Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to: Microsoft R Server 9.x (Looking for the Machine Learning Server article)
To benefit from Microsoft R Server’s deployment and operationalization features, you can configure R Server after installation to act as a deployment server and host analytic web services.
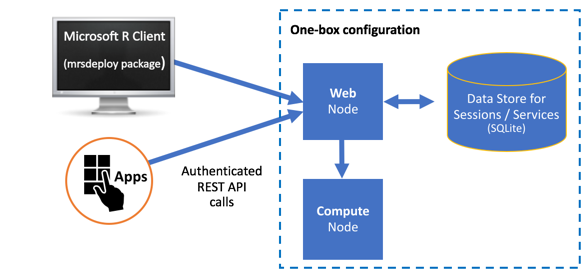
One-box vs enterprise architectures
All configurations have at least a single web node, single compute node, and a database.
Web nodes act as HTTP REST endpoints with which users can interact directly to make API calls. These nodes also access the data in the database and send requests to the compute node for processing. Web nodes are stateless, and therefore, session persistence ("stickiness") is not required. A single web node can route multiple requests simultaneously. However, you must have multiple web nodes to load balance your requests to multiple compute nodes.
Compute nodes are used to execute R code as a session or service. Each compute node has its own pool of R shells and can therefore execute multiple requests at the same time. Scaling up compute nodes enables you to have more R execution shells and benefit from load balancing across these compute nodes.
The database. An SQLite 3.7+ database is installed by default, but you can, and in some cases must, use a SQL Server (Windows) or PostgreSQL (Linux) database instead.
R Server offers two types of configuration for operationalizing analytics and remote execution:
One-box configuration: as the name suggests, one web node and one compute node run on a single machine. Set-up is a breeze. This configuration is useful when you want to explore what it is to operationalize R analytics using R Server. It is perfect for testing, proof-of-concepts, and small-scale prototyping, but might not be appropriate for production usage. This configuration is covered in this article.
Enterprise configuration: a configuration where multiple nodes are configured on multiple machines along with other enterprise features. This configuration can be scaled up or down by adding or removing nodes. Learn more about this setup in the enterprise configuration article.
For added security, you can configure SSL and authenticate against Active Directory (LDAP) or Azure Active Directory.
Supported platforms
The web nodes and compute nodes are supported on:
- Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016
- Ubuntu 14.04, Ubuntu 16.04,
- CentOS/RHEL 7.x
How to upgrade from 9.0 to 9.1
To replace an older version of a one-box configuration, you can uninstall the older distribution before installing the new version (there is no in-place upgrade). Carefully review the following steps.
Important
Before you begin, back up the appsettings.json file on each node you can restore in the event of an upgrade issue.
If you used the default SQLite database,
deployrdb_9.0.0.dbin R Server 9.0 and want to persist the data, then you must back up the SQLite database before uninstalling Microsoft R Server. Make a copy of the database file and put it outside of the Microsoft R Server directory structure.(If you are using a SQL Server or PostgreSQL database, you can skip this step.)
Warning
If you skip this SQLite database backup step and uninstall Microsoft R Server 9.0 first, you cannot retrieve your database data.
Uninstall Microsoft R Server 9.0 using the instructions in the article Uninstall Microsoft R Server to upgrade to a newer version. The uninstall process stashes away a copy of your 9.0 configuration files under this directory so you can seamlessly upgrade to R Server 9.1 in the next step:
On Windows:
C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\DeployR\currentOn Linux:
/etc/deployr/current
If you backed up a SQLite database in Step 1, manually move
deployrdb_9.0.0.dbunder this directory so it can be found during the upgrade:- Windows:
C:\Users\Default\AppData\Local\DeployR\current\frontend - Linux:
/etc/deployr/current/frontend
(If you are using a SQL Server or PostgreSQL database, you can skip this step.)
- Windows:
Install Microsoft R Server:
- On Windows: follow these instructions Installation steps | Offline steps
Important
For SQL Server Machine Learning Services, you must also:
- Add a registry key called
H_KEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\R Server\Pathwith a value of the parent path to theR_SERVERfolder (for example,C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\140). - Manually install .NET Core 2.0
- Add a registry key called
- On Linux: follow these instructions Installation steps | Offline steps
- On Windows: follow these instructions Installation steps | Offline steps
Launch the administration utility with administrator privileges. The utility checks to see if any 9.0 configuration files are present under the
currentfolder previously mentioned.From the menus, choose Configure server (or in previously releases, Configure R Server for Operationalization) and then choose Configure for one box. The configuration script begins.
