Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
PEAP is an EAP method that encapsulates another instance of EAP (with slightly modified messages) within a TLS tunnel. During phase 1 of PEAP, the PEAP client and PEAP server exchange TLS messages encapsulated within EAP packets to establish a TLS tunnel on top of EAP between the PEAP peer and the PEAP server.
The following diagram shows protocol layering during phase 1 of PEAP:

Figure 2: Protocol layering during phase 1 of PEAP
During phase 2 of PEAP, a new EAP method is negotiated and an EAP authentication exchange is performed between the PEAP peer and the PEAP server as described in [RFC3748] section 2, encapsulated in the TLS tunnel established in phase 1.
The following diagram shows protocol layering during phase 2 of PEAP:
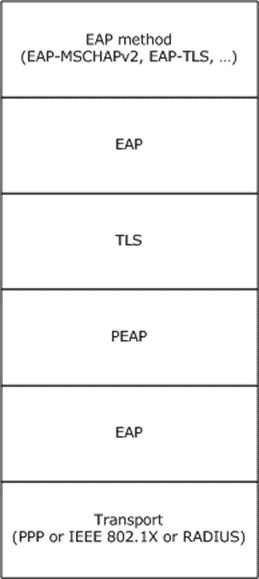
Figure 3: Protocol layering during phase 2 of PEAP
PEAP, like EAP, can run over any EAP transport that is compliant with [RFC3748], such as PPP (for more information, see [RFC1661]).
There are a number of configurable settings for the protocol; for example, isFastReconnectAllowed, isSoHEnable, and so on, as specified in section 3.1.1. The EAP peer which initializes this protocol is responsible for configuring these settings as well. The peer itself might be configured through the group policy. For example, the Group Policy: Wireless/Wired Protocol Extension [MS-GPWL] specifies the group policy protocol to configure and deploy wireless local area network (WLAN). This configuration also carries the EAP method configuration as a part of it. The peer can use this configuration to initialize the PEAP method.