Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies To:# OData Web API 8 supported OData Web API v8
OData Web API v8
This tutorial shows how to create and run an ASP.NET Core OData 8 application
You'll learn how to:
✅ Create an ASP.NET Core application
✅ Add Microsoft.AspNetCore.OData library package
✅ Define the CLR types
✅ Add an OData controller
✅ Build the Edm model and configure the service
✅ Run the OData service
✅ Interact with the OData service from an API client
Prerequisites
Visual Studio 2022 with the ASP.NET and web development workload
Create an ASP.NET Core application
Start Visual Studio 2022 and select Create a new project.
In the Create a new project dialog:
Enter
Emptyin the Search for templates search box.Select ASP.NET Core Empty project template and select Next.
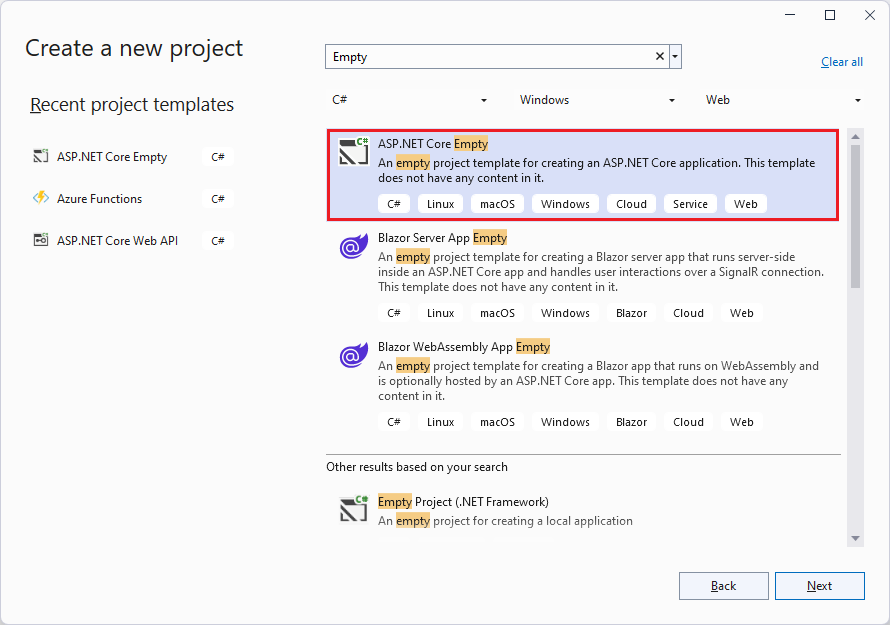
Name the project Lab01 and select Next.
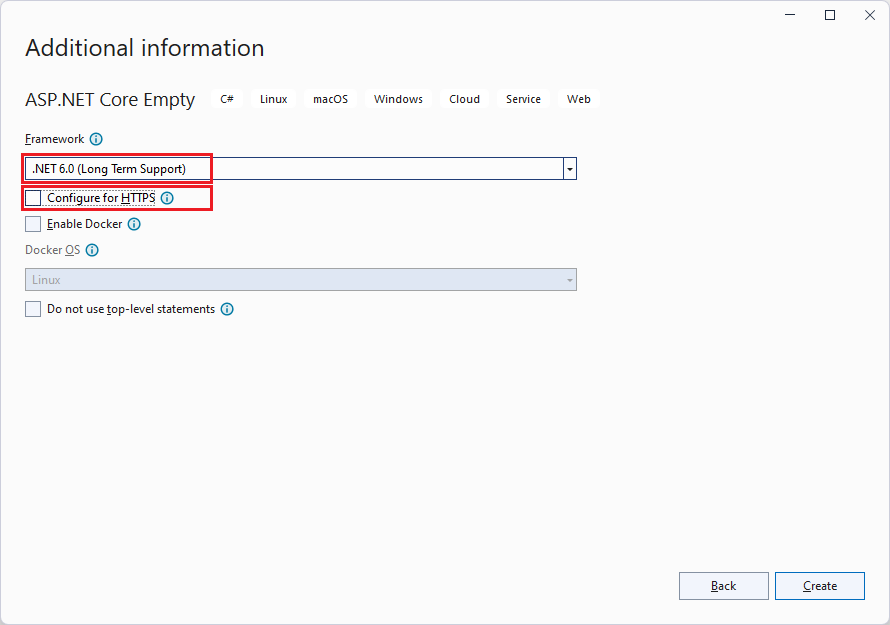
In the Additional information dialog:
- Select .NET 6.0 (Long Term Support).
