Advanced hunting in the Microsoft Defender portal
Advanced hunting in the unified portal allows you to view and query all data from Microsoft Defender XDR. This includes data from various Microsoft security services and Microsoft Sentinel, which includes data from non-Microsoft products, in a single platform. You can also access and use all your existing Microsoft Sentinel workspace content, including queries and functions.
Querying from a single portal across different data sets makes hunting more efficient and removes the need for context-switching.
Important
Microsoft Sentinel is available as part of the public preview for the unified security operations platform in the Microsoft Defender portal. For more information, see Microsoft Sentinel in the Microsoft Defender portal.
How to access
Required roles and permissions
To query across Microsoft Sentinel and Microsoft Defender XDR data in the unified advanced hunting page, you must have access to Microsoft Defender XDR advanced hunting (see Required roles and permissions) and at least Microsoft Sentinel Reader (see Microsoft Sentinel-specific roles).
In the unified portal, you can query any data in any workload that you can currently access based on the roles and permissions you have.
Connect a workspace
In Microsoft Defender, you can connect workspaces by selecting Connect a workspace in the top banner. This button appears if you're eligible to onboard a Microsoft Sentinel workspace onto the unified Microsoft Defender portal. Follow the steps in: Onboarding a workspace.
After connecting your Microsoft Sentinel workspace and Microsoft Defender XDR advanced hunting data, you can start querying Microsoft Sentinel data from the advanced hunting page. For an overview of advanced hunting features, read Proactively hunt for threats with advanced hunting.
What to expect for Defender XDR tables streamed to Microsoft Sentinel
- Use tables with longer data retention period in queries – Advanced hunting follows the maximum data retention period configured for the Defender XDR tables (see Understand quotas). If you stream Defender XDR tables to Microsoft Sentinel and have a data retention period longer than 30 days for said tables, you can query for the longer period in advanced hunting.
- Use Kusto operators you've used in Microsoft Sentinel – In general, queries from Microsoft Sentinel work in advanced hunting, including queries that use the
adx()operator. There might be cases where IntelliSense warns you that the operators in your query don't match the schema, however, you can still run the query and it should still be executed successfully. - Use the time filter dropdown instead of setting the time span in the query – If you're filtering ingestion of Defender XDR tables to Sentinel instead of streaming the tables as is, don't filter the time in the query as this might generate incomplete results. If you set the time in the query, the streamed, filtered data from Sentinel is used because it usually has the longer data retention period. If you would like to make sure you're querying all Defender XDR data for up to 30 days, use the time filter dropdown provided in the query editor instead.
- View
SourceSystemandMachineGroupcolumns for Defender XDR data that have been streamed from Microsoft Sentinel – Since the columnsSourceSystemandMachineGroupare added to Defender XDR tables once they're streamed to Microsoft Sentinel, they also appear in results in advanced hunting in Defender. However, they remain blank for Defender XDR tables that weren't streamed (tables that follow the default 30-day data retention period).
Note
Using the unified portal, where you can query Microsoft Sentinel data after connecting a Microsoft Sentinel workspace, does not automatically mean you can also query Defender XDR data while in Microsoft Sentinel. Raw data ingestion of Defender XDR should still be configured in Microsoft Sentinel for this to happen.
Where to find your Microsoft Sentinel data
You can use advanced hunting KQL (Kusto Query Language) queries to hunt through Microsoft Defender XDR and Microsoft Sentinel data.
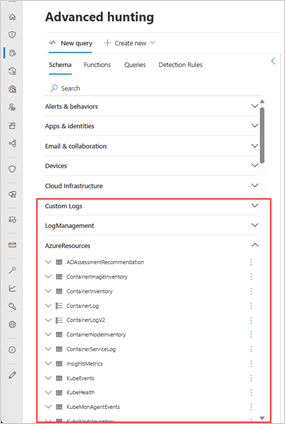
When you open the advanced hunting page for the first time after connecting a workspace, you can find many of that workspace's tables organized by solution after the Microsoft Defender XDR tables under the Schema tab.
Likewise, you can find the functions from Microsoft Sentinel in the Functions tab, and your shared and sample queries from Microsoft Sentinel can be found in the Queries tab inside folders marked Sentinel.
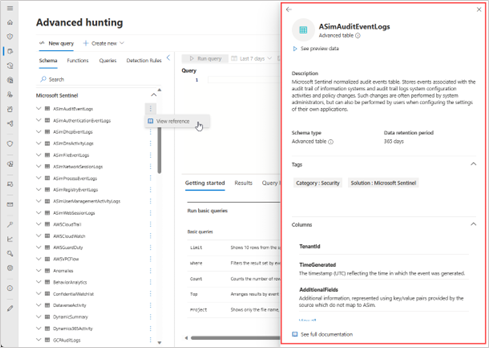
View schema information
To learn more about a schema table, select the vertical ellipses (  ) to the right of any schema table name under the Schema tab, then select View schema.
) to the right of any schema table name under the Schema tab, then select View schema.
In the unified portal, in addition to viewing the schema column names and descriptions, you can also view:
- Sample data – select See preview data, which loads a simple query like
TableName | take 5 - Schema type – whether the table supports full query capabilities (advanced table) or not (basic logs table)
- Data retention period – how long the data is set to be kept
- Tags – available for Sentinel data tables
Use functions
To use a function from Microsoft Sentinel, go to the Functions tab and scroll until you find the function that you want. Double-click the function name to insert the function in the query editor.
You can also select the vertical ellipses (  ) to the right of the function and select Insert to query to insert the function into a query in the query editor.
