Internet-facing devices
Applies to:
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Plan 1
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Plan 2
- Microsoft Defender XDR
- Microsoft Defender for Business
Want to experience Defender for Endpoint? Sign up for a free trial.
As threat actors continuously scan the web to detect exposed devices they can exploit to gain a foothold in internal corporate networks, mapping your organization's external attack surface is a key part of your security posture management. Devices that can be connected to or are approachable from the outside pose a threat to your organization.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint automatically identifies and flags onboarded, exposed, internet-facing devices in the Microsoft Defender portal. This critical information provides increased visibility into an organization's external attack surface and insights into asset exploitability.
Note
Currently, only Windows devices onboarded to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint can be identified as internet-facing. Support for other platforms will be available in upcoming releases.
Devices flagged as internet-facing
Devices that are successfully connected through TCP or identified as host reachable through UDP will be flagged as internet-facing in the Microsoft Defender portal. Defender for Endpoint uses different data sources to identify the devices to flag:
- External scans are used to identify which devices are approachable from the outside.
- Device network connections, captured as part of Defender for Endpoint signals, help to identify external incoming connections that reach internal devices.
Devices can be flagged as internet-facing when a configured firewall policy (host firewall rule or enterprise firewall rule) allows inbound internet communication.
Understanding your firewall policy, and your devices that are intentionally internet-facing as opposed to those that may compromise your organization, provides critical information when it comes to mapping your external attack surface.
View internet-facing devices
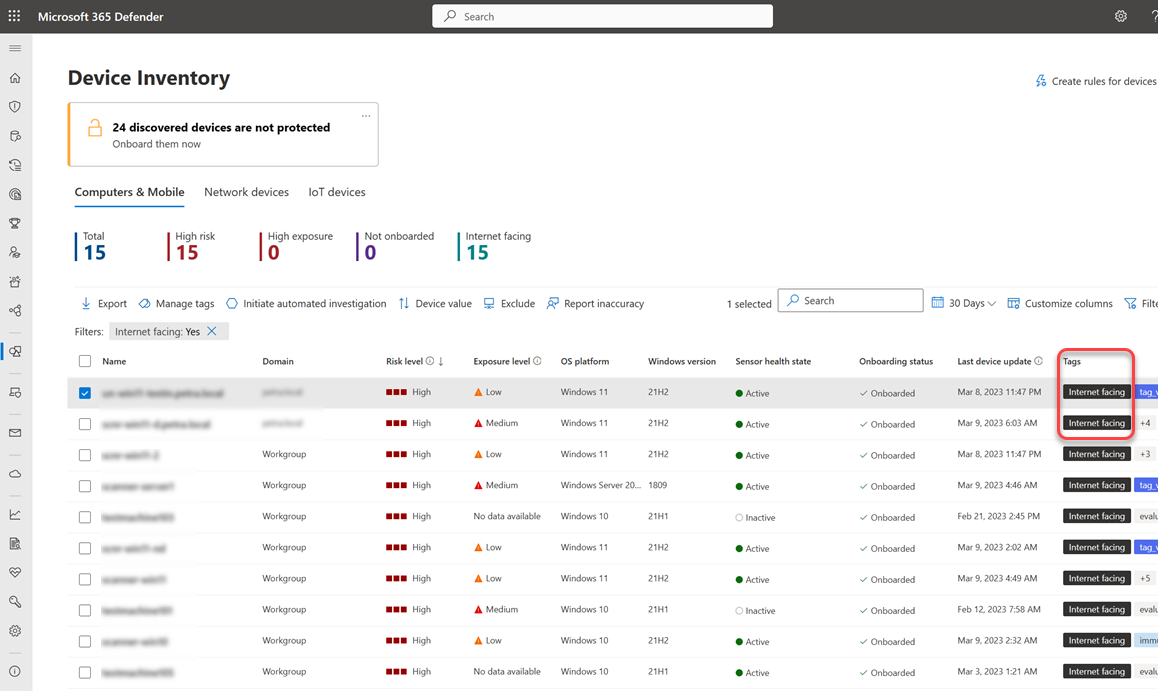
For each onboarded device identified as internet-facing, the internet facing tag appears in the Tags column in the device inventory in the Microsoft Defender portal. To view internet-facing devices:
Go to Assets > Device in the Microsoft Defender portal.
Hover over the internet-facing tag to see why it was applied, possible reasons are:
- This device was detected by an external scan
- This device received external incoming communication
At the top of the page, you can view a counter that shows the number of devices that have been identified as internet-facing and are potentially less secure.
