Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Overview
The <site> configuration element controls the configuration of a specific Web site that you run on your IIS 7 and later server. For example, the Default Web Site and its settings are defined in a <site> element, which is found between the opening and closing tags of the <sites> element.
You configure a <site> element when you create a new Web site on IIS 7 and later. The <site> element contains a name attribute that defines the name you have assigned the Web site, and an id attribute that defines the numeric identifier for the Web site. The <site> element contains child elements that define the applications and virtual directories that run on the site, as well as port, protocol, logging, and tracing configuration settings for the Web site.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The <site> element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The <site> element was not modified in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The <site> element was not modified in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | The <site> element was not modified in IIS 7.5. |
| IIS 7.0 | The <site> element of the <sites> collection was introduced in IIS 7.0. |
| IIS 6.0 | The <sites> collection replaces the IIS 6.0 IIsWebServer metabase object. |
Setup
The <site> element is included in the default installation of IIS 7 and later.
How To
When you configure a new Web site on IIS 7, you must assign the Web site a site name and a physical path. There are also a number of optional configuration settings you can set. If you plan to continue to use the Default Web Site on your IIS 7 server, you must alter the binding information for the new site. You can do this by changing either the port or entering a host name for the new Web site.
How to create a new Web site
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, and then click Sites.
In the Actions pane, click Add Web Site
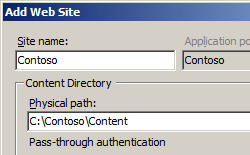
In the Add Web Site dialog box, at a minimum, enter information in the Site name and Physical path text boxes and choose whether you want to enter information in the Host name text box or change the number in the Port box.
On IIS Manager, click the refresh button to verify that the site has started.
How to enable or disable Anonymous authentication for an FTP site
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand the Sites node, and then click the name of the site.
In the site's Home pane, double-click the FTP Authentication feature.
On the FTP Authentication page, select Anonymous Authentication.
In the Actions pane, click Enable to enable Anonymous authentication or click Disable to disable Anonymous authentication.

How to use the FTP Site Wizard to Create an FTP Site with Anonymous Read Access
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, click the Sites node in the tree.
Right-click the Sites node in the tree and click Add FTP Site, or click Add FTP Site in the Actions pane.
When the Add FTP Site wizard appears:
Enter "My New FTP Site" in the FTP site name box.
For the Physical path box, you can use one of the following options to specify your content directory:
- Click the ellipsis (...) button, and then navigate to the folder that contains the content for your FTP site.
- Type in the path to your content folder in the box. Note that if you choose to type the path, you can use environment variables in your paths. For example, you can use "%SystemDrive%\inetpub\ftproot" for your content directory.
On the second page of the Add FTP Site wizard:
Choose an IP address for your FTP site from the IP Address drop-down, or choose to accept the default selection of "All Unassigned."
Enter the TCP/IP port for the FTP site in the Port box. By default, FTP sites and clients use port 21. (Note: To specify Implicit FTPS, you need to use port 990.)
To use an FTP virtual host name, select the box for Enable Virtual Host Names, then enter the virtual host name in the Virtual Host box.
For the SSL options, choose one of the following options:
- Select No SSL to disable the SSL options.
- Select Allow SSL to allow FTP clients to optionally use FTP over SSL when they connect with the FTP server.
- Select Require SSL to allow FTP clients to always use FTP over SSL when they connect with the FTP server.
- If you choose Allow SSL or Require SSL, choose a certificate from the SSL Certificate drop-down menu.
On the next page of the wizard:
Configuration
You configure the <site> element at the server level in the ApplicationHost.config file.