- Uncheck Configure for HTTPS checkbox.
- Select Create.
Add Microsoft.AspNetCore.OData library package
Install the Microsoft.AspNetCore.OData 8.x Nuget package:
In the Visual Studio Package Manager Console:
Install-Package Microsoft.AspNetCore.OData
Define the CLR types
Add a folder named Models to the project and then add the following C# classes.
Order class
namespace Lab01.Models
{
public class Order
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public decimal Amount { get; set; }
}
}
Customer class
namespace Lab01.Models
{
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class Customer
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public List<Order> Orders { get; set; }
}
}
The Order and Customer classes both contain an Id property that is conventionally treated as the key property of the entity. Note also that the Customer class has a collection property named Orders of type List<Order>.
Add an OData controller
Add a folder named Controllers and then add the following C# class.
namespace Lab01.Controllers
{
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using Lab01.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.OData.Query;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.OData.Routing.Controllers;
public class CustomersController : ODataController
{
private static Random random = new Random();
private static List<Customer> customers = new List<Customer>(
Enumerable.Range(1, 3).Select(idx => new Customer
{
Id = idx,
Name = $"Customer {idx}",
Orders = new List<Order>(
Enumerable.Range(1, 2).Select(dx => new Order
{
Id = (idx - 1) * 2 + dx,
Amount = random.Next(1, 9) * 10
}))
}));
[EnableQuery]
public ActionResult<IEnumerable<Customer>> Get()
{
return Ok(customers);
}
[EnableQuery]
public ActionResult<Customer> Get([FromRoute] int key)
{
var item = customers.SingleOrDefault(d => d.Id.Equals(key));
if (item == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(item);
}
}
}
In the controller, we define a Customer collection (List<Customer>) and initialize it with 3 Customer objects. This will serve as our in-memory data source for the OData service.
We also define two overloads of the Get method. The first overload does not accept any arguments while the second one accepts a single integer argument. In addition, the first overload returns a collection of Customer objects while the second one returns a single Customer object. These two methods will handle HTTP GET requests from the client. Both overloads are decorated with the EnableQuery attribute. This attribute is responsible for applying the query options that are passed in the query string.
Build the Edm model and configure the service
// Program.cs
using Lab01.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.OData;
using Microsoft.OData.ModelBuilder;
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
var modelBuilder = new ODataConventionModelBuilder();
modelBuilder.EntityType<Order>();
modelBuilder.EntitySet<Customer>("Customers");
builder.Services.AddControllers().AddOData(
options => options.Select().Filter().OrderBy().Expand().Count().SetMaxTop(null).AddRouteComponents(
"odata",
modelBuilder.GetEdmModel()));
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => endpoints.MapControllers());
app.Run();
In the preceding code block, we define the Edm model. As part of the model, we register Order as an entity type and Customers as an entity set - Customer entity type also gets registered as a result. In this case, the ODataConventionalModelBuilder is being used to build the Edm model.
We then proceed to add essential OData services by calling the AddOData method, in the process enabling different OData query capabilities - $select, $filter, $orderby, $expand, $count, $top and $skip. The AddRouteComponents method is used to register a route, passing along the Edm model to associate it with.
