Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Overview
The <hostNameSupport> element specifies domain name syntax is supported for virtual host names.
FTP virtual host names were introduced in FTP 7.0, and an FTP virtual host name is specified as part of a binding in the same way that you specify HTTP host header names. For example, you might specify the bindings by using host names like www.contoso.com or www.fabrikam.com for the HTTP bindings and ftp.contoso.com or ftp.fabrikam.com for the FTP bindings. HTTP provides a way to pass the host name in the headers that are passed between the client and server, but FTP currently does not provide this same functionality. Because of this FTP limitation, the virtual host name is used as part of the user name during the login process. By default, an FTP client would need to specify its login credentials by using the pipe (vertical line) character with syntax like ftp.contoso.com|username or ftp.fabrikam.com|username. By setting the useDomainNameAsHostName attribute to true, you can specify the virtual host and user name by using domain name syntax; this lets you use a backslash character instead of the pipe (vertical line) character; so the syntax would look like ftp.contoso.com\username or ftp.fabrikam.com\username.
Note
Both FTP 7.0 and FTP 7.5 support the proposed FTP HOST command, which does not require that you use the virtual host name as part of the user name.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The <hostNameSupport> element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The <hostNameSupport> element was not modified in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The <hostNameSupport> element was not modified in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | The <hostNameSupport> element of the <system.ftpServer> element ships as a feature of IIS 7.5. |
| IIS 7.0 | The <hostNameSupport> element of the <system.ftpServer> element was introduced in FTP 7.5, which was a separate download for IIS 7.0. |
| IIS 6.0 | N/A |
Note
The FTP 7.0 and FTP 7.5 services shipped out-of-band for IIS 7.0, which required downloading and installing the modules from the following URL:
With Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008 R2, the FTP 7.5 service ships as a feature for IIS 7.5, so downloading the FTP service is no longer necessary.
Setup
To support FTP publishing for your Web server, you must install the FTP service. To do so, use the following steps.
Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2
On the taskbar, click Server Manager.
In Server Manager, click the Manage menu, and then click Add Roles and Features.
In the Add Roles and Features wizard, click Next. Select the installation type and click Next. Select the destination server and click Next.
On the Server Roles page, expand Web Server (IIS), and then select FTP Server.
Note
To support ASP.Membership authentication or IIS Manager authentication for the FTP service, you will need to select FTP Extensibility, in addition to FTP Service.
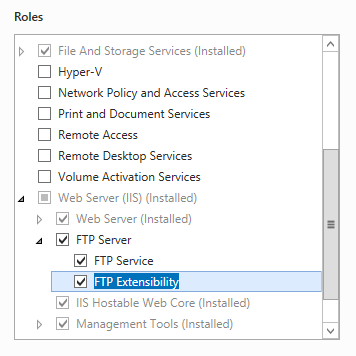
Click Next, and then on the Select features page, click Next again.
On the Confirm installation selections page, click Install.
On the Results page, click Close.
Windows 8 or Windows 8.1
On the Start screen, move the pointer all the way to the lower left corner, right-click the Start button, and then click Control Panel.
In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows features on or off.
Expand Internet Information Services, and then select FTP Server.
Note
To support ASP.Membership authentication or IIS Manager authentication for the FTP service, you will also need to select FTP Extensibility.
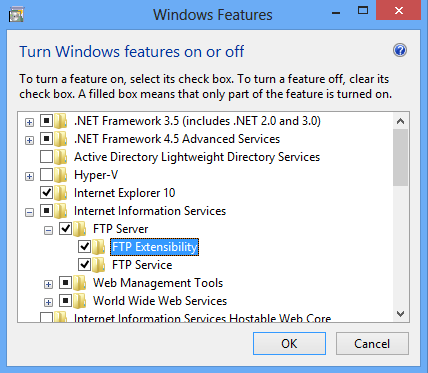
Click OK.
Click Close.
Windows Server 2008 R2
On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Server Manager.
In the Server Manager hierarchy pane, expand Roles, and then click Web Server (IIS).
