == "country-B")
Despite alterations, autotune identifies the fundamental structure of the new query, implementing previously learned optimizations. This capability ensures sustained high efficiency without the need for manual reconfiguration for each new query iteration.
Logs
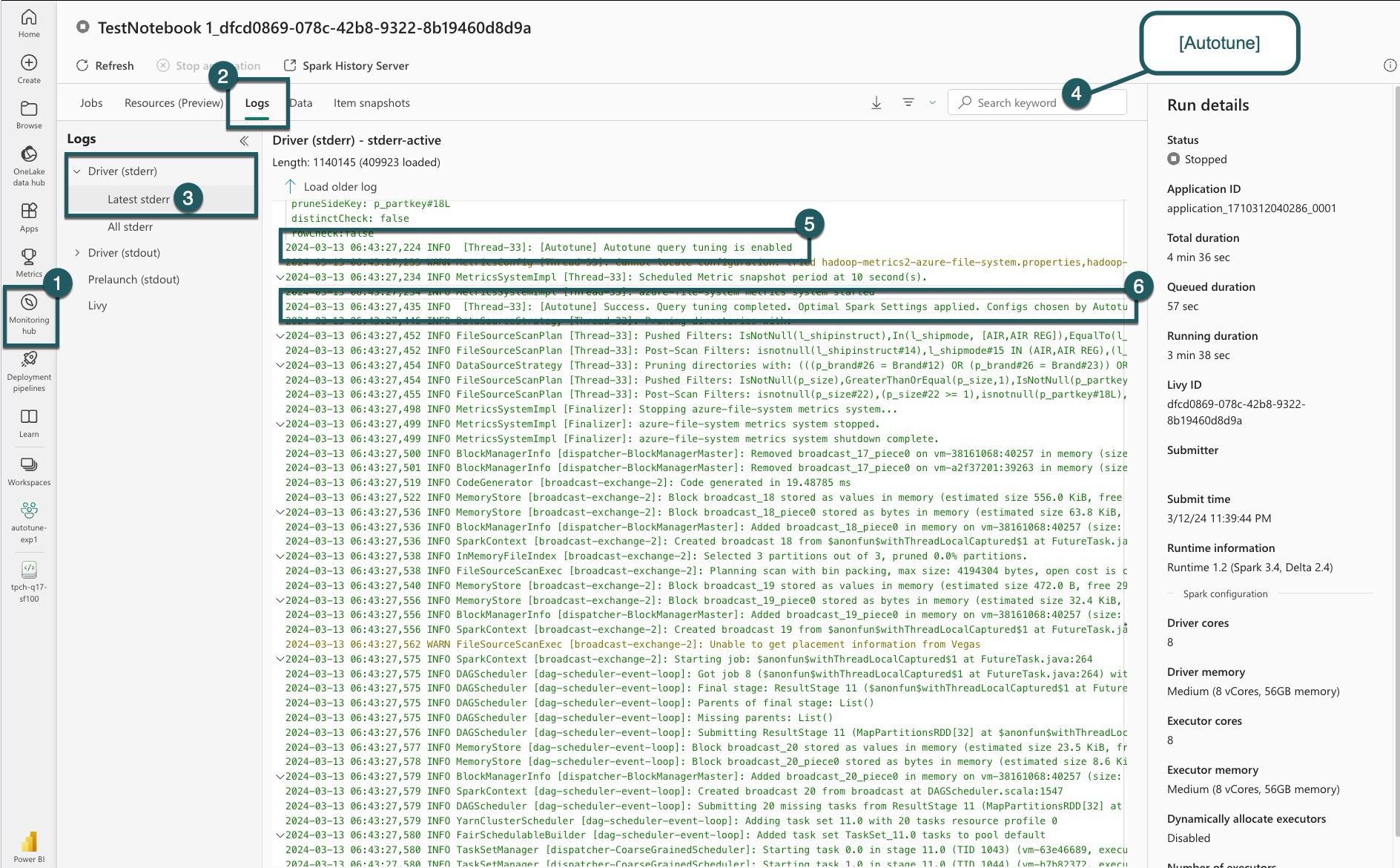
For each of your queries, autotune determines the most optimal settings for three Spark configurations. You can view the suggested settings by navigating to the logs. The configurations recommended by autotune are located in the driver logs, specifically those entries starting with [Autotune].
You can find various types of entries in your logs. The following include the key ones:
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| AUTOTUNE_DISABLED | Skipped. Autotune is disabled; preventing telemetry data retrieval and query optimization. Enable Autotune to fully use its capabilities while respecting customer privacy.". |
| QUERY_TUNING_DISABLED | Skipped. Autotune query tuning is disabled. Enable it to fine-tune settings for your Spark SQL queries. |
| QUERY_PATTERN_NOT_MATCH | Skipped. Query pattern didn't match. Autotune is effective for read-only queries. |
| QUERY_DURATION_TOO_SHORT | Skipped. Your query duration too short to optimize. Autotune requires longer queries for effective tuning. Queries should run for at least 15 seconds. |
| QUERY_TUNING_SUCCEED | Success. Query tuning completed. Optimal spark settings applied. |
Transparency note
In adherence to the Responsible AI Standard, this section aims to clarify the uses and validation of the Autotune feature, promoting transparency and enabling informed decision-making.
Purpose of autotune
Autotune is developed to enhance Apache Spark workload efficiency, primarily for data professionals. Its key functions include:
- Automating Apache Spark configuration tuning to reduce execution times.
- Minimizing manual tuning efforts.
- Utilizing historical workload data to refine configurations iteratively.
Validation of autotune
Autotune undergoes extensive testing to ensure its effectiveness and safety:
- Rigorous tests with diverse Spark workloads to verify tuning algorithm efficacy.
- Benchmarking against standard Spark optimization methods to demonstrate performance benefits.
- Real-world case studies highlighting autotune's practical value.
- Adherence to strict security and privacy standards to safeguard user data.
User data is exclusively used to enhance your workload's performance, with robust protections to prevent misuse or exposure of sensitive information.