Import and analyze your on-premises GPOs using Group Policy analytics in Microsoft Intune
Tip
Looking for on-premises GPO analysis? There are tools available in the Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit.
Microsoft Intune has many of the same settings as your on-premises GPOs. Group Policy analytics is a tool in Microsoft Intune that:
- Imports and analyzes your on-premises GPOs.
- Shows the settings that cloud-based MDM providers support, including Microsoft Intune.
- Shows any deprecated settings, or settings not available.
- Can migrate your imported GPOs to a settings catalog policy that can be deployed to your devices.
If your organization uses on-premises GPOs to manage Windows 10/11 devices, then Group Policy analytics can help. With Group Policy analytics, it's possible Intune can replace your on-premises GPOs. Windows 10/11 devices are inherently cloud native. So depending on your configuration, these devices might not require access to an on-premises Active Directory.
If you're ready to remove the dependency to on on-premises AD, then analyzing your GPOs with Group Policy analytics is a good first step. Some older settings aren't supported, or don't apply to cloud native Windows devices. After you analyze your GPOs, you know the settings that are still valid.
This feature applies to:
- Windows 11
- Windows 10
This article shows you how to export your on-premises GPOs, import the GPOs into Intune, and review the analysis and results. To migrate or transfer your imported GPOs to an Intune policy, go to Create a Settings Catalog policy using your imported GPOs in Microsoft Intune.
Before you begin
In the Microsoft Intune admin center, sign in as the Intune administrator or with a role that has the Security baselines and the Device Configuration permission. For more information on the built-in roles, see role-based access control.
Export a GPO as an XML file
The following steps can be different on your server, depending on the GPMC version you're using. When you export the GPO, make sure you export as an XML file.
On your on-premises computer, open the
Group Policy Managementconsole (GPMC.msc).In the management console, expand your domain name.
Expand Group Policy Objects to see all the available GPOs.
Right-click the GPO you want to migrate and choose Save report:

Select an easily accessible folder for your export. In Save as type, select XML File. In another step, you add this file to group policy analytics in Intune.
Make sure that the file is less than 4 MB and has a proper Unicode encoding. If the exported file is greater than 4 MB, then reduce the number of settings in the group policy object.
Import GPOs and run analytics
In the Microsoft Intune admin center, select Devices > Manage devices > Group Policy analytics.
Select Import, select your saved XML file > Next.
You can select multiple files at the same time.
Check the sizes of your individual GPO XML files. A single GPO can't be bigger than 4 MB. If a single GPO is larger than 4 MB, then the import fails. XML files without the appropriate unicode ending also fail.
In Scope tags, select the existing scope tag you want to apply to the imported GPO. If you don't select an existing scope tag, then the Default scope tag is automatically used:
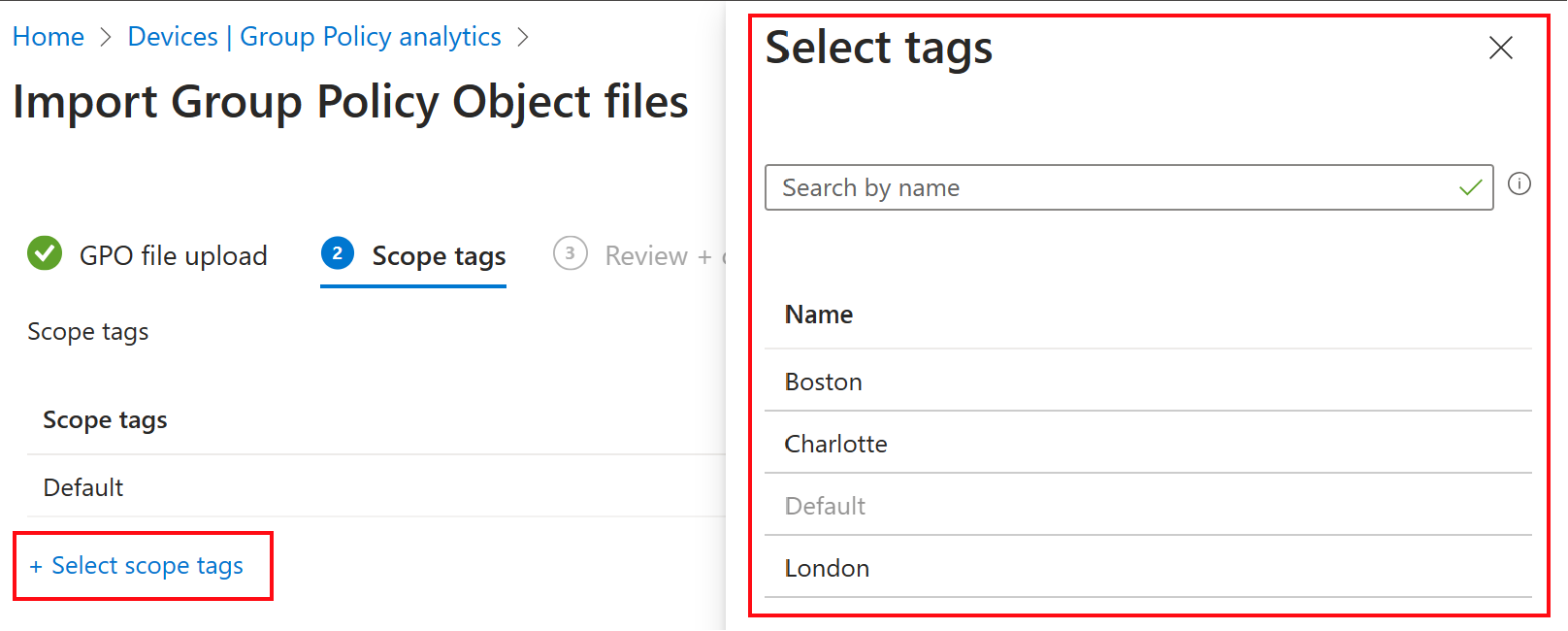
Only admins included in the scope tags you select can see the imported GPO. For more information on scope tags on your imported GPOs, go to Select a scope tag when you import (in this article).
Select Next > Create.
When you select Create, Intune automatically analyzes the GPO in the XML file.