The final step in configuring the service is adding the two middlewares responsible for matching incoming HTTP requests and dispatching those requests to the application's executable endpoints. We do this by calling UseRouting and UseEndpoints - the former adds route matching to the middleware pipeline while the latter adds endpoint execution.
Run the OData service
Before running the service, select the debugging profile named after the project - Lab01 - to use ASP.NET Core Kestrel web server.
Press F5 to build and run the application.
The following window will be displayed:
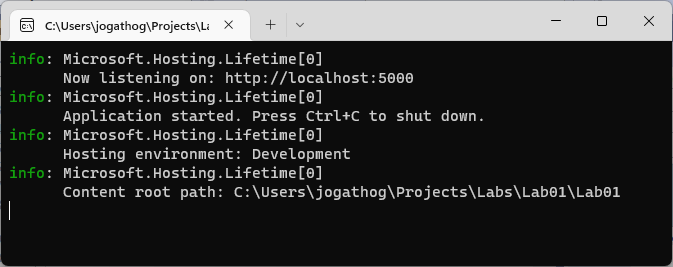
Take note of the endpoint that the application is listening on - http://localhost:5000. The port might differ depending on the version of Visual Studio and other environmental settings.
Interact with the OData service from an API client
You can use any API client of your choice to interact with the OData service.
Below is a list of endpoints exposed by the OData service created in this tutorial:
| Method | Endpoint | Description | Response |
|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /odata |
Retrieve service document | JSON-based respresentation of the service document listing all the top-level feeds / entity sets |
| GET | /odata/$metadata |
Retrieve service metadata | Service metadata document describing the Entity Data Model (EDM) for the service |
| GET | /odata/Customers |
Retrieve all customers | Collection of customers |
| GET | /odata/Customers/$count |
Retrieve number of customers | Number of customers |
| GET | /odata/Customers({key}) |
Retrieve customer by ID | Customer object |
| GET | /odata/Customers/{key} |
Retrieve customer by ID | Customer object |
Query service metadata
To query service metadata, send a GET request to the service metadata endpoint - /odata/$metadata
Request
GET http://localhost:5000/odata/$metadata
Response
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<edmx:Edmx Version="4.0" xmlns:edmx="http://docs.oasis-open.org/odata/ns/edmx">
<edmx:DataServices>
<Schema Namespace="Lab01.Models" xmlns="http://docs.oasis-open.org/odata/ns/edm">
<EntityType Name="Order">
<Key>
<PropertyRef Name="Id" />
</Key>
<Property Name="Id" Type="Edm.Int32" Nullable="false" />
<Property Name="Amount" Type="Edm.Decimal" Nullable="false" Scale="Variable" />
</EntityType>
<EntityType Name="Customer">
<Key>
<PropertyRef Name="Id" />
</Key>
<Property Name="Id" Type="Edm.Int32" Nullable="false" />
<Property Name="Name" Type="Edm.String" />
<NavigationProperty Name="Orders" Type="Collection(Lab01.Models.Order)" />
</EntityType>
</Schema>
<Schema Namespace="Default" xmlns="http://docs.oasis-open.org/odata/ns/edm">
<EntityContainer Name="Container">
<EntitySet Name="Customers" EntityType="Lab01.Models.Customer" />
</EntityContainer>
</Schema>
</edmx:DataServices>
</edmx:Edmx>
Notice the Order and Customer entity types as well as the Customers entity set - nested within the EntityContainer element. Notice also the Property and NavigationProperty elements used to define the structure of the schema types.
Querying service data
The query capabilities offered by OData are immense. Covering all supported capabilities is beyond the scope of this tutorial. Let's take a look at a few:
Example 1: Retrieve all customers
To retrieve all customers, use the following query:
Request
GET http://localhost:5000/odata/Customers
Response
{
"@odata.context": "http://localhost:5000/odata/$metadata#Customers",
"value": [
{
"Id": 1,
"Name": "Customer 1"
},
{
"Id": 2,
"Name": "Customer 2"
},
{
"Id": 3,
"Name": "Customer 3"
}
]
}
NOTE: When you query an entity or entity collection, the default response does not include any related entities or entity collections. The response above does not include the
Orderscollection, even though theCustomerentity has anOrdersnavigation property.
