Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) is a set of processes, people, and tools that govern an agent's lifecycle. It starts with the initial idea and requirements gathering and continues through development, testing, deployment, and ongoing maintenance until decommissioning. The result is greater efficiency and a predictable, repeatable way of delivering agents.
What are the benefits of ALM?
The benefits of practicing healthy ALM include:
- Reliable releases: Reduces risk of errors and ensures consistent deployments.
- Governance and compliance: Helps enforce organizational policies and security standards.
- Scalability and reuse: Enables solutions to grow without reinventing processes.
- Quality at speed: Balances rapid delivery with high-quality standards.
- Business continuity: Minimizes downtime and disruption during updates.
- Team collaboration: Improves coordination across developers, testers, and operations.
- End-to-end discipline: Brings structure to every phase of the application lifecycle.
Apply Power Platform ALM best practices
Copilot Studio is built on the same foundation as Power Platform and offers rich options when it comes to Application Lifecycle Management. Therefore, both platforms follow some common guidance:
- Define an environment strategy to ensure makers can build inside of secure, lightweight, low-audience environments before following vetted guidelines to deploy agents to test and production environments and expand usage.
- Use solutions as containers to transport artifacts and customizations across environments.
- Apply environment variables for environment-specific settings and configure connection references for environment-specific connections and credentials.
- Implement continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) deployment options for both no-code and pro-dev setups (pipelines, Azure DevOps, or GitHub integrations).
- Enable source control with native Git integration.
Configure and secure environments
A healthy ALM strategy includes at least three environments: development, test, and production. After a developer makes changes to the agent in the development environment, they promote it to the test environment. If testers uncover bugs, the developer fixes them in development and promotes the agent again. Once testing passes, the agent is deployed to production.
Configure the production environment as a production type environment. Configure all other environments, including development and test, as sandbox type environments.
Secure every environment by applying an Entra Security Group to limit access to only its members.
Follow the ALM golden rules
Use these rules to ensure a consistent and reliable application lifecycle management process.
- Don't customize outside of a development environment.
- Always work in the context of solutions.
- Use a custom publisher and prefix.
- Create separate solutions only if you need to deploy components independently.
- Use environment variables for settings and secrets that change across environments.
- Export and deploy solutions as managed, unless setting up a development environment.
- Consider automating ALM for source control and automated deployments.
Review Copilot Studio specific ALM considerations
Copilot Studio includes a few specific items that aren't solution-aware. These items don't follow the normal solution deployment process and require post-deployment steps on the downstream environment, such as:
- Azure Application Insights settings
- Manual authentication settings
- Direct Line / Web channel security settings
- Deployed channels
- Sharing (with other makers, or with end-users)
Create reusable component collections
A component collection is a set of reusable agent components. These components include topics, knowledge, actions, and entities. The main benefit of component collections is that you can share them among multiple agents within an environment.