In the Web Server (IIS) pane, scroll to the Role Services section, and then click Add Role Services.
On the Select Role Services page of the Add Role Services Wizard, expand FTP Server.
Select FTP Service.
Note
To support ASP.Membership authentication or IIS Manager authentication for the FTP service, you will also need to select FTP Extensibility.
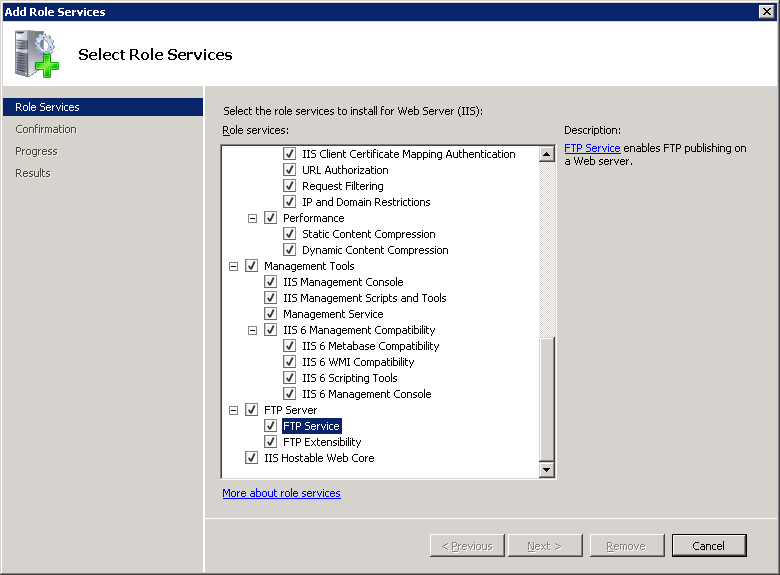
Click Next.
On the Confirm Installation Selections page, click Install.
On the Results page, click Close.
Windows 7
On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
In Control Panel, click Programs and Features, and then click Turn Windows Features on or off.
Expand Internet Information Services, and then FTP Server.
Select FTP Service.
Note
To support ASP.Membership authentication or IIS Manager authentication for the FTP service, you will also need to select FTP Extensibility.
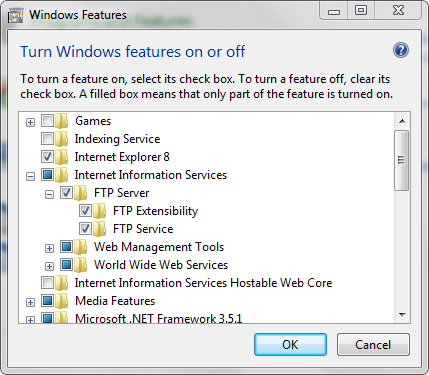
Click OK.
Windows Server 2008 or Windows Vista
Download the installation package from the following URL:
Follow the instructions in the following walkthrough to install the FTP service:
How To
How to configure domain name syntax for virtual host names
Note
There is no direct user interface that lets you configure the <hostNameSupport> element; therefore the following steps will use the IIS Configuration Editor feature.
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, click the server name.
In the Home pane, double-click the Configuration Editor feature.
In the Section drop-down menu, expand system.ftpServer, and then click serverRuntime.
Expand hostNameSupport in the list view.
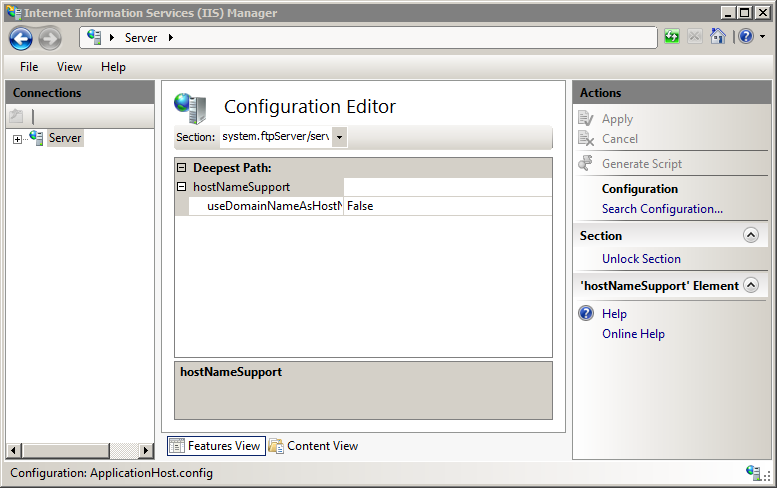
Choose True or False in the drop-down list for the useDomainNameAsHostName attribute.
