Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Microsoft 365 Copilot maps your organization’s data into an advanced lexical and semantic index to power search relevance and accuracy. Copilot can access the context and relationships within your data by utilizing Microsoft Graph, enabling more contextually precise information retrieval. The index enhances interactions with your data, offering users a richer and more seamless experience. Built with a comprehensive approach to security, compliance, and privacy, Copilot ensures that all organizational boundaries within your tenant are respected. With Microsoft 365 Copilot, users can trust that their searches are relevant, accurate, and secure.
What is an index?
Microsoft 365 Copilot enhances search with an advanced lexical and semantic understanding of your organization’s data.
The concept of indexing data is well established in Microsoft 365. Indexing is one of the important ways that Microsoft 365 services access the tremendous amount of data in Microsoft Graph, where your Microsoft 365 tenant resides. With indexing, users see search results from Microsoft Graph, including content and signals from most Microsoft 365 applications in your tenant. This ensures that search results are personalized and elevated based on your connections between content and people in your network.
The semantic index is generated from content in Microsoft Graph. It's used to aid in the production of contextually relevant responses to user queries. It allows organizations to search through billions of vectors (mathematical representations of features or attributes) and return related results. Combined with enhancements across Microsoft Graph, the semantic index connects you with relevant information in your organization. It’s built on Microsoft’s comprehensive approach to security, compliance, and privacy, and respects all organizational boundaries within your tenant.
Interactions with data in Microsoft Graph are based on keyword matching, personalization, and social matching. Keyword search queries against an index in the Microsoft Graph, which maps to locations in documents or a set of documents. Microsoft 365 uses the Microsoft Graph to rank the most relevant content based on its knowledge of additional signals for users and their close network. This is known as personalization and social matching in Microsoft 365, which drives relevance for queries against the content in your organization. Access to tenant data in Microsoft Graph is gated by role-based access control. Organizations are always in control of Microsoft Search capabilities via the Search and Intelligence portal in the Microsoft 365 admin center.
How semantic indexing helps manage your data
Semantic index enhances the Microsoft 365 Copilot experience in both Microsoft 365 Chat and in the Microsoft 365 apps. It supports an enhanced content grounding and conceptual understanding of your online data that is automatically enabled by Microsoft. It does this by creating vectorized indices. A vector is a numerical representation of a word, image pixel, or other data point. The vector is arranged or mapped with close numbers placed in proximity to one another to represent similarity. Vectors are stored in multi-dimensional spaces where semantically similar data points are clustered together in the vector space, enabling Microsoft 365 to handle a broader set of search queries beyond “exact match."
In practical terms, this means that Microsoft 365 services such as Microsoft 365 Copilot can:
- Understand relationships between different forms of words (for example, tech, technology, technologies; USA, U.S.A, United States, United States of America; dog, cat, pet).
- Capture synonyms to expand the amount of searchable information, including the intent of sentences, snippets, documents, and meetings.
- Identify related assets to your query or sample content.
The following graphic uses text (instead of numbers used by vectorized indices) to show an example of similarity between data points:

Semantic indexing provides for fast and accurate similarity search and retrieval of data based on their vector distance or similarity. This means that in addition to using traditional lexical methods for querying based on exact matches or predefined criteria, semantic indexing can find the most similar or relevant data based on the semantic or contextual meaning.
Features
The following semantic indexing features do more than enhance search results; they work together to help you understand your data, find information more quickly, and improve your productivity. Users can interact with the semantic index initially through Microsoft 365 Copilot integration. We generate a semantic index for users with a paid Microsoft 365 Copilot license. Here are the details of how each feature works.
Microsoft 365 Copilot with Microsoft Graph
Semantic indexing provides the grounding data for knowledge retrieval via Microsoft Copilot by understanding the intent of your query and appending additional information to your Microsoft Copilot prompt.
Relevant information is obtained in the Microsoft Graph and the semantic index to provide the large language model (LLM) with more information to reason over. As an example, suppose you want Microsoft Copilot to locate an email where a colleague praised the design work of a vendor. Semantic indexing includes nearby words (for example, elated, excited, amazed) into the search to broaden the search area and give the best result. All of this work takes place behind the scenes to add relevance to results that you search for with Microsoft Copilot, without adding complexity.
How semantic indexing works
Semantic indexing powers Microsoft 365 Copilot’s search results by enabling a conceptual understanding of your online data to complement the lexical understanding we also have. Indexing is automatically enabled by Microsoft.
Today, a semantic index is created for every subscription at the tenant and user level. It's an organization-wide index generated from text-based SharePoint Online files. However, it only surfaces the results to a user if the user already has access to the content controlled by role-based access control. Additionally, the SharePoint Online site must remain searchable. In time, we'll also generate user-level index content. This adds personalized index of a working set of data that is accessible for users performing everyday tasks. This includes any text-based content you make or interact with, such as emails, documents that mention you, or that you comment on or share.
