Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
You can reduce the complexity involved with data integration scenarios by using the Upsert message. When loading data into Microsoft Dataverse from an external system, for example in a bulk data integration scenario, you may not know if a record already exists in Dataverse. In such cases, you can't know if you should use the Update or a Create message. You must retrieve the record first to determine if it exists before performing the appropriate operation. You can reduce this complexity and load data into Dataverse more efficiently by using the Upsert message.
There's a performance penalty in using Upsert versus using Create. If you're sure the record doesn't exist, use Create.
Note
While you can use primary key values with Upsert, it is generally expected that you will be using alternate keys because the common use case is data integration scenarios. More information: Use an alternate key to reference a record
Elastic table upsert
Elastic table behavior for Upsert is different than standard tables. With elastic tables, the Upsert operation doesn't call the Create or Update message depending on whether the record already exists or not. Upsert directly applies the changes in the entity.
- If the record exists: All the data in the record is overwritten by the data in the entity. There's no
Updateevent. - If the record doesn't exist: A new record is created. There's no
Createevent.
This has implications for where you apply business logic for events. A new record can be created using either Create or Upsert. A record may be updated using either Update or Upsert. If you need to apply logic consistently for Create or Update in elastic tables, you must also include that logic in Upsert. More information: Upsert a record in an elastic table
Understanding the upsert process for standard tables
Upsert messages are processed on the server. The SDK for .NET classes use the same objects used on the server. Therefore, the following explanation uses the SDK for .NET classes to describe how an UpsertRequest instance is processed and the UpsertResponse instance returned.
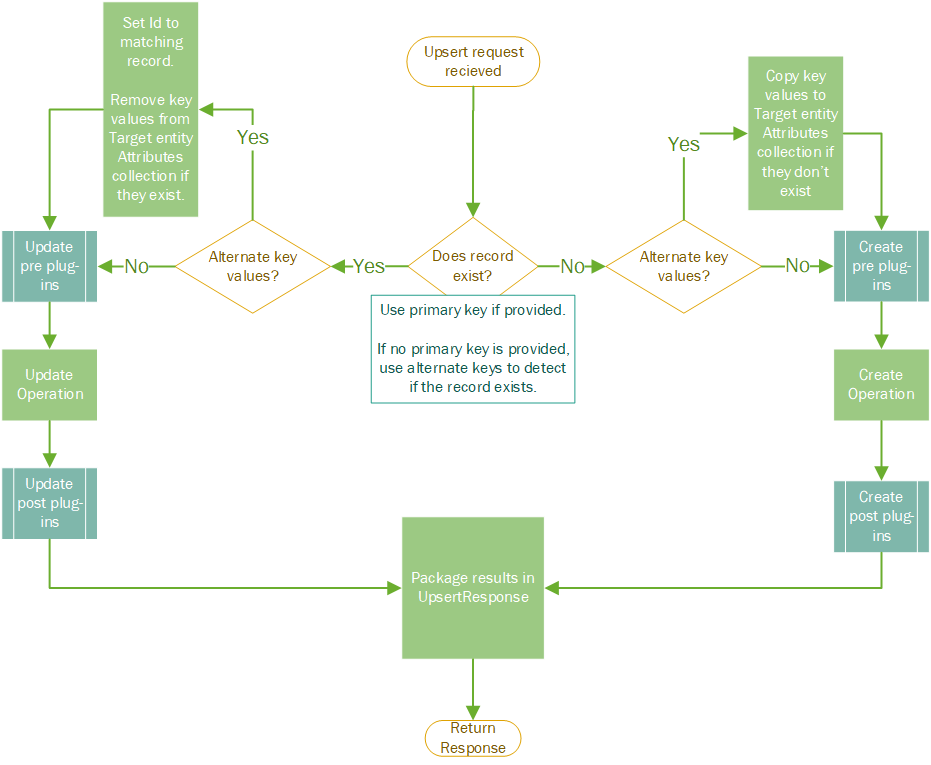
The following steps describe the processing logic on the server when an UpsertRequest is received for a standard table:
- The UpsertRequest instance arrives with the Target Property set with an Entity instance containing the data for a
CreateorUpdateoperation.- The Entity instance will typically have the Entity.KeyAttributes Property set with values used to identify the record using alternate keys.
- If it exists, Dataverse will try to look up the record using the Entity.Id property of the Entity instance set to the Target property. Otherwise it uses the alternate key values from the Entity.KeyAttributes Property.
- If the record exists:
- Set the
TargetEntity.Id with the primary key value of the found record. - Remove any data from the
TargetEntity.Attributes collection that use the same keys used in theTargetEntity.KeyAttributes collection. - Call
Update. - Set the UpsertResponse.RecordCreated property to
false. - Create an EntityReference from the
Targetentity as the value for UpsertResponse.Target. - Return the UpsertResponse.
- Set the
- If the record doesn't exist:
- Copy any data from the
TargetEntity.KeyAttributes that theTargetdoesn't already have in its Entity.Attributes collection into theTargetEntity.Attributes. - Call
Create. - Set the UpsertResponse.RecordCreated to
true. - Create an EntityReference from the
Targetentity and theidresult of theCreateoperation as the value for UpsertResponse.Target. - Return the UpsertResponse.
- Copy any data from the
The following diagram shows the process on the server when an UpsertRequest is received.
Guidance for composing requests
When using alternate keys to identify a record, including the alternate key data in the portion of the request that represents the data to be saved isn't recommended or necessary.