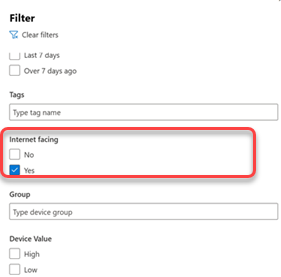
You can use filters to focus in on internet-facing devices and investigate the risk they may introduce into your organization.
The internet-facing device tag also appears in Microsoft Defender Vulnerability Management. This allows you to filter for internet-facing devices from the weaknesses and the security recommendations pages in the Microsoft Defender portal.
Note
If no new events for a device occur for 48 hours, the Internet-facing tag is removed and it will no longer be visible in the Microsoft Defender portal.
Investigate your internet-facing devices
To learn more about an internet-facing device, select the device in the device inventory to open its flyout pane:
This pane includes details on whether the device was detected by a Microsoft external scan or received an external incoming communication. The external network interface address and port fields provide details on the external IP and port that were scanned at the time this device was identified as internet facing.
The local network interface address and port for this device, along with the last time the device was identified as internet facing are also shown.
Use advanced hunting
Use advanced hunting queries to gain visibility and insights into the internet-facing devices in your organization, for example:
Get all internet facing devices
Use this query to find all devices that are internet facing.
// Find all devices that are internet-facing
DeviceInfo
| where Timestamp > ago(7d)
| where IsInternetFacing
| extend InternetFacingInfo = AdditionalFields
| extend InternetFacingReason = extractjson("$.InternetFacingReason", InternetFacingInfo, typeof(string)), InternetFacingLocalPort = extractjson("$.InternetFacingLocalPort", InternetFacingInfo, typeof(int)), InternetFacingScannedPublicPort = extractjson("$.InternetFacingPublicScannedPort", InternetFacingInfo, typeof(int)), InternetFacingScannedPublicIp = extractjson("$.InternetFacingPublicScannedIp", InternetFacingInfo, typeof(string)), InternetFacingLocalIp = extractjson("$.InternetFacingLocalIp", InternetFacingInfo, typeof(string)), InternetFacingTransportProtocol=extractjson("$.InternetFacingTransportProtocol", InternetFacingInfo, typeof(string)), InternetFacingLastSeen = extractjson("$.InternetFacingLastSeen", InternetFacingInfo, typeof(datetime))
| summarize arg_max(Timestamp, *) by DeviceId
This query returns the following fields for each internet-facing device with their aggregated evidence in the "AdditionalFields" column.
- InternetFacingReason: Whether the device was detected by an external scan or received incoming communication from the internet
- InternetFacingLocalIp: The local IP address of the internet facing interface
- InternetFacingLocalPort: The local port where internet facing communication was observed
- InternetFacingPublicScannedIp: The public IP address that was externally scanned
- InternetFacingPublicScannedPort: The internet facing port that was externally scanned
- InternetFacingTransportProtocol: The transport protocol used (TCP/UDP)
Get information on inbound connections
For TCP connections, you can gain further insights into applications or services identified as listening on a device by querying DeviceNetworkEvents.
Use the following query for devices tagged with the reason This device received external incoming communication:
// Use this function to obtain the device incoming communication from public IP addresses
// Input:
// DeviceId - the device ID that you want to investigate.
// The function will return the last 7 days of data.
InboundExternalNetworkEvents("<DeviceId>")
Note
Process related information is only available for TCP connections.
Use the following query for devices tagged with the reason This device was detected by an external scan:
DeviceNetworkEvents
| where Timestamp > ago(7d)
| where DeviceId == ""
| where Protocol == "Tcp"
| where ActionType == "InboundInternetScanInspected"
For UDP connections, gain insights into devices that were identified as host reachable but may not have established a connection (for example, as a result of the host firewall policy) using the following query:
DeviceNetworkEvents
| where Timestamp > ago(7d)
| where DeviceId == ""
| where Protocol == "Udp"
| where ActionType == "InboundInternetScanInspected"
If the above queries fail to provide the relevant connections, you can use socket collection methods to retrieve the source process. To learn more about different tools and capabilities available to do this, see:
Report inaccuracy
You can report an inaccuracy for a device with incorrect internet-facing information. For the internet-facing device:
- Open the device flyout from the Device inventory page
- Select Report device inaccuracy
- In the What part is inaccurate dropdown, select Device information
- For Which information is inaccurate select the internet facing classification checkbox from the dropdown
- Fill in the requested details about what the correct information should be
- Provide an email address (optional)
- Select Submit Report
See also
Tip
Do you want to learn more? Engage with the Microsoft Security community in our Tech Community: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Tech Community.