The following section explains how to enable each index, how the data flow in Microsoft 365 Copilot uses semantic indexing, what file types each index can handle, and how each index deals with updates.
Enablement
Every Microsoft 365 Copilot customer now has a tenant-level index. The indexing process requires no administrative involvement.
Data flows
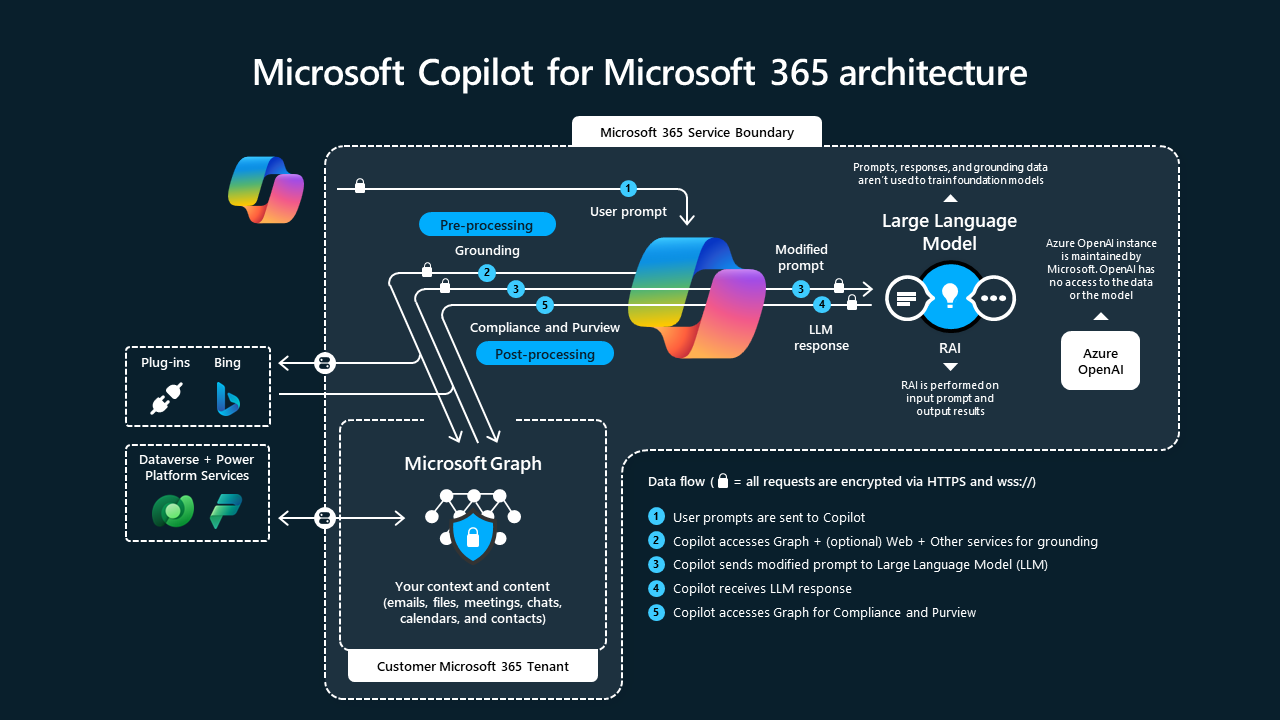
Microsoft 365 Copilot boosts search precision by utilizing advanced lexical and semantic insights from Microsoft Graph data.The following diagram shows how the flow of data works for a request using Microsoft 365 Copilot.
User prompts from Microsoft 365 apps are sent to Copilot (1), and Copilot accesses the Microsoft Graph and semantic index for processing (2). Copilot sends the modified prompt to the Large Language Model (3), receives the LLM response (4), and then accesses the Microsoft Graph and semantic index for post-processing (5). Copilot then sends the response and app command back to Microsoft 365 apps. All requests are encrypted by HTTPS and customer data remains encrypted at rest.
Supported content types
Microsoft Graph grounded responses can utilize semantic understanding of user mailbox and file types listed in the following table, with more file types supported over time. A list of supported file types for the user-level index and tenant-level index is included in the table.
| Content/file type | User level | Tenant level |
|---|---|---|
| User Mailbox | Supported | Not applicable |
| Delegated Mailbox | Not supported | Not applicable |
| Shared Mailbox | Not supported | Not applicable |
| Archived Mailbox Data | Not supported | Not applicable |
| Archived SharePoint Data | Not supported | Not supported |
| Word documents (doc/docx) | Supported | Supported |
| PowerPoint (pptx) | Supported | Supported |
| PDF files | Supported | Supported |
| Web pages (aspx) | Supported | Supported |
| OneNote files (one) | Supported | Supported |
| Copilot connector data | Not applicable | Supported |
Note
Files up to 512 MB are now supported for PDF, PPTX, and DOCX extensions. This enhancement allows Copilot users to effectively analyze, summarize, and generate insights from these large files.
