1.4 Relationship to Other Protocols
The Message Queuing (MSMQ): Directory Service Protocol depends on RPC for its transport and uses RPC, as specified in section 2.1.
The following diagram illustrates protocol layering.
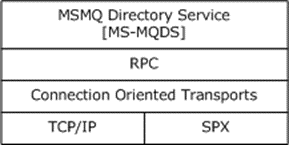
Figure 1: Protocol layering
This protocol is deprecated. Implementers are strongly urged to use the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) [MS-ADTS] in conjunction with the algorithm specified in [MS-MQDSSM] instead of this protocol, except where compatibility requirements necessitate use of this protocol.<1>
This protocol relies on the Private Communication Technology (PCT) Protocol, as specified in [PCT1], for authentication and message security. This protocol uses PCT as the security mechanism underlying the GSS API, as specified in [RFC2743], and cannot be configured to use other security mechanisms, such as SSL or TLS.
The MSMQ: Directory Service Protocol uses shared state and processing rules defined in [MS-MQDMPR] and shared data structures defined in [MS-MQMQ]. The abstract local events described in section 3.2.6 are raised by the processing rules within the common processing rules defined in [MS-MQDMPR]. These events act as a simple translation layer to the RPC methods defined for this protocol, describing the conversion of arguments from abstract to concrete and the conversion of return values from concrete to abstract. The server side of the MSMQ: Directory Service Protocol processes those RPC methods either by maintaining a private abstract data model that leverages the data model types defined in [MS-MQDMPR] or by accessing an LDAP-based directory service using the [MS-MQDSSM] algorithm.