Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Authorization Code Flow is used for applications to request permission from a LinkedIn member to access their account data. The level of access or profile detail is explicitly requested using the scope parameter during the authorization process outlined below. This workflow will send a consent prompt to a selected member, and once approved your application may begin making API calls on behalf of that member.
This approval process ensures that LinkedIn members are aware of what level of detail an application may access or action it may perform on their behalf.
If multiple scopes are requested, the user must be consent to all of them and may not select individual scopes. For the benefit of your LinkedIn users, please ensure that your application requests the least number of scope permissions.
Note
Generate a Token Manually Using the Developer Portal
The LinkedIn Developer Portal has a token generator for manually creating tokens. Visit the LinkedIn Developer Portal Token Generator or follow the steps outlined in Developer Portal Tools.
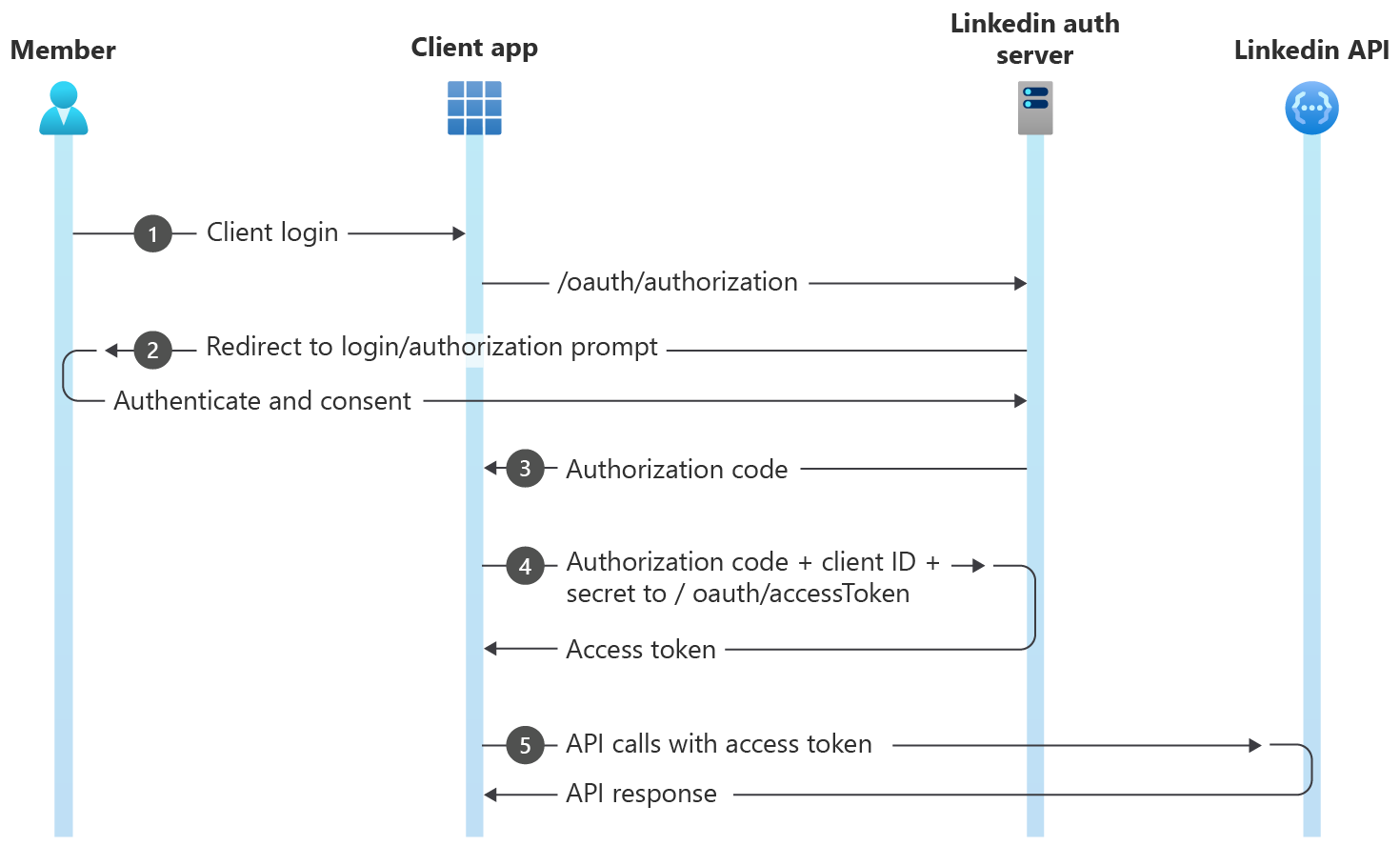
Authorization Code Flow
- Configure your application in the Developer Portal to obtain Client ID and Client Secret.