) to the right of the function and select Insert to query to insert the function into a query in the query editor.
Other options include:
- View details – opens the function side pane containing its details
- Load function code – opens a new tab containing the function code
For editable functions, more options are available when you select the vertical ellipses:
- Edit details – opens the function side pane to allow you to edit details about the function (except folder names for Sentinel functions)
- Delete – deletes the function
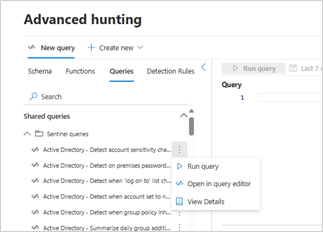
Use saved queries
To use a saved query from Microsoft Sentinel, go to the Queries tab and scroll until you find the query that you want. Double-click the query name to load the query in the query editor. For more options, select the vertical ellipses (  ) to the right of the query. From here, you can perform the following actions:
) to the right of the query. From here, you can perform the following actions:
Run query – loads the query in the query editor and runs it automatically
Open in query editor – loads the query in the query editor
View details – opens the query details side pane where you can inspect the query, run the query, or open the query in the editor
For editable queries, more options are available:
- Edit details – opens the query details side pane with the option to edit the details like description (if applicable) and the query itself; only the folder names (location) of Microsoft Sentinel queries can't be edited
- Delete – deletes the query
- Rename – allows you to modify the query name
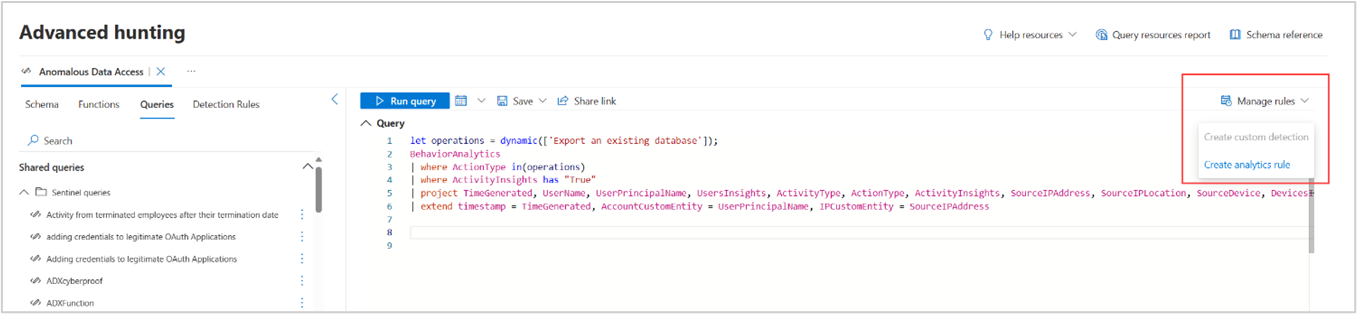
Create custom analytics and detection rules
To help discover threats and anomalous behaviors in your environment, you can create custom detection policies.
For analytics rules that apply to data ingested through the connected Microsoft Sentinel workspace, select Manage rules > Create analytics rule.
The Analytics rule wizard appears. Fill up the required details as described in Analytics rule wizard—General tab.
For custom detection rules that apply to Microsoft Defender XDR data, select Manage rules > Create custom detection. Read Create and manage custom detection rules for more information.
Explore results
Results of queries that were run appear in the Results tab. You can export the results to a CSV file by selecting Export.
You can also explore the results in-line with the following features:
- Expand a result by selecting the dropdown arrow at the left of each result
- Where applicable, expand details for results that are in JSON or array format by selecting the dropdown arrow at the left of applicable result row for added readability
- Open the side pane to see a record's details (concurrent with expanded rows)
You can also right-click on any result value in a row so that you can use it to:
- Add more filters to the existing query
- Copy the value for use in further investigation
- Update the query to extend a JSON field to a new column
For Microsoft Defender XDR data, you can take further action by selecting the checkboxes to the left of each result row. Select Link to incident to link the selected results to an incident (read Link query results to an incident) or Take actions to open the Take actions wizard (read Take action on advanced hunting query results).
Known issues
- The
IdentityInfo tablefrom Microsoft Sentinel isn't available, as theIdentityInfotable remains as is in Defender XDR. Microsoft Sentinel features like analytics rules that query this table aren't impacted as they're querying the Log Analytics workspace directly. - The Microsoft Sentinel
SecurityAlerttable is replaced byAlertInfoandAlertEvidencetables, which both contain all the data on alerts. While SecurityAlert isn't available in the schema tab, you can still use it in queries using the advanced hunting editor. This provision is made so as not to break existing queries from Microsoft Sentinel that use this table. - Guided hunting mode is supported for Defender XDR data only.
- Custom detections, links to incidents, and take actions capabilities are supported for Defender XDR data only.
- Bookmarks aren't supported in the advanced hunting experience. They're supported in the Microsoft Sentinel > Threat management > Hunting feature.
- If you're streaming Defender XDR tables to Log Analytics, there might be a difference between the
TimestampandTimeGeneratedcolumns. In case the data arrives to Log Analytics after 48 hours, it's being overridden upon ingestion tonow(). Therefore, to get the actual time the event happened, we recommend relying on theTimestampcolumn. - The Microsoft Graph API for running an advanced hunting query doesn't support querying data from Microsoft Sentinel yet.
Feedback
Coming soon: Throughout 2024 we will be phasing out GitHub Issues as the feedback mechanism for content and replacing it with a new feedback system. For more information see: https://aka.ms/ContentUserFeedback.
Submit and view feedback for