Example 2: Retrieve customer entity by key
Entities are required to define a key property. In the case of the Customer entity, the Id property is conventionally designated as the key property - on account of the naming.
To retrieve a customer with a key value of 2, use the following query:
Request
GET http://localhost:5000/odata/Customers(2)
Response
{
"@odata.context": "http://localhost:5000/odata/$metadata#Customers/$entity",
"Id": 2,
"Name": "Customer 2"
}
Example 3: Retrieve customers with Id equal to 1 or 3
By using the $filter query option, you can specify the expressions to be used to limit the results to be returned.
To retrieve customers with Id equal to 1 or 3, use the following query:
Request
GET http://localhost:5000/odata/Customers?$filter=Id eq 1 or Id eq 3
Response
{
"@odata.context": "http://localhost:5000/odata/$metadata#Customers",
"value": [
{
"Id": 1,
"Name": "Customer 1"
},
{
"Id": 3,
"Name": "Customer 3"
}
]
}
Example 4: Retrieve customers ordered by Id in descending order
By using the $orderby query option, you can specify a custom sort order for the returned results - either ascending order using asc or descending order using desc. The $orderby query option takes a comma-separated list of sort columns together with the corresponding sort order. A missing sort order implies ascending order.
To retrieve all the customers ordered by Id in descending order, use the following query:
Request
GET http://localhost:5000/odata/Customers?$orderby=Id desc
Response
{
"@odata.context": "http://localhost:5000/odata/$metadata#Customers",
"value": [
{
"Id": 3,
"Name": "Customer 3"
},
{
"Id": 2,
"Name": "Customer 2"
},
{
"Id": 1,
"Name": "Customer 1"
}
]
}
Example 5: Retrieve customer with Id equal to 2 and expand their list of orders
By using the $expand query option, you can include related entities or entity collections in the response. The $expand option takes a comma-separated list of navigation properties to expand.
To include all the orders for a particular customer, use the following query:
Request
GET http://localhost:5000/odata/Customers(2)?$expand=Orders
Response
{
"@odata.context": "http://localhost:5000/odata/$metadata#Customers(Orders())/$entity",
"Id": 2,
"Name": "Customer 2",
"Orders": [
{
"Id": 3,
"Amount": 20
},
{
"Id": 4,
"Amount": 20
}
]
}
Example 6: Retrieve customer names only
By using the $select query option, you can specify a subset of properties to be included in the response. The $select query option takes a comma-separated list of properties to be returned.
To retrieve only the name of each customer, use the following query:
Request
GET http://localhost:5000/odata/Customers?$select=Name
Response
{
"@odata.context": "http://localhost:5000/odata/$metadata#Customers(Name)",
"value": [
{
"Name": "Customer 1"
},
{
"Name": "Customer 2"
},
{
"Name": "Customer 3"
}
]
}
Example 7: Combine multiple query options together
To retrieve names of top 2 customers ordered by Id in descending order and expand their list of orders, use the following query:
Request
GET http://localhost:5000/odata/Customers?$orderby=Id desc&$expand=Orders&$top=2&select=Name
Response
{
"@odata.context": "http://localhost:5000/odata/$metadata#Customers(Name,Orders())",
"value": [
{
"Name": "Customer 3",
"Orders": [
{
"Id": 5,
"Amount": 10
},
{
"Id": 6,
"Amount": 80
}
]
},
{
"Name": "Customer 2",
"Orders": [
{
"Id": 3,
"Amount": 20
},
{
"Id": 4,
"Amount": 20
}
]
}
]
}