- Your application directs the browser to LinkedIn's OAuth 2.0 authorization page where the member authenticates.
- After authentication, LinkedIn's authorization server passes an authorization code to your application.
- Your application sends this code to LinkedIn and LinkedIn returns an access token.
- Your application uses this token to make API calls on behalf of the member.
How to Implement 3-legged OAuth
Follow the steps given below to implement the 3-legged OAuth for LinkedIn APIs:
Prerequisites
- A LinkedIn Developer application to create a new application or select your existing application
- Prior authorization access granted for at least one 3-legged OAuth permission.
The permission request workflow is outlined in the Getting Access section.
Step 1: Configure Your Application
- Select your application in the LinkedIn Developer Portal.
- Click the Auth tab to view your application credentials.
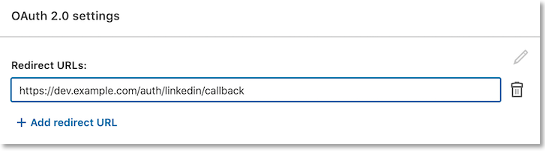
- Add the redirect (callback) URL via
HTTPSto your server.
Note
LinkedIn servers will only communicate with URLs that you have identified as trusted.
- URLs must be absolute:
https://dev.example.com/auth/linkedin/callback- not
/auth/linkedin/callback
- parameters are ignored:
https://dev.example.com/auth/linkedin/callback?id=1- will be
https://dev.example.com/auth/linkedin/callback
- URLs cannot include a #
https://dev.example.com/auth/linkedin/callback#linkedinis invalid.
If you are using Postman to test this flow, use https://oauth.pstmn.io/v1/callback as your redirect URL and enable Authorize using browser.
Each application is assigned a unique Client ID (Consumer key/API key) and Client Secret. Please make a note of these values as they will be integrated into your application. Your Client Secret protects your application's security so be sure to keep it secure!
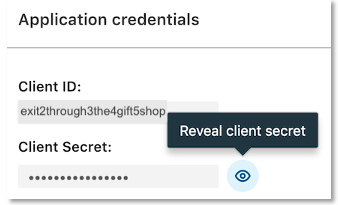
Warning
Do not share your Client Secret value with anyone, and do not pass it in the URL when making API calls, or URI query-string parameters, or post in support forums, chat, etc.
Step 2: Request an Authorization Code
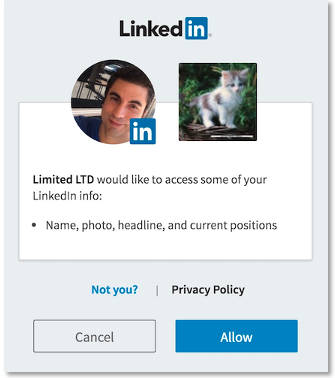
To request an authorization code, you must direct the member's browser to LinkedIn's OAuth 2.0 authorization page, where the member either accepts or denies your application's permission request.
Once the request is made, one of the following occurs:
If it is a first-time request, the permission request timed out, or was manually revoked by the member: the browser is redirected to LinkedIn's authorization consent window.
If there is an existing permission grant from the member: the authorization screen is bypassed and the member is immediately redirected to the URL provided in the
redirect_uriquery parameter.
When the member completes the authorization process, the browser is redirected to the URL provided in the redirect_uri query parameter.
Note
If the scope permissions are changed in your app, your users must re-authenticate to ensure that they have explicitly granted your application all of the permissions that it is requesting on their behalf.
GET https://www.linkedin.com/oauth/v2/authorization
| Parameter | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| response_type | string | The value of this field should always be: code |
Yes |
| client_id | string | The API Key value generated when you registered your application. | Yes |
| redirect_uri | url | The URI your users are sent back to after authorization. This value must match one of the Redirect URLs defined in your application configuration. For example, https://dev.example.com/auth/linkedin/callback. |
Yes |
| state | string | A unique string value of your choice that is hard to guess. Used to prevent CSRF. For example, state=DCEeFWf45A53sdfKef424. |
No |
| scope | string | URL-encoded, space-delimited list of member permissions your application is requesting on behalf of the user. These must be explicitly requested. For example, scope=liteprofile%20emailaddress%20w_member_social. See Permissions and Best Practices for Application Development for additional information. |
Yes |
The scopes available to your app depend on which Products or Partner Programs your app has access to. This information is available in the Developer Portal. Your app's Auth tab will show current scopes available. You can apply for new Products under the Products tab. If approved, your app will have access to new scopes.