You can also use a solution to export and import component collections. This approach enables you to move content across multiple environments to support ALM scenarios. It allows multiple teams to develop parts of agents in different environments with independent release cadences.
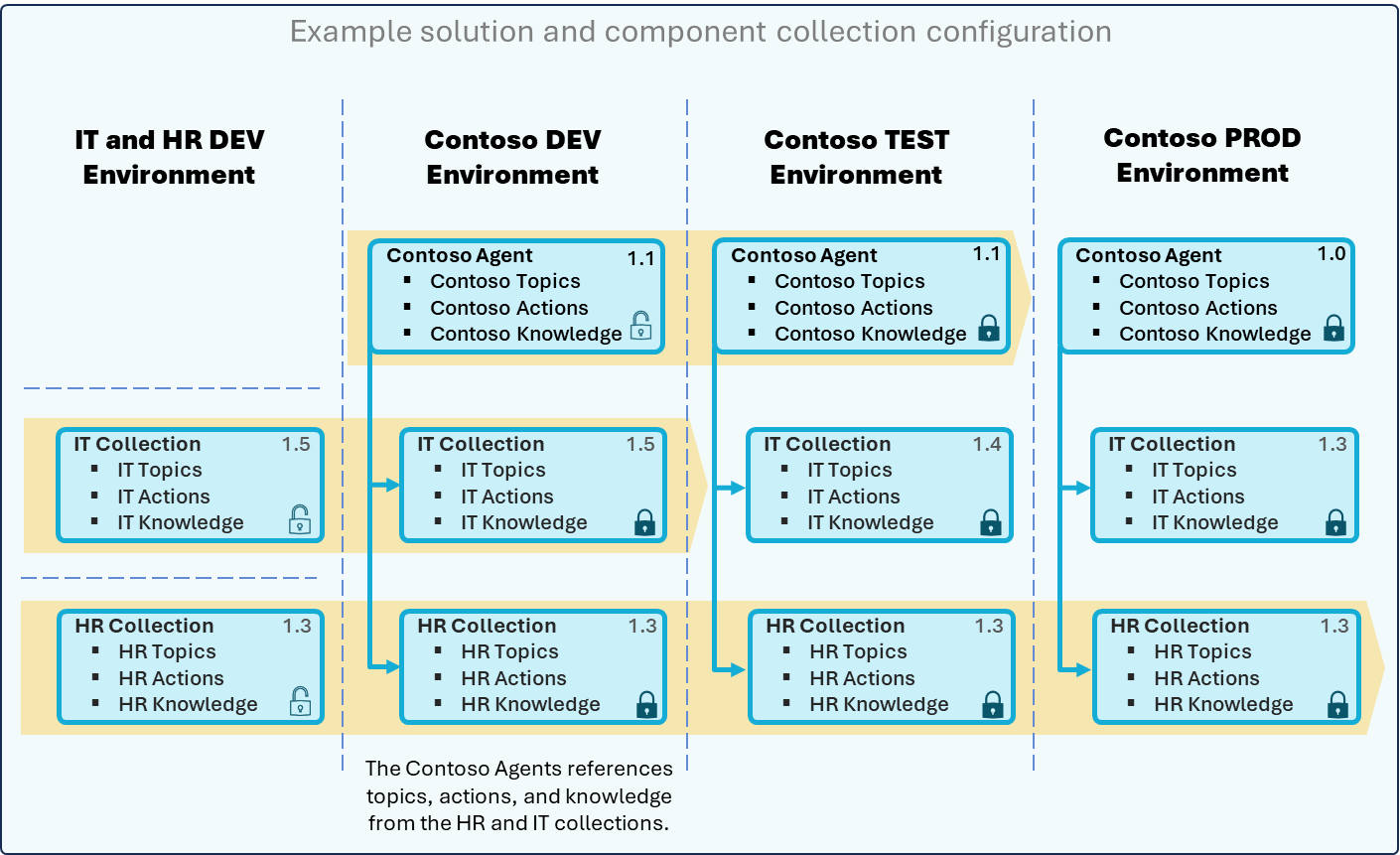
The image illustrates how component collections are configured across multiple environments to support ALM. It shows four environments:
- IT and HR DEV environment
- Contoso DEV environment
- Contoso TEST environment
- Contoso PROD environment
Each environment contains agents and collections that you can reuse and reference across environments.
Purpose
- Enable reuse of agent components (topics, actions, knowledge) across multiple environments.
- Support ALM scenarios by allowing modular development and independent release cadences.
- Facilitate collaboration among multiple teams by sharing collections and exporting and importing solutions.
Activities
- Create component collections for IT and HR (for example, IT Topics, HR Actions).
- Develop agents (for example, Contoso Agent) that reference these collections.
- Implement ALM tooling to export and import solutions to move collections between DEV, TEST, and PROD environments.
- Version control: Ensure all changes are version-controlled and documented.
Key practices for each environment
- IT and HR DEV Environment
- Maintain the IT Collection and HR Collection with topics, actions, and knowledge.
- Make changes to these collections in this environment and deploy them to upstream environments.
- Contoso DEV Environment
- Build the Contoso Agent referencing Contoso Topics, Actions, and Knowledge.
- Integrate IT and HR collections with the same versions as the DEV environment.
- Use this environment for development and initial integration of agent components.
- Contoso TEST Environment
- Deploy the Contoso Agent for testing.
- Import IT and HR collections with the same versions as the DEV environment.
- Use this environment for validation and QA before production release.
- Contoso PROD Environment
- Final deployment of the Contoso Agent.
- Import collections with stable versions, such as IT Collection v1.0 and HR Collection v1.0.
- Use this environment for production-ready configuration ensuring reliability.
Best practices
- Reuse over duplication: Share collections across agents and environments.
- Version control: Track versions for consistency and rollback.
- Modular design: Separate IT and HR components for flexibility.
- Independent release cadence: Allow updates without disrupting other environments.
Select ALM automation tools for deploying agents
Copilot Studio supports multiple ALM automation tools to assist with deploying agents. Each option offers different capabilities and targets a different audience:
- Azure DevOps: An enterprise-grade solution for managing ALM with advanced CI/CD and source control capabilities.
- GitHub Actions for Power Platform: Automates ALM-related tasks for developers and admins using the GitHub platform.
- Pipelines in Power Platform for Copilot Studio: Simplifies deployments for citizen developers using deployment pipelines built into the Power Platform.
The following table provides a detailed comparison of the available ALM tools:
| Feature or benefit | Azure DevOps | GitHub Actions for Power Platform | Power Platform Pipelines for Copilot Studio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Best for | Enterprise teams needing full ALM control | Dev/Admin teams managing multiple environments | Organizations empowering citizen developers |
| Key capabilities |
|
|
|
| Setup complexity | High (requires configuration and expertise) | Moderate (requires GitHub setup and scripts) | Low (few minutes setup) |
Establish a testing strategy
Testing agents before deployment is an important part of an ALM strategy for Copilot Studio. Learn more in Design a testing strategy for your agents.
Next step
Prepare to operate your solution at scale by reviewing how to track usage, maintain compliance, and ensure your environments have the capacity they need.