IIS 8.0 CPU Throttling: Sand-boxing Sites and Applications
by Shaun Eagan
Compatibility
| Version | Notes |
|---|---|
| IIS 8.0 | CPU throttling was updated in IIS 8.0 to include additional throttling options. |
| IIS 7.5 | CPU throttling was not modified in IIS 7.5. |
| IIS 7.0 | CPU throttling was introduced in IIS 7.0. |
Problem
In a multi-tenanted deployment, such as a shared hosting environment, it is important to create a sand-box for each tenant. Without the sand-box, a tenant could intentionally or unintentionally impact other tenants negatively by accessing other tenants' contents or by monopolizing resources, such as memory, CPU, and bandwidth.
Solution
On Internet Information Services (IIS) on Windows Server 2012, the sand-box is scoped to an IIS application pool. It offers both security boundaries at the Windows process level by running each tenant in separate user identity and the resource limitations are also enforced at the process.
On Windows Server 2012, IIS CPU Throttling feature enables customers to truly limit how much CPU each tenant can consume as a percentage of CPU. Furthermore, this feature is configurable per IIS application pool, which means each tenant could have different limits, which can lead to a new business model in which tenants can pay more for higher limits.
It is important to clarify that IIS CPU Throttling is not a reservation of a CPU resource. Rather it is a way to limit the maximum usage.
Step by Step Instructions
Prerequisites:
IIS is installed on Windows Server 2012.
- IIS CPU Throttling is part of IIS application pool configuration. Therefore, a default install of IIS will have this feature installed. There is no specific IIS feature that needs to be installed from Server Manager.
There is at least one site with a corresponding IIS application pool.
- Default Web Site and DefaultAppPool can be used for this exercise.
Workarounds for known bugs:
There are no known bugs for this feature at this time.
Configure CPU Throttling
Open IIS Manager.
Select Application Pools in the left navigation window:
Select DefaultAppPool:
In the Action pane, select Advanced Settings:
Under CPU group, locate the following configurations:
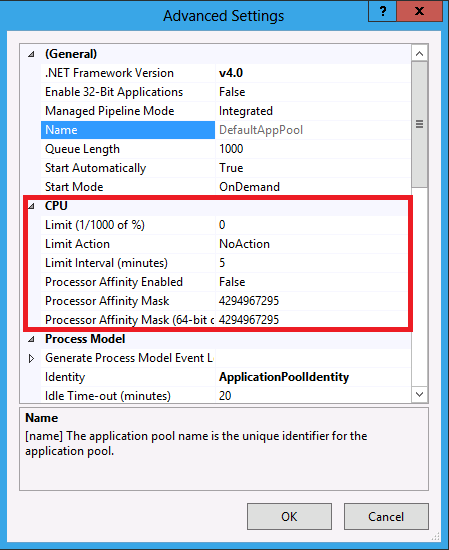
Limit: Indicates the maximum CPU usage (in 1000th of a percent) for this application pool. If there are multiple processes associated to this application pool, the limit is applied to the total sum of all processes under this application pool.
LimitAction: Indicates what action to take when the limit value is met above.
- For Windows Server 8, new actions, Throttle and ThrottleUnderLoad have been added:
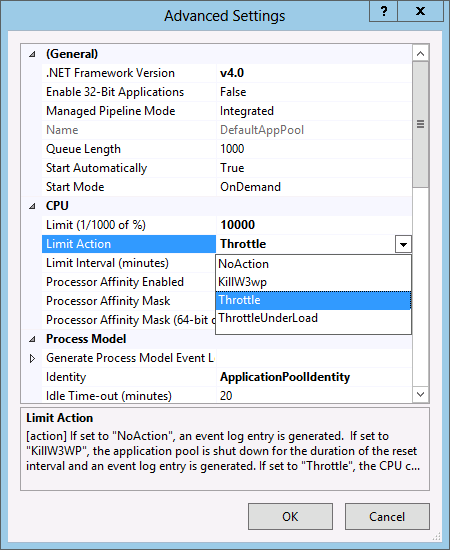
- Throttle: The feature will throttle the CPU consumption to the value set for Limit.
- ThrottleUnderLoad: The feature will throttle the CPU consumption to the value set for Limit, but only if there is a contention on the CPU. This means that the application pool may consume more CPU activity when the CPU is idle.
- For Windows Server 8, new actions, Throttle and ThrottleUnderLoad have been added:
LimitInterval: Not used for both Throttle and ThrottleUnderLoad. This configuration attribute is carried over from previous versions of Windows for backward compatibility.
To set the maximum limit of 30%, enter:
- Limit: 30000 (30% in 1000th of a percent)
- LimitAction: Throttle
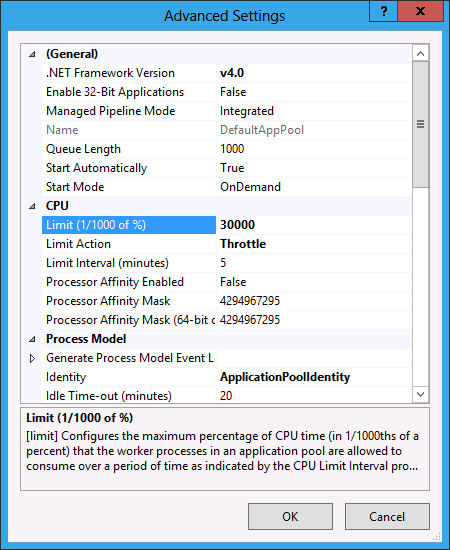
That's it. Using a load generating tool, send requests to the Default Web Site. A tool such as WCAT can be used (https://www.iis.net/community/default.aspx?tabid=34&g=6&i=1467) to generate traffic.
Note that the configuration settings in question can be set as default values so that they don't have to be configured individually per application pool. To configure the application pool defaults, select Set Application Pool Defaults under Actions pane:
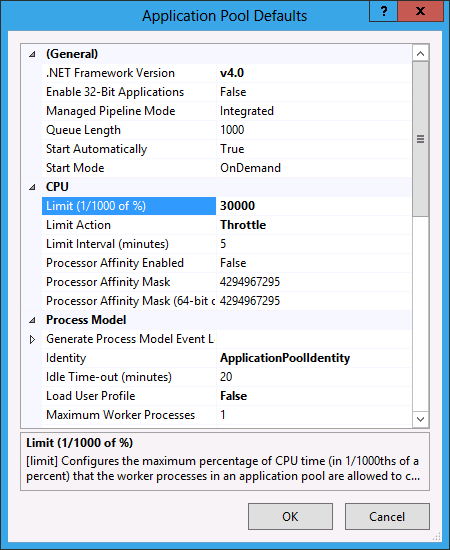
The same settings are exposed there to configure the application pool defaults:
Scenarios
Try deploying the following scenarios:
- IIS CPU Throttling feature is designed for a multi-tenanted environment. Try these settings in an environment where there are thousands of sites and applications, like a shared hosting deployment.
- Set different limits for different "groups" of tenants to simulate those customers who are allowed to consume more CPU resources than others.
- Set ThrottleUnderLoad as LimitAction to observe the behavior. It functions like Throttle, if there are contentions on the CPU. If there aren't any contentions on the CPU, the application pool is allowed to use more CPU resources than the value set for Limit.
- Create a sand-box with memory and bandwidth limits, along with IIS CPU Throttling feature on Windows Server 2012. Memory and bandwidth limits are not discussed specifically in this documentation because these features exist on Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2.
Summary
You have successfully explored IIS CPU Throttling feature in Windows Server 2012.