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
id |
Optional uint attribute. Specifies the random numeric identifier that is assigned by IIS when the site is created. The Default Web Site is numbered 1. Other Web sites have random numbers composed of multiple digits. |
name |
Optional string attribute. Specifies a friendly name that uniquely identifies a Web site, for example, "Contoso HR Forms." |
serverAutoStart |
Optional Boolean attribute. Specifies whether the site should start automatically when the Management Service is started. The default value is true. |
Child Elements
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
application |
Optional element. Specifies a collection of configuration settings for applications in the site. |
applicationDefaults |
Optional element. Specifies default settings for all applications in the parent site. |
bindings |
Optional element. Specifies bindings to access the site. |
ftpServer |
Optional element. Specifies FTP settings for the site. Note: This requires installing FTP 7.0 or FTP 7.5. |
limits |
Optional element. Configures settings to limit the amount of bandwidth, the number of connections, or the amount of time for connections to a site. |
logFile |
Optional element. Configures settings for handling and storage of log files for the site. |
traceFailedRequestsLogging |
Optional element. Specifies settings for logging failed-request traces for the site. |
virtualDirectoryDefaults |
Optional element. Specifies default settings for all virtual directories in the site. |
Configuration Sample
The following configuration example displays a <site> element in the ApplicationHost.config file. The name attribute defines the site name as Contoso, and the id attribute defines the IIS-specific identifier as 2. The physicalPath attribute in the <virtualDirectory> element defines the physical location of the new site's content. The protocol attribute of the <binding> element defines the protocol the site will use, and the bindingInformation attribute defines www.contoso.com as the host header used by the new Web site.
<site name="Contoso" id="2">
<application path="/">
<virtualDirectory path="/" physicalPath="C:\inetpub\Contoso" />
</application>
<bindings>
<binding protocol="http" bindingInformation="*:80:www.contoso.com" />
</bindings>
</site>
Sample Code
The following examples create a new Web site named Contoso with an ID of 2, and sets a binding for the HTTP protocol over port 80 with a host header of "www.contoso.com". The physical path for the new Web site is C:\Inetpub\www.contoso.com\wwwroot.
AppCmd.exe
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.applicationHost/sites /+"[name='Contoso',id='2',serverAutoStart='True']" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.applicationHost/sites /+"[name='Contoso',id='2'].bindings.[protocol='http',bindingInformation='*:80:www.contoso.com']" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.applicationHost/sites /+"[name='Contoso',id='2'].[path='/']" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.applicationHost/sites /+"[name='Contoso',id='2'].[path='/'].[path='/',physicalPath='C:\Inetpub\www.contoso.com\wwwroot']" /commit:apphost
Note
You must be sure to set the commit parameter to apphost when you use AppCmd.exe to configure these settings. This commits the configuration settings to the appropriate location section in the ApplicationHost.config file.
C#
using System;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.Web.Administration;
internal static class Sample
{
private static void Main()
{
using (ServerManager serverManager = new ServerManager())
{
Configuration config = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration();
ConfigurationSection sitesSection = config.GetSection("system.applicationHost/sites");
ConfigurationElementCollection sitesCollection = sitesSection.GetCollection();
ConfigurationElement siteElement = sitesCollection.CreateElement("site");
siteElement["name"] = @"Contoso";
siteElement["id"] = 2;
siteElement["serverAutoStart"] = true;
ConfigurationElementCollection bindingsCollection = siteElement.GetCollection("bindings");
ConfigurationElement bindingElement = bindingsCollection.CreateElement("binding");
bindingElement["protocol"] = @"http";
bindingElement["bindingInformation"] = @"*:80:www.contoso.com";
bindingsCollection.Add(bindingElement);
ConfigurationElementCollection siteCollection = siteElement.GetCollection();
ConfigurationElement applicationElement = siteCollection.CreateElement("application");
applicationElement["path"] = @"/";
ConfigurationElementCollection applicationCollection = applicationElement.GetCollection();
ConfigurationElement virtualDirectoryElement = applicationCollection.CreateElement("virtualDirectory");
virtualDirectoryElement["path"] = @"/";
virtualDirectoryElement["physicalPath"] = @"C:\Inetpub\www.contoso.com\wwwroot";