After the analysis runs, the GPO you imported is listed with the following information:
Group Policy name: The name is automatically generated using information in the GPO.
Active Directory Target: The target is automatically generated using the organizational unit (OU) target information in the GPO.
MDM Support: Shows the percentage of group policy settings in the GPO that have the same setting in Intune.
Note
Whenever the Microsoft Intune product team makes changes to the mapping in Intune, the percentage under MDM Support automatically updates to reflect those changes.
Unknown Settings: There are some CSPs that can't be analyzed. Unknown Settings lists the GPOs that can't be analyzed.
Targeted in AD: Yes means the GPO is linked to an OU in on-premises group policy. No means the GPO isn't linked to an on-premises OU.
Last imported: Shows the date of the last import.
You can Import more GPOs for analysis, Refresh the page, and Filter the output. You can also Export this view to a
.csvfile:
Select the MDM Support percentage for a listed GPO. More detailed information about the GPO is shown:
Setting Name: The name is automatically generated using information in the GPO setting.
Group Policy Setting Category: Shows the setting category for ADMX settings, such as Internet Explorer and Microsoft Edge. Not all settings have a setting category.
MDM Support:
- Yes means there's a matching setting available in Intune. You can configure this setting in the Settings Catalog.
- No means there isn't a matching setting available to MDM providers, including Intune.
- Other values: If you import older settings that aren't supported anymore, then the tool suggests migrating to a newer supported version. For more information on migrate scenarios, go to Imported GPOs in Intune - What you need to know.
Value: Shows the value imported from the GPO. It shows different values, such
true,900,Enabled,false, and so on.Scope: Shows if the imported GPO targets users or targets devices.
Min OS Version: Shows the minimum Windows OS version build numbers that the GPO setting applies. It can show
18362(1903),17130(1803), and other Windows client versions.For example, if a policy setting shows
18362, then the setting supports build18362and newer builds.CSP Name: A Configuration Service Provider (CSP) exposes device configuration settings in Windows client. This column shows the CSP that includes the setting. For example, you can see Policy, BitLocker, PassportforWork, and so on.
The CSP reference lists the available CSPs, shows the supported OS editions, and more.
CSP Mapping: Shows the OMA-URI path for the on-premises policy. You can use the OMA-URI in a custom device configuration profile. For example, you might see
./Device/Vendor/MSFT/BitLocker/RequireDeviceEnryption.
For the settings that have MDM support, you can create a Settings Catalog policy with these settings. For the specific steps, go to Create a Settings Catalog policy using your imported GPOs in Microsoft Intune.
Select a scope tag when you import
When you import a GPO, you can select existing scope tags. If you don't select a scope tag, then the Default scope tag is automatically used. Only admins scoped to the Default scope tag can see the imported GPO. Admins that aren't scoped to the Default scope tag don't see the imported GPO.
This behavior applies to any scope tag you select when you import a GPO. Admins only see the imported GPOs if they have one of the same scope tags selected during the import. If an admin doesn't have the scope tag, then they don't see the imported GPO in the reporting or in the list of GPOs.