Sample Request
GET https://www.linkedin.com/oauth/v2/authorization?response_type=code&client_id={your_client_id}&redirect_uri={your_callback_url}&state=foobar&scope=liteprofile%20emailaddress%20w_member_social
Once redirected, the member is presented with LinkedIn's authentication screen. This identifies your application and outlines the particular member permissions/scopes that your application is requesting. You can change the logo and application name in the Developer Portal under My apps > Settings

Member Approves Request
By providing valid LinkedIn credentials and clicking Allow, the member approves your application's request to access their member data and interact with LinkedIn on their behalf. This approval instructs LinkedIn to redirect the member to the redirect URL that you defined in your redirect_uriparameter.
https://dev.example.com/auth/linkedin/callback?state=foobar&code=AQTQmah11lalyH65DAIivsjsAQV5P-1VTVVebnLl_SCiyMXoIjDmJ4s6rO1VBGP5Hx2542KaR_eNawkrWiCiAGxIaV-TCK-mkxDISDak08tdaBzgUYfnTJL1fHRoDWCcC2L6LXBCR_z2XHzeWSuqTkR1_jO8CeV9E_WshsJBgE-PWElyvsmfuEXLQbCLfj8CHasuLafFpGb0glO4d7M
Attached to the redirect_uri are two important URL arguments that you need to read from the request:
code— The OAuth 2.0 authorization code.state— A value used to test for possible CSRF attacks.
The code is a value that you exchange with LinkedIn for an OAuth 2.0 access token in the next step of the authentication process. For security reasons, the authorization code has a 30-minute lifespan and must be used immediately. If it expires, you must repeat all of the previous steps to request another authorization code.
Warning
Before you use the authorization code, your application should ensure that the value returned in the state parameter matches the state value from your original authorization code request. This ensures that you are dealing with the real member and not a malicious script. If the state values do not match, you are likely the victim of a CSRF attack and your application should return a 401 Unauthorized error code in response.
Failed Requests
If the member chooses to cancel, or the request fails for any reason, the client is redirected to your redirect_uri with the following additional query parameters appended:
error- A code indicating one of these errors:user_cancelled_login- The member declined to log in to their LinkedIn account.user_cancelled_authorize- The member refused to authorize the permissions request from your application.
error_description- A URL-encoded textual description that summarizes the error.state- A value passed by your application to prevent CSRF attacks.
For more error details, refer here
Step 3: Exchange Authorization Code for an Access Token
The next step is to get an access token for your application using the authorization code from the previous step.
POST https://www.linkedin.com/oauth/v2/accessToken
To do this, make the following HTTP POST request with a Content-Type header of x-www-form-urlencoded using the following parameters:
| Parameter | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| grant_type | string | The value of this field should always be: authorization_code |
Yes |
| code | string | The authorization code you received in Step 2. | Yes |
| client_id | string | The Client ID value generated in Step 1. | Yes |
| client_secret | string | The Secret Key value generated in Step 1. See the Best Practices Guide for ways to keep your client_secret value secure. |
Yes |
| redirect_uri | url | The same redirect_uri value that you passed in the previous step. |
Yes |
Sample Request
POST https://www.linkedin.com/oauth/v2/accessToken
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
grant_type=authorization_code
code={authorization_code_from_step2_response}
client_id={your_client_id}
client_secret={your_client_secret}
redirect_uri={your_callback_url}
Response
A successful access token request returns a JSON object containing the following fields:
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| access_token | string | The access token for the application. This value must be kept secure as specified in the API Terms of Use. The length of access tokens is ~500 characters. We recommend that you plan for your application to handle tokens with length of at least 1000 characters to accommodate any future expansion plans. This applies to both access tokens and refresh tokens. |
| expires_in | int | The number of seconds remaining until the token expires. Currently, all access tokens are issued with a 60-day lifespan. |
| refresh_token | string | Your refresh token for the application. This token must be kept secure. |
| refresh_token_expires_in | int | The number of seconds remaining until the refresh token expires. Refresh tokens usually have a longer lifespan than access tokens. |
| scope | string | URL-encoded, space-delimited list of member permissions your application has requested on behalf of the user. |
{
"access_token":"AQUvlL_DYEzvT2wz1QJiEPeLioeA",
"expires_in":5184000,
"scope":"r_basicprofile"
}
For more error details, refer to the API Error Details table.
