Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
An ACCESS_MASK is a 32-bit set of flags that are used to encode the user rights to an object. An access mask is used both to encode the rights to an object assigned to a principal and to encode the requested access when opening an object.
The bits with an X value in the table below are used for object-specific user rights. A file object would encode, for example, Read Access and Write Access. A registry key object would encode Create Subkey and Read Value, for example.
Note The bits with a value of X are reserved for use by specific protocols that make use of the ACCESS_MASK data type. The nature of this usage differs according to each protocol and is implementation-specific.
The bits in positions 0 through 3 in the following table are generic rights that can be mapped to object-specific user rights by the resource manager for the requested object. The mapping of these rights is implementation-specific.
The bits with an R value in the table below are reserved.
The bits in positions 6 and 7 are for maximum allowed and access system security rights.
The bits in positions 11 through 15 are standard rights that are common to all objects.
If the GR/GW/GX/GA bits are set in an ACE structure that is already attached to an object, requesting access might produce unintended results. This is because the Access Check algorithm does not map generic rights to object-specific rights for ACE structures. This mapping is only made for the requested ACCESS_MASK passed as a parameter to the Access Check algorithm, as specified in section 2.5.3.2.
-
typedef DWORD ACCESS_MASK; typedef ACCESS_MASK* PACCESS_MASK;
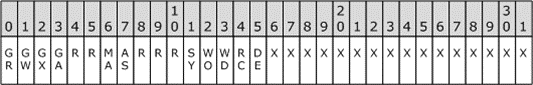
Figure 2: Access mask bitmap table
Where the bits are defined as shown in the following table.
|
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
GR GENERIC_READ 0x80000000L |
When used in an Access Request operation: When read access to an object is requested, this bit is translated to a combination of bits. These are most often set in the lower 16 bits of the ACCESS_MASK. (Individual protocol specifications MAY specify a different configuration.) The bits that are set are implementation dependent. During this translation, the GR bit is cleared. The resulting ACCESS_MASK bits are the actual permissions that are checked against the ACE structures in the security descriptor that attached to the object. When used to set the Security Descriptor on an object: When the GR bit is set in an ACE that is to be attached to an object, it is translated into a combination of bits, which are usually set in the lower 16 bits of the ACCESS_MASK. (Individual protocol specifications MAY specify a different configuration.) The bits that are set are implementation dependent. During this translation, the GR bit is cleared. The resulting ACCESS_MASK bits are the actual permissions that are granted by this ACE.
|
|
GW GENERIC_WRITE 0x4000000L |
When used in an Access Request operation: When write access to an object is requested, this bit is translated to a combination of bits, which are usually set in the lower 16 bits of the ACCESS_MASK. (Individual protocol specifications MAY specify a different configuration.) The bits that are set are implementation dependent. During this translation, the GW bit is cleared. The resulting ACCESS_MASK bits are the actual permissions that are checked against the ACE structures in the security descriptor that attached to the object. When used to set the Security Descriptor on an object: When the GW bit is set in an ACE that is to be attached to an object, it is translated into a combination of bits, which are usually set in the lower 16 bits of the ACCESS_MASK. (Individual protocol specifications MAY specify a different configuration.) The bits that are set are implementation dependent. During this translation, the GW bit is cleared. The resulting ACCESS_MASK bits are the actual permissions that are granted by this ACE.
|
|
GX GENERIC_EXECUTE 0x20000000L |
When used in an Access Request operation: When execute access to an object is requested, this bit is translated to a combination of bits, which are usually set in the lower 16 bits of the ACCESS_MASK. (Individual protocol specifications MAY specify a different configuration.) The bits that are set are implementation dependent. During this translation, the GX bit is cleared. The resulting ACCESS_MASK bits are the actual permissions that are checked against the ACE structures in the security descriptor that attached to the object. When used to set the Security Descriptor on an object: When the GX bit is set in an ACE that is to be attached to an object, it is translated into a combination of bits, which are usually set in the lower 16 bits of the ACCESS_MASK. (Individual protocol specifications MAY specify a different configuration.) The bits that are set are implementation dependent. During this translation, the GX bit is cleared. The resulting ACCESS_MASK bits are the actual permissions that are granted by this ACE.
|
|
GA GENERIC_ALL 0x10000000L |
When used in an Access Request operation: When all access permissions to an object are requested, this bit is translated to a combination of bits, which are usually set in the lower 16 bits of the ACCESS_MASK. (Individual protocol specifications MAY specify a different configuration.) Objects are free to include bits from the upper 16 bits in that translation as required by the objects semantics. The bits that are set are implementation dependent. During this translation, the GA bit is cleared. The resulting ACCESS_MASK bits are the actual permissions that are checked against the ACE structures in the security descriptor that attached to the object. When used to set the Security Descriptor on an object: When the GA bit is set in an ACE that is to be attached to an object, it is translated into a combination of bits, which are usually set in the lower 16 bits of the ACCESS_MASK. (Individual protocol specifications MAY specify a different configuration.) Objects are free to include bits from the upper 16 bits in that translation, if required by the objects semantics. The bits that are set are implementation dependent. During this translation, the GA bit is cleared. The resulting ACCESS_MASK bits are the actual permissions that are granted by this ACE.
|
|
MA MAXIMUM_ALLOWED 0x02000000L |
When used in an Access Request operation: When requested, this bit grants the requestor the maximum permissions allowed to the object through the Access Check Algorithm. This bit can only be requested; it cannot be set in an ACE. When used to set the Security Descriptor on an object: Specifying the Maximum Allowed bit in the SECURITY_DESCRIPTOR has no meaning. The MA bit SHOULD NOT be set and SHOULD be ignored when part of a SECURITY_DESCRIPTOR structure.
|
|
AS ACCESS_SYSTEM_SECURITY 0x01000000L |
When used in an Access Request operation: When requested, this bit grants the requestor the right to change the SACL of an object. This bit MUST NOT be set in an ACE that is part of a DACL. When set in an ACE that is part of a SACL, this bit controls auditing of accesses to the SACL itself.
|
|
SY SYNCHRONIZE 0x00100000L |
Specifies access to the object sufficient to synchronize or wait on the object. |
|
WO WRITE_OWNER 0x00080000L |
Specifies access to change the owner of the object as listed in the security descriptor. |
|
WD WRITE_DACL 0x00040000L |
Specifies access to change the discretionary access control list of the security descriptor of an object. |
|
RC READ_CONTROL 0x00020000L |
Specifies access to read the security descriptor of an object. |
|
DE DELETE 0x00010000L |
Specifies access to delete an object. |