Index updates
When Microsoft Graph data is indexed for a customer for the first time, documents created by users are indexed in near real-time in the user's mailbox. New documents that are added to SharePoint Online sites that are accessible, via site inheritance, by two or more users are indexed daily. When an indexed user and tenant level document is updated, the changes are immediately indexed.
Administration
We provide administrators with optional activities to prepare and manage semantic indexing via the Microsoft 365 admin center. There's no administrative involvement required to enable semantic indexing, as the service is automatically enabled by Microsoft. Semantic indexing is an improvement to Microsoft 365 Search and can't be disabled.
Administrators can choose to prepare and manage semantic indexing by reviewing the considerations for planning and deploying a file collaboration in SharePoint and sharing permissions in the SharePoint modern experience. Administrators can choose to exclude files from semantic indexing by reviewing the considerations for excluding data with Microsoft Purview Data Loss Prevention (DLP). If a DLP solution isn't present, administrators can exclude SharePoint Online sites from the tenant level index.
Excluding SharePoint Online Sites
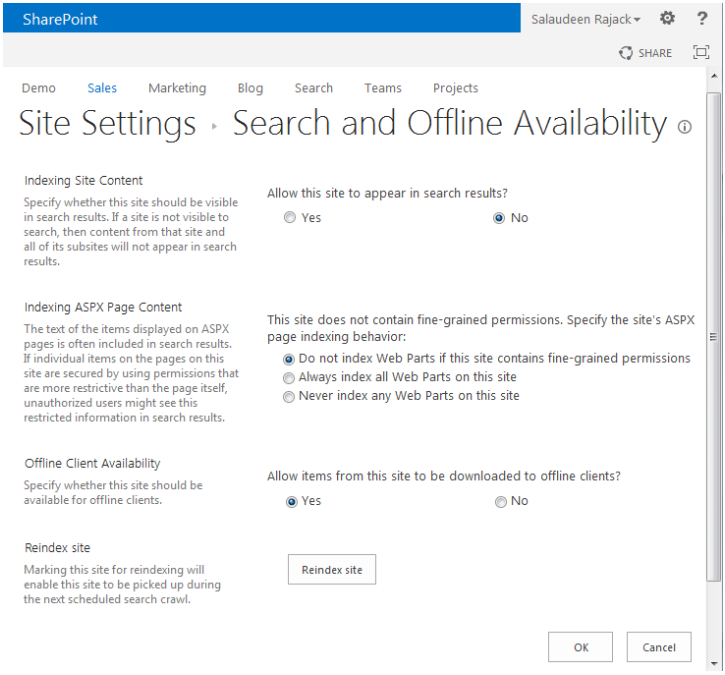
There are times when organizations without Microsoft Purview Data Loss Prevention might want to exclude a SharePoint Online site from having its data indexed by Microsoft Search. These steps should only be considered for sensitive data, such as payroll, HR, or financial information. To exclude a SharePoint Online site, follow these steps:
Browse to the site with appropriate administrator permissions.
Select Settings then Site information from the drop-down menu.
Select View all site settings to bring up the Site Settings page.
Select Search and offline availability under the Search category and select No for Allow this site to appear in search results to exclude it from both Microsoft Search and the semantic index search. This can also be performed with PowerShell for multiple sites.
Microsoft Search and semantic indexing support the exclusion of SharePoint online content from the tenant-level index only. There's no option to exclude results from Microsoft Search only or semantic indexing only; actions apply to both at the same time.
Configuring item insights
On the Search and Intelligence page in the Microsoft 365 admin center, Item insights are enabled by default. Turning off people or item insights reduces the Microsoft Search and semantic index experience, as results won't include relevant people that would have been derived from distribution groups or from the organizational chart.
People insights provide a list of relevant people to a user based on their public collaborative work in Microsoft 365. Public collaboration includes members of a public distribution group and individuals connected in the organizational chart.
Item insights allow recommendations for people in your organization based on their collaborative work in Microsoft 365. These recommendations might include but aren't limited to documents or other types of content and show up in people cards (contacts), Delve, The Microsoft 365 app, Microsoft Copilot results, and other locations.
Both Item insights and People insights don't cover personalization features based on a user's own data.
Incorporating third party information
Using Copilot connectors, organizations can bring organizational data or content from external sources into Microsoft Graph. Once in Microsoft Graph, that content is indexed so that Copilot may access it - while maintaining access controls for content. This expands the types of content sources that are searchable in your Microsoft 365 productivity apps and the broader Microsoft ecosystem. Note that this process works best when the connector content is text rich. The third-party data can be hosted on-premises or in a public or private cloud. Learn more about Copilot connector licensing requirements for Microsoft 365 Enterprise and Microsoft 365 Copilot at License requirements and pricing.