Note
Access Token Scopes and Lifetime
Access tokens stay valid until the number of seconds indicated in the expires_in field in the API response. You can go through the OAuth flow on multiple clients (browsers or devices) and simultaneously hold multiple valid access tokens if the same scope is requested. If you request a different scope than the previously granted scope, all the previous access tokens are invalidated.
Step 4: Make Authenticated Requests
Once you've obtained an access token, you can start making authenticated API requests on behalf of the member by including an Authorization header in the HTTP call to LinkedIn's API.
Sample Request
curl -X GET https://api.linkedin.com/v2/me' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer {INSERT_TOKEN}'
Step 5: Refresh Access Token
Tip
To protect members' data, LinkedIn does not generate long-lived access tokens.
Make sure your application refreshes access tokens before they expire, to avoid unnecessarily sending your application's users through the authorization process again.
Refreshing an access token is a seamless user experience. To refresh an access token, go through the authorization process again to fetch a new token. This time however, in the refresh workflow, the authorization screen is bypassed, and the member is redirected to your redirect URL, provided the following conditions are met:
- The member is still logged into www.linkedin.com
- The member's current access token has not expired
If the member is no longer logged in to www.linkedin.com or their access token has expired, they are sent through the normal authorization process.
Programmatic refresh tokens are available for a limited set of partners. If this feature has been enabled for your application, see Programmatic Refresh Tokens for instructions.
API Error Details
Following are the API errors and its resolution for 3-legged OAuth. If you wish to view the standard HTTP status codes and its meaning, see Error Handling page.
/oauth/v2/authorization
| HTTP STATUS CODE | ERROR MESSAGE | ERROR DESCRIPTION | RESOLUTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 401 | Redirect_uri doesn’t match | Redirect URI passed in the request does not match the redirect URI added to the developer application. | Ensure that the redirect URI passed in the request match the redirect URI added in the developer application under the Authorization tab. |
| 401 | Client_id doesn’t match | Client ID passed in the request does not match the client ID of the developer application. | Ensure that the client ID passed is in match with the developer application. |
| 401 | Invalid scope | Permissions passed in the request is invalid | Ensure that the permissions sent in scope parameter is assigned to the developer application in the developer portal. |
/oauth/v2/accessToken
| HTTP STATUS CODE | ERROR MESSAGE | ERROR DESCRIPTION | RESOLUTION |
|---|---|---|---|
| 401 | invalid_request "Unable to retrieve access token: authorization code not found" | Authorization code sent is invalid or not found. | Check whether the sent authorization code is valid. |
| 400 | invalid_request "A required parameter "redirect_uri" is missing" | Redirect_uri in the request is missing. It is mandatory parameter. | Pass the redirect_uri in the request to route user back to correct landing page. |
| 400 | invalid_request "A required parameter "code" is missing" | Authorization code in the request is missing. It is mandatory parameter. | Pass the Authorization code received as part of authorization API call. |
| 400 | invalid_request "A required parameter "grant_type" is missing" | Grant type in the request is missing. It is mandatory parameter. | Add grant_type as "authorization_code" in the request. |
| 400 | invalid_request "A required parameter "client_id" is missing" | Client ID in the request is missing. It is mandatory parameter. | Pass the client id of the app in request. |
| 400 | invalid_request "A required parameter "client_secret" is missing" | Client Secret in the request is missing. It is mandatory parameter. | Pass the client secret of the app in request. |
| 400 | invalid_redirect_uri "Unable to retrieve access token: appid/redirect uri/code verifier does not match authorization code. Or authorization code expired. Or external member binding exists" | Invalid redirect uri is passed in the request. | Pass the right redirect uri tagged to the developer application. |
| 400 | invalid_redirect_uri "Unable to retrieve access token: appid/redirect uri/code verifier does not match authorization code. Or authorization code expired. Or external member binding exists | Invalid Authorization code is sent as part of the request" | Authorization code expired and re-authenticate member to generate new authorization code and pass the fresh authorization code to exchange for access token. |