When the script asks you if you'd like to upgrade, enter
y. The nodes are automatically setup using the configuration you had for R Server 9.0. Note: You can safely ignore the Python warning during upgrade.From the main menu, choose the option to Run Diagnostic Tests to test the configuration.
Exit the utility. Your web and compute nodes are now upgraded and configured as they were in version 9.0.
Repeat these steps for each node.
Warning
The entities created by users, specifically web services and snapshots, are tied to their usernames. For this reason, you must be careful to prevent changes to the user identifier over time. Otherwise, pre-existing web services and snapshots cannot be mapped to the users who created them. For this reason, we strongly recommend that you DO NOT change the unique LDAP identifier in appsettings.json once users start publishing service or creating snapshots.
How to perform a one-box configuration
Important
For your convenience, Azure Management Resource (ARM) templates are available to quickly deploy and configure Microsoft R Server for operationalization in Azure.
Get one of these templates on GitHub. Then, learn how to use it with this blog post.
To configure on a single machine:
Install Microsoft R Server and any dependencies:
On Windows: Follow these instructions: R Server installation steps | Offline steps
On Linux: Follow these instructions: R Server installation steps | Offline stepsAdditional dependencies for R Server on Linux 9.0.1. If you have installed R Server 9.0.1 on Linux, you must add a few symlinks:
R Server 9.0.1
LinuxCentOS 7.x Ubuntu 14.04 Ubuntu 16.04 Symlinks cd /usr/lib64
sudo ln -s libpcre.so.1 libpcre.so.0
sudo ln -s libicui18n.so.50 libicui18n.so.36
sudo ln -s libicuuc.so.50 libicuuc.so.36
sudo ln -s libicudata.so.50 libicudata.so.36sudo apt-get install libicu-dev
cd /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu
ln -s libpcre.so.3 libpcre.so.0
ln -s liblzma.so.5 liblzma.so.0
cd /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu
ln -s libicui18n.so.52 libicui18n.so.36
ln -s libicuuc.so.52 libicuuc.so.36
ln -s libicudata.so.52 libicudata.so.36cd /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu
ln -s libpcre.so.3 libpcre.so.0
ln -s liblzma.so.5 liblzma.so.0
cd /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu
ln -s libicui18n.so.55 libicui18n.so.36
ln -s libicuuc.so.55 libicuuc.so.36
ln -s libicudata.so.55 libicudata.so.36Note: If there are issues with starting the compute node, see here.
Launch the administration utility with administrator privileges (Windows) or
root/sudoprivileges (Linux) so you can begin to configure a one-box setup.Note
Bypass the interactive configuration steps using the argument
-silentoneboxinstalland specifying a password for the local 'admin' account when you launch the administration utility. If you choose this method, you can skip the next three substeps. For R Server 9.1 on Windows, for example, the syntax might be:dotnet Microsoft.RServer.Utils.AdminUtil\Microsoft.RServer.Utils.AdminUtil.dll -silentoneboxinstall my-password. Learn about all command line switches for this script, here.Choose the option to Configure server (or in previously releases, Configure R Server for Operationalization).
Choose the option to Configure for one box to set up the web node and compute node onto the same machine.
Important
Do not choose the suboptions Configure a web node or Configure a compute node unless you intend to have them on separate machines. This multi-machine configuration is described as an Enterprise configuration.
When prompted, provide a password for the built-in, local operationalization administrator account called 'admin'.
Return to the main menu of the utility when the configuration ends.
If on Linux and using the IPTABLES firewall or equivalent service, then use the
iptablescommand (or the equivalent) to open port 12800 to the public IP of the web node so that remote machines can access it.
Important
R Server uses Kestrel as the web server for its operationalization web nodes. Therefore, if you expose your application to the Internet, we recommend that you review the guidelines for Kestrel regarding reverse proxy setup.
You are now ready to begin operationalizing your R analytics with R Server.