applicationCollection.Add(virtualDirectoryElement);
siteCollection.Add(applicationElement);
sitesCollection.Add(siteElement);
serverManager.CommitChanges();
}
}
}
VB.NET
Imports System
Imports System.Text
Imports Microsoft.Web.Administration
Module Sample
Sub Main()
Dim serverManager As ServerManager = New ServerManager
Dim config As Configuration = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration
Dim sitesSection As ConfigurationSection = config.GetSection("system.applicationHost/sites")
Dim sitesCollection As ConfigurationElementCollection = sitesSection.GetCollection
Dim siteElement As ConfigurationElement = sitesCollection.CreateElement("site")
siteElement("name") = "Contoso"
siteElement("id") = 2
siteElement("serverAutoStart") = True
Dim bindingsCollection As ConfigurationElementCollection = siteElement.GetCollection("bindings")
Dim bindingElement As ConfigurationElement = bindingsCollection.CreateElement("binding")
bindingElement("protocol") = "http"
bindingElement("bindingInformation") = "*:80:www.contoso.com"
bindingsCollection.Add(bindingElement)
Dim siteCollection As ConfigurationElementCollection = siteElement.GetCollection
Dim applicationElement As ConfigurationElement = siteCollection.CreateElement("application")
applicationElement("path") = "/"
Dim applicationCollection As ConfigurationElementCollection = applicationElement.GetCollection
Dim virtualDirectoryElement As ConfigurationElement = applicationCollection.CreateElement("virtualDirectory")
virtualDirectoryElement("path") = "/"
virtualDirectoryElement("physicalPath") = "C:\Inetpub\www.contoso.com\wwwroot"
applicationCollection.Add(virtualDirectoryElement)
siteCollection.Add(applicationElement)
sitesCollection.Add(siteElement)
serverManager.CommitChanges()
End Sub
End Module
JavaScript
var adminManager = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager');
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST";
var sitesSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.applicationHost/sites", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST");
var sitesCollection = sitesSection.Collection;
var siteElement = sitesCollection.CreateNewElement("site");
siteElement.Properties.Item("name").Value = "Contoso";
siteElement.Properties.Item("id").Value = 2;
siteElement.Properties.Item("serverAutoStart").Value = true;
var bindingsCollection = siteElement.ChildElements.Item("bindings").Collection;
var bindingElement = bindingsCollection.CreateNewElement("binding");
bindingElement.Properties.Item("protocol").Value = "http";
bindingElement.Properties.Item("bindingInformation").Value = "*:80:www.contoso.com";
bindingsCollection.AddElement(bindingElement);
var siteCollection = siteElement.Collection;
var applicationElement = siteCollection.CreateNewElement("application");
applicationElement.Properties.Item("path").Value = "/";
var applicationCollection = applicationElement.Collection;
var virtualDirectoryElement = applicationCollection.CreateNewElement("virtualDirectory");
virtualDirectoryElement.Properties.Item("path").Value = "/";
virtualDirectoryElement.Properties.Item("physicalPath").Value = "C:\\Inetpub\\www.contoso.com\\wwwroot";
applicationCollection.AddElement(virtualDirectoryElement);
siteCollection.AddElement(applicationElement);
sitesCollection.AddElement(siteElement);
adminManager.CommitChanges();
VBScript
Set adminManager = createObject("Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager")
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST"
Set sitesSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.applicationHost/sites", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST")
Set sitesCollection = sitesSection.Collection
Set siteElement = sitesCollection.CreateNewElement("site")
siteElement.Properties.Item("name").Value = "Contoso"
siteElement.Properties.Item("id").Value = 2
siteElement.Properties.Item("serverAutoStart").Value = True
Set bindingsCollection = siteElement.ChildElements.Item("bindings").Collection
Set bindingElement = bindingsCollection.CreateNewElement("binding")
bindingElement.Properties.Item("protocol").Value = "http"
bindingElement.Properties.Item("bindingInformation").Value = "*:80:www.contoso.com"
bindingsCollection.AddElement bindingElement
Set siteCollection = siteElement.Collection
Set applicationElement = siteCollection.CreateNewElement("application")
applicationElement.Properties.Item("path").Value = "/"
Set applicationCollection = applicationElement.Collection
Set virtualDirectoryElement = applicationCollection.CreateNewElement("virtualDirectory")
virtualDirectoryElement.Properties.Item("path").Value = "/"
virtualDirectoryElement.Properties.Item("physicalPath").Value = "C:\Inetpub\www.contoso.com\wwwroot"
applicationCollection.AddElement(virtualDirectoryElement)
siteCollection.AddElement applicationElement
sitesCollection.AddElement siteElement
adminManager.CommitChanges()