For example, admins have Charlotte, London, or Boston scope tags assigned to their role:
- An admin with the "Charlotte" scope tag imports a GPO.
- During the import, they select the "Charlotte" scope tag. The "Charlotte" scope tag is applied to the imported GPO.
- All admins with the "Charlotte" scope tag can see the imported object.
- Admins with only the "London" or only the "Boston" scope tags can't see the imported object from the "Charlotte" admin.
For admins to see the analytics or migrate the imported GPO to an Intune policy, these admins must have one of the same scope tags selected during the import.
For more information on scope tags, go to RBAC and scope tags for distributed IT.
Supported CSPs and group policies
Group Policy analytics can parse the following CSPs for MDM support:
If your imported GPO has settings that aren't in the supported CSPs and Group Policies, then the settings might be listed in the Unknown Settings column. This behavior means the settings were identified in your GPO.
Even though Group Policy analytics can parse the CSPs, there are some things you should know when migrating your imported GPOs. For more information, go to Migrate your imported GPO to a Settings Catalog policy - What you need to know.
Group Policy migration readiness report
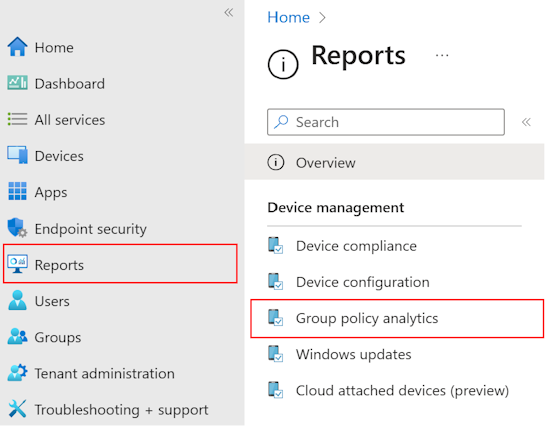
In the Microsoft Intune admin center, select Reports > Device management > Group policy analytics:
In the Summary tab, a summary of the GPO and its policies are shown. Use this information to determine the status of the policies in your GPO:
Ready for migration: The policy has a matching setting in Intune, and is ready to be migrated to Intune.
Not supported: The policy doesn't have a matching setting. Typically, policy settings that show this status aren't exposed to MDM providers, including Intune.
Deprecated: The policy can apply to older Windows versions, older Microsoft Edge versions, and more policies that aren't used anymore.
Note
When the Microsoft Intune product team updates the mapping logic, your imported GPOs are automatically updated. You don't need to reimport your GPOs.
Select the Reports tab > Group policy migration readiness. In this report, you can:
- See the number of settings in your GPO that can be configured in a device configuration profile. It also shows if the settings can be in a custom profile, aren't supported, or are deprecated.
- Filter the report output using the Migration Readiness, Profile type, and CSP Name filters.
- Select Generate report or Generate again to get current data.
- See the list of settings in your GPO.
- Use the search bar to find specific settings.
- Get a time stamp of when the report was last generated.
Note
After you add or remove your imported GPOs, it can take about 20 minutes to update the Migration Readiness reporting data.
Known issues
Currently, the Group Policy analytics tool only supports non-ADMX settings in the English language. If you import a GPO with settings in languages other than English, then your MDM Support percentage is inaccurate.
Send product feedback
You can provide feedback on Group Policy Analytics. In the Microsoft Intune admin center, select Devices > Manage devices > Group Policy analytics > Got feedback.
Examples of feedback areas:
- You received errors during GPO import or analytics, and you need more specific information.
- How easy is it to use Group Policy analytics to find the supported group policies in Microsoft Intune?
- Will this tool help you move some workloads to Intune? If yes, what workloads are you considering?
To get information on the customer experience, the feedback is aggregated, and sent to Microsoft. Entering an email is optional, and can be used to get more information.
Privacy and security
Any use of customer data, such as the GPOs that your organization uses, is aggregated. It's not sold to any third parties. This data might be used to make business decisions within Microsoft. Your customer data is stored securely.
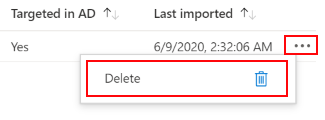
At any time, you can delete imported GPOs:
Go to Devices > Manage devices > Group Policy analytics.
Select the context menu > Delete:
Next steps
Create a Settings Catalog policy using your imported GPOs in Microsoft Intune
Use Windows 10/11 Administrative Templates to configure group policy settings in Microsoft Intune
See also
Learn more about Configuration Service Providers (CSP).
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for