In the Actions pane, click Apply.
Note
This section contains information about how to modify your IIS settings by using the IIS Configuration Editor. Incorrectly editing your IIS configuration settings can severely damage your IIS installation. Therefore, make sure that you follow these steps carefully. For added security, you should back up your IIS configuration settings before you use the IIS Configuration Editor to make any modifications. For more information about how to back up your IIS configuration settings and how to use the IIS Configuration Editor, see the following topics:
- How to Back Up an IIS 7 Configuration
https://technet.microsoft.com/library/dd819406.aspx - Configuration Editor Page
https://technet.microsoft.com/library/dd569081.aspx
Configuration
The <hostNameSupport> element of the <serverRuntime> element is configured at the global level in ApplicationHost.config.
Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
useDomainNameAsHostName |
Optional Boolean attribute. true if domain name syntax is supported for virtual host names; otherwise, false. The default value is false. |
Child Elements
None.
Configuration Sample
The following sample displays a <serverRuntime> element that configures the server allow domain name syntax for virtual host names.
<system.ftpServer>
<serverRuntime>
<hostNameSupport useDomainNameAsHostName="true" />
</serverRuntime>
</system.ftpServer>
Sample Code
The following examples configure the <serverRuntime> element for an FTP server to allow domain name syntax for FTP virtual host names.
AppCmd.exe
appcmd.exe set config -section:system.ftpServer/serverRuntime /hostNameSupport.useDomainNameAsHostName:"True" /commit:apphost
Note
You must be sure to set the commit parameter to apphost when you use AppCmd.exe to configure these settings. This commits the configuration settings to the appropriate location section in the ApplicationHost.config file.
C#
using System;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.Web.Administration;
internal static class Sample
{
private static void Main()
{
using (ServerManager serverManager = new ServerManager())
{
Configuration config = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration();
ConfigurationSection serverRuntimeSection = config.GetSection("system.ftpServer/serverRuntime");
ConfigurationElement hostNameSupportElement = serverRuntimeSection.GetChildElement("hostNameSupport");
hostNameSupportElement["useDomainNameAsHostName"] = true;
serverManager.CommitChanges();
}
}
}
VB.NET
Imports System
Imports System.Text
Imports Microsoft.Web.Administration
Module Sample
Sub Main()
Dim serverManager As ServerManager = New ServerManager
Dim config As Configuration = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration
Dim serverRuntimeSection As ConfigurationSection = config.GetSection("system.ftpServer/serverRuntime")
Dim hostNameSupportElement As ConfigurationElement = serverRuntimeSection.GetChildElement("hostNameSupport")
hostNameSupportElement("useDomainNameAsHostName") = True
serverManager.CommitChanges()
End Sub
End Module
JavaScript
var adminManager = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager');
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST";
var serverRuntimeSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.ftpServer/serverRuntime", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST");
var hostNameSupportElement = serverRuntimeSection.ChildElements.Item("hostNameSupport");
hostNameSupportElement.Properties.Item("useDomainNameAsHostName").Value = true;
adminManager.CommitChanges();
VBScript
Set adminManager = createObject("Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager")
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST"
Set serverRuntimeSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.ftpServer/serverRuntime", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST")
Set hostNameSupportElement = serverRuntimeSection.ChildElements.Item("hostNameSupport")
hostNameSupportElement.Properties.Item("useDomainNameAsHostName").Value = True
adminManager.CommitChanges()