Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This element specifies a vertical separator line between two sets of controls, either in the Quick Access Toolbar or within group elements.
For example, consider a vertical separator control between two buttons, as follows:
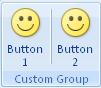
Figure 21: A vertical separator control
This is specified using the following XML fragment:
-
<button id="button1" label="Button 1" imageMso="HappyFace" size="large" /> <separator id="separator" /> <button id="button2" label="Button 2" imageMso="HappyFace" size="large" />
The following table summarizes the elements that are parents of this element.
|
Parent Elements |
|---|
|
documentControls (section 2.2.16); group (section 2.2.23); sharedControls (section 2.2.35) |
The following table summarizes the attributes of this element.
|
Attributes |
Description |
|---|---|
|
getVisible (getVisible callback) |
Specifies the name of a callback function to be called to determine the visibility state of this control. The getVisible and visible attributes are mutually exclusive. If neither attribute is specified, the control SHOULD default to being visible. For example, consider the following XML fragment:
In this example, the IsButtonVisible callback function is called when the application needs to determine the visibility of the button. The possible values for this attribute are defined by the ST_Delegate simple type, as specified in section 2.3.2. |
|
id (control identifier) |
Specifies the identifier for a custom control. All custom controls MUST have unique identifiers. The identifier of a control SHOULD be passed to callback functions to identify which control corresponds to the function call. The id and idQ attributes are mutually exclusive. At least one of these attributes MUST be specified. For example, consider the following XML fragment:
This specifies a custom button control with an identifier of "MyButton". The possible values for this attribute are defined by the ST_UniqueID simple type, as specified in section 2.3.13. |
|
idQ (qualified control identifier) |
Specifies a qualified identifier for a control. The idQ attribute can be used to reference controls or containers created by other Custom UI documents. The id and idQ attributes are mutually exclusive. At least one of these attributes MUST be specified. For example, consider the following XML fragment:
In this case, ex is an XML namespace prefix for the namespace http://www.example.com. This XML fragment refers to a tab in that namespace with an identifier of "OtherTab". If that tab cannot be found, it is created. A new group belonging to this file is added to the tab. The possible values for this attribute are defined by the ST_QID simple type, as specified in section 2.3.9. |
|
insertAfterMso (identifier of built-in control to insert after) |
Specifies the identifier of a built-in control that this control SHOULD be inserted after. If the value of this attribute is not understood, it SHOULD be ignored. The insertAfterMso, insertAfterQ, insertBeforeMso, and insertBeforeQ attributes are mutually exclusive. If none of these attributes are specified, the controls SHOULD be appended to the existing set of controls, in the order they are defined in the XML. For example, consider the following XML fragment:
In this example, a new custom tab with an identifier of "MyTab" is to be inserted after the built-in tab with an identifier of "TabHome". The possible values for this attribute are defined by the ST_ID simple type, as specified in section 2.3.5. |
|
insertAfterQ (qualified identifier of control to insert after) |
Specifies the qualified identifier of a control that this control SHOULD be inserted after. If the value of this attribute is not understood, it SHOULD be ignored. The insertAfterMso, insertAfterQ, insertBeforeMso, and insertBeforeQ attributes are mutually exclusive. If none of these attributes are specified, the controls SHOULD be appended to the existing set of controls, in the order they are defined in the XML. For example, consider the following XML fragment:
In this example, a new custom tab with an identifier of "MyTab" is to be inserted after the custom tab with a qualified identifier of "x:OtherTab". The possible values for this attribute are defined by the ST_QID simple type, as specified in section 2.3.9. |
|
insertBeforeMso (identifier of built-in control to insert before) |
Specifies the identifier of a built-in control that this control SHOULD be inserted before. If the value of this attribute is not understood, it SHOULD be ignored. The insertAfterMso, insertAfterQ, insertBeforeMso, and insertBeforeQ attributes are mutually exclusive. If none of these attributes are specified, the controls SHOULD be appended to the existing set of controls, in the order they are defined in the XML. For example, consider the following XML fragment:
In this example, a new custom tab with an identifier of "MyTab" is to be inserted before the built-in tab with an identifier of "TabHome". The possible values for this attribute are defined by the ST_ID simple type, as specified in section 2.3.5. |
|
insertBeforeQ (qualified identifier of control to insert before) |
Specifies the qualified identifier of a control that this control SHOULD be inserted before. If the value of this attribute is not understood, it SHOULD be ignored. The insertAfterMso, insertAfterQ, insertBeforeMso, and insertBeforeQ attributes are mutually exclusive. If none of these attributes are specified, the controls SHOULD be appended to the existing set of controls, in the order they are defined in the XML. For example, consider the following XML fragment:
In this example, a new custom tab with an identifier of "MyTab" is to be inserted before the custom tab with a qualified identifier of "x:OtherTab". The possible values for this attribute are defined by the ST_QID simple type, as specified in section 2.3.9. |
|
visible (control visibility) |
Specifies the visibility state of the control. The getVisible and visible attributes are mutually exclusive. If these attributes are omitted, the control SHOULD default to being visible. For example, consider the following XML fragment:
In this example, the built-in tab with an identifier of "TabHome" is hidden. The possible values for this attribute are defined by the XML schema boolean datatype. |
The following XML schema fragment defines the contents of this element:
-
<xsd:complexType name="CT_Separator"> <xsd:attributeGroup ref="AG_IDCustom"/> <xsd:attributeGroup ref="AG_Visible"/> <xsd:attributeGroup ref="AG_PositionAttributes"/> </xsd:complexType>