Privacy, compliance, and security
The permissions model within your Microsoft 365 tenant can help ensure that data won't unintentionally leak between users, groups, and tenants. Microsoft 365 Copilot presents only data that each individual can access using the same underlying controls for data access used in other Microsoft 365 services. When data is indexed, we continue to honor the user identity-based access boundary so that the grounding process only accesses content that the current user is authorized to access. For more information, see Microsoft's privacy policy and service documentation.
Microsoft 365 Copilot is compliant with our existing privacy, security, and compliance commitments to Microsoft 365 commercial customers, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and European Union (EU) Data Boundary. Prompts, responses, and data accessed through semantic indexing aren't used to train foundation LLMs, including those used by Microsoft 365 Copilot. For more information, see Data, Privacy, and Security for Microsoft 365 Copilot.
Storage and processing
Data generated by indexing remains within your company’s tenant, and complies with your security, compliance, identity, and privacy policies and processes. Semantic indexing works only with content to which your users already have permission and doesn't affect storage quotas.
User-level index information is stored where the user's mailbox is located. Tenant-level index information, on the other hand, is stored in an isolated and protected customer’s tenant container. This container is located in the region where the SharePoint site is located, which can be the Home region or another region specified by the tenant admin. For customers within the European Union Data Boundary (EUDB), the index is stored in an EU/EFTA based datacenter. Processing other customers can take place either in a tenant region or in the United States. For multi-geo organizations, all geographical boundaries are respected. In-region data is stored and processed in each region.
Microsoft Purview Customer Key (BYOK) support
Microsoft provides bring your own key (BYOK) support for enterprises that have enabled BYOK in their environment. Microsoft automatically enables semantic indexing for BYOK enabled customers without any administrative involvement.
Information protection
In the context of search, there are no other ways to exclude data from semantic indexing using information protection capabilities. Semantic indexing inherits security and privacy settings from Microsoft Search, and data brought in from third party connectors are provided the same storage and protections as other Microsoft 365 data. For organizations that are investigating additional information protection options, Microsoft 365 provides built-in capabilities in Microsoft 365 apps. Add-on products are also available to help Administrators protect organizational data through data minimization and reducing oversharing. The following sections outline the options available for organizations for reference only.
Data minimization
Data minimization reduces the amount of available data your organization might access. Retaining and deleting content is often needed for compliance and regulatory requirements, but deleting content that no longer has business value also helps you manage risk and liability. Microsoft Purview Data Lifecycle Management, which is licensed separately, can be used to delete content that is no longer needed with retention policies for management at scale, and retention labels for exceptions and granular control.
Reduce oversharing
Organizations have long been able to take action to reduce oversharing in Microsoft 365 using existing controls in the Microsoft 365 admin center and SharePoint Online. It's important to note that indexing data doesn't change access permissions to content and doesn't change the principles of how users should share information with colleagues. For example, sharing content with a link that works with everyone in my organization doesn’t make the information part of the tenant level index. Only users that select a link that they have access to will have the information added to their user index. It's recommended that organizations consider the following when exploring information protection options:
Plan secure file collaboration – Review Plan and deploy a file collaboration to understand more about recommended practices to operate a secure and productive file collaboration environment for your users.
Right size user access to data to reduce the list – reduce oversharing by inheriting exclusion lists for SharePoint Online sites and performing access control checks in real time. Organizations can consider using the Syntex SharePoint Advanced Management add-on to manage and govern these permissions.
Use sensitivity labels - Another way to reduce content oversharing is to use Microsoft Purview Information Protection to apply sensitivity labels, which allow you to classify data based on its sensitivity, and apply protections like encryption and content marketing. Sensitivity labels are also included in search trimming (that is, supported for filtering and application-side rules used for visual marking and access restrictions).
Limit access – Microsoft Purview Data Loss Prevention is available in Microsoft 365 E5 and could be used to retroactively and temporarily limit access to documents that have been reported as overshared. Organizations that you do not have Microsoft 365 E5 licenses can use the 90-day Microsoft Purview solutions trial to explore how additional Purview capabilities can help manage your data security and compliance needs.
For customers interested in exploring how to deploy advanced information protection solutions, review the following article that explains how to deploy an information protection solution with Microsoft Purview. For more information about how Microsoft Purview can help you strengthen your data security and compliance requirements for Microsoft 365 Copilot, see Protect and manage Microsoft 365 Copilot interactions with Microsoft Purview.
Additional resources
To learn more about Microsoft 365 Copilot, check out these resources: