Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Overview
The <anonymousAuthentication> element controls how Internet Information Services (IIS) 7 processes requests from anonymous users. You can modify the <anonymousAuthentication> element to disable Anonymous authentication, or you can configure Internet Information Services (IIS) to use a custom user account to process anonymous requests.
Anonymous authentication gives users access to the public areas of your Web or FTP site without prompting them for a user name or password. By default, the IUSR account, which was introduced in IIS 7.0 and replaces the IIS 6.0 IUSR_computername account, is used to allow anonymous access. An application is a grouping of files that delivers content or provides services over protocols, such as HTTP. When you create an application in IIS, the application's path becomes part of the site's URL.
By default, IIS 7 uses Anonymous authentication. You must disable Anonymous authentication for any Web site, Web application, or Web service for which you want to enable other authentication methods such as Basic or Windows authentication.
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 10.0 | The <anonymousAuthentication> element was not modified in IIS 10.0. |
| IIS 8.5 | The <anonymousAuthentication> element was not modified in IIS 8.5. |
| IIS 8.0 | The <anonymousAuthentication> element was not modified in IIS 8.0. |
| IIS 7.5 | The <anonymousAuthentication> element was not modified in IIS 7.5. |
| IIS 7.0 | The <anonymousAuthentication> element was introduced in IIS 7.0. |
| IIS 6.0 | The <anonymousAuthentication> element replaces the IIS 6.0 AuthFlags, AnonymousUserName, and AnonymousUserPassword metabase properties. |
Setup
The <anonymousAuthentication> element is included in the default installation of IIS 7.
How To
How to disable anonymous authentication
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and go to the level in the hierarchy pane that you want to configure, and then click the Web site or Web application.
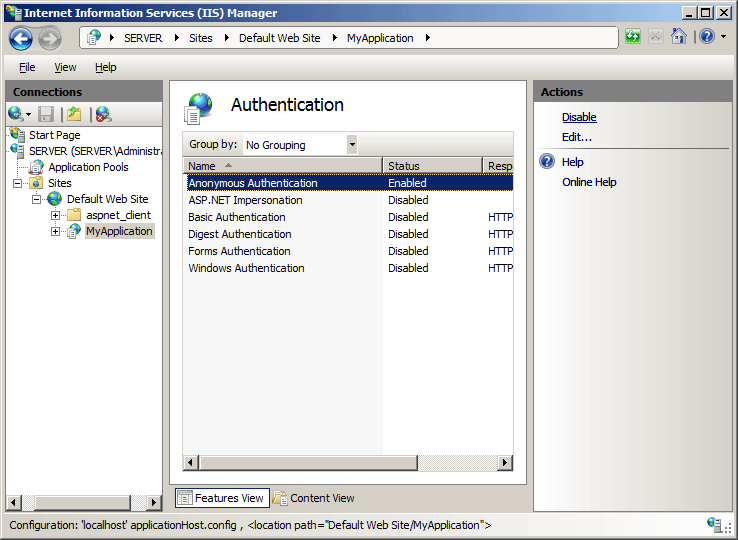
Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication.
In the Authentication pane, select Anonymous Authentication, and then click Disable in the Actions pane.
How to change anonymous authentication credentials from the IUSR account
Open Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager:
If you are using Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Hold down the Windows key, press the letter X, and then click Control Panel.
- Click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Server 2008 or Windows Server 2008 R2:
- On the taskbar, click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
If you are using Windows Vista or Windows 7:
- On the taskbar, click Start, and then click Control Panel.
- Double-click Administrative Tools, and then double-click Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
In the Connections pane, expand the server name, expand Sites, and navigate to the level in the hierarchy pane that you want to configure, and then click the Web site or Web application.
Scroll to the Security section in the Home pane, and then double-click Authentication.
In the Authentication pane, select Anonymous Authentication, and then click Edit... in the Actions pane.
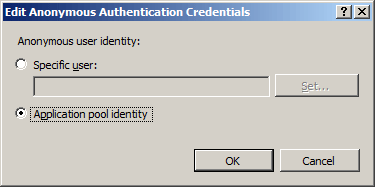
In the Edit Anonymous Authentication Credentials dialog box, do one of the following:
Select Application pool identity to use the identity set for the application pool, and then click OK.
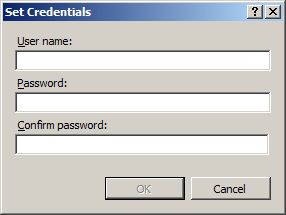
Click Set..., and then in the Set Credentials dialog box, enter the user name for the account in the User name box, enter the password for the account in the Password and Confirm password boxes, click OK, and then click OK again.
Note
If you use this procedure, only grant the new account minimal privileges on the IIS server computer.
Configuration
The <anonymousAuthentication> element is configurable at the site and application level in the Web.config file.
Attributes
| Attribute | Description | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
enabled |
Optional Boolean attribute. Specifies whether Anonymous authentication is enabled. The default value is true. |
||||||||||
logonMethod |
Optional enum attribute. The logonMethod attribute can be one of the following possible values. The default is ClearText.
|
||||||||||
password |
Optional String attribute. Specifies the password for Anonymous authentication. Note: To avoid storing unencrypted password strings in configuration files, always use AppCmd.exe or IIS Manager to enter passwords. If you use these management tools, the password strings will be encrypted automatically before they are written to the XML configuration files. This provides better password security than storing unencrypted passwords. |
||||||||||
username |
Optional String attribute. Specifies the username for Anonymous authentication. If you leave this value blank (that is, username=""), Anonymous authentication uses the application pool identity to authenticate anonymous users. The default value is IUSR. |
Child Elements
None.
Configuration Sample
The following configuration example configures anonymous authentication for an IIS 7 Web site or Web application to use a local account on the Web server. (IIS 7 automatically uses AES encryption to encrypt the password.)
<security> <authentication>
<anonymousAuthentication
userName="User1"
password="[enc:AesProvider:57686f6120447564652c2049495320526f636b73:enc]" />
</authentication>
</security>
Sample Code
The following examples enable anonymous authentication and change the default username and password used for anonymous authentication to an account named IUSR and a password of P@ssw0rd.
AppCmd.exe
appcmd.exe set config "Contoso" -section:system.webServer/security/authentication/anonymousAuthentication /enabled:"True" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config "Contoso" -section:system.webServer/security/authentication/anonymousAuthentication /userName:"IUSR" /commit:apphost
appcmd.exe set config "Contoso" -section:system.webServer/security/authentication/anonymousAuthentication /password:"P@ssw0rd" /commit:apphost
Note
You must be sure to set the commit parameter to apphost when you use AppCmd.exe to configure these settings. This commits the configuration settings to the appropriate location section in the ApplicationHost.config file.
C#
using System;
using System.Text;
using Microsoft.Web.Administration;
internal static class Sample {
private static void Main() {
using (ServerManager serverManager = new ServerManager()) {
Configuration config = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration();
ConfigurationSection anonymousAuthenticationSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/security/authentication/anonymousAuthentication", "Contoso");
anonymousAuthenticationSection["enabled"] = true;
anonymousAuthenticationSection["userName"] = @"IUSR";
anonymousAuthenticationSection["password"] = @"P@ssw0rd";
serverManager.CommitChanges();
}
}
}
VB.NET
Imports System
Imports System.Text
Imports Microsoft.Web.Administration
Module Sample
Sub Main()
Dim serverManager As ServerManager = New ServerManager
Dim config As Configuration = serverManager.GetApplicationHostConfiguration
Dim anonymousAuthenticationSection As ConfigurationSection = config.GetSection("system.webServer/security/authentication/anonymousAuthentication", "Contoso")
anonymousAuthenticationSection("enabled") = True
anonymousAuthenticationSection("userName") = "IUSR"
anonymousAuthenticationSection("password") = "P@ssw0rd"
serverManager.CommitChanges()
End Sub
End Module
JavaScript
var adminManager = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager');
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST";
var anonymousAuthenticationSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/security/authentication/anonymousAuthentication", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Contoso");
anonymousAuthenticationSection.Properties.Item("enabled").Value = true;
anonymousAuthenticationSection.Properties.Item("userName").Value = "IUSR";
anonymousAuthenticationSection.Properties.Item("password").Value = "P@ssw0rd";
adminManager.CommitChanges();
VBScript
Set adminManager = CreateObject("Microsoft.ApplicationHost.WritableAdminManager")
adminManager.CommitPath = "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST"
Set anonymousAuthenticationSection = adminManager.GetAdminSection("system.webServer/security/authentication/anonymousAuthentication", "MACHINE/WEBROOT/APPHOST/Contoso")
anonymousAuthenticationSection.Properties.Item("enabled").Value = True
anonymousAuthenticationSection.Properties.Item("userName").Value = "IUSR"
anonymousAuthenticationSection.Properties.Item("password").Value = "P@ssw0rd"
adminManager.CommitChanges()