If you're using the Web API and not familiar with the SDK for .NET, the server-side process described above may be difficult to follow. The Web API doesn't have the same object model as the SDK objects used in the description and the diagram above, but the data can be mapped as shown in the table below.
| Web API | SDK | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Key values in URL | Entity.KeyAttributes Property | Contains the alternate key data to identify the record. |
| Body of request | The Entity set to the UpsertRequest.Target Property | Contains the data to use for Create or Update. |
Although these requests are processed on the server as described above, you can think of it this way:
- If the record exists: The data set in the body of the request for those alternate key values in the Url are removed, so there's no point in including it. This practice ensures that you can't update the alternate key values of a record when you're using those alternate key values to identify it. You can change alternate key values using the primary key or a different set of alternate keys.
- If the record doesn't exist: Any alternate key values set in the body of the request are used to create the new record, even if the data is different than the values specified by the alternate keys in the Url. If there's no alternate key data in the body of the request, the alternate key data from the URL are copied into the body of the request. To avoid a situation where the key values in the Url and the corresponding key values in the body don't match, it's best to not include them in the body at all.
Using Web API
With the Web API, the Upsert and Update messages are both initiated using http PATCH against a specified EntitySet resource identified by the keys in the Url.
The difference between Upsert and Update is defined by whether the If-Match: * request header is included. If the If-Match: * request header is included and no resource matches the key values in the Url, the request returns a 404 Not Found status code. The If-Match: * request header ensures that the PATCH request is an Update operation.
If the If-Match: * request header isn't included, the PATCH request is treated like an Upsert and a new record is created if no records matching the keys in the URL are found. However, unlike the SDK, the response doesn't tell you whether a record was created. The status response is 204 No Content in either case.
If you include a Prefer: return=representation request header the system returns a 201 Created status for Create, and a 200 OK status for Update. Adding this header adds an extra Retrieve operation so it has an impact on performance. If you use this option, make sure that the $select query option you add only includes the primary key value. More information:
With a PATCH request, you can also include the If-None-Match: * request header to block an Update if you only want to create records. More information: Limit upsert operations
Web API Sample code
The following examples show Upsert operations using a table with two alternate key columns:
Create with Upsert
This request creates a record.
Request:
PATCH [Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.2/example_records(example_key1=2,example_key2=2) HTTP/1.1
OData-MaxVersion: 4.0
OData-Version: 4.0
If-None-Match: null
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json
{ "example_name": "2:2" }
Response:
HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
OData-Version: 4.0
OData-EntityId: [Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.2/example_records(example_key1=2,example_key2=2)
Update with Upsert
This request updates the record created by the request above.
Request:
PATCH [Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.2/example_records(example_key1=2,example_key2=2) HTTP/1.1
OData-MaxVersion: 4.0
OData-Version: 4.0
If-None-Match: null
Accept: application/json
Content-Type: application/json
{ "example_name": "2:2 Updated" }
Response:
HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
OData-Version: 4.0
OData-EntityId: [Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.2/example_records(example_key1=2,example_key2=2)
Note
The response is identical for Create or Update operations.
Create with Upsert and return=representation preference
When you use the Prefer: return=representation header, you can get a different status code in the response to indicate whether the record was created or updated.
The following request creates a new record and returns status 201 Created.
Request:
PATCH [Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.2/example_records(example_key1=3,example_key2=3)?$select=example_recordid HTTP/1.1
OData-MaxVersion: 4.0
OData-Version: 4.0
If-None-Match: null
Accept: application/json
Prefer: return=representation
Content-Type: application/json
{ "example_name": "3:3" }
Response:
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Content-Type: application/json; odata.metadata=minimal
ETag: W/"71004878"
Preference-Applied: return=representation
OData-Version: 4.0
{
"@odata.context": "[Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.2/$metadata#example_records(example_recordid)/$entity",
"@odata.etag": "W/\"71004878\"",
"example_recordid": "ef0d112e-d70e-ed11-82e5-00224822577b"
}
Update with Upsert and return=representation preference
This request updates the record created by the request above and returns status 200 OK to show that this was an update operation.
Request:
PATCH [Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.2/example_records(example_key1=3,example_key2=3)?$select=example_recordid HTTP/1.1
OData-MaxVersion: 4.0
OData-Version: 4.0
If-None-Match: null
Accept: application/json
Prefer: return=representation
Content-Type: application/json
{ "example_name": "3:3 Updated" }
Response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json; odata.metadata=minimal
ETag: W/"71004880"
OData-Version: 4.0
{
"@odata.context": "[Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.2/$metadata#example_records(example_recordid)/$entity",
"@odata.etag": "W/\"71004880\"",
"example_recordid": "ef0d112e-d70e-ed11-82e5-00224822577b"
}
Using the SDK for .NET
Your client application uses the IOrganizationService.Execute Method with an UpsertRequest instance that has the Target Property set with an Entity instance containing the data for a Create or Update operation. The Entity instance will typically have the Entity.KeyAttributes Property set with values used to identify the record using alternate keys.
The UpsertResponse.RecordCreated Property tells you whether the record was created, and the UpsertResponse.Target contains a reference to the record that was created or updated.
SDK for .NET Sample code
The SampleMethod.cs file in the Insert record using Upsert sample contains the following ProcessUpsert method to apply the UpsertRequest message on the contents of an XML file to create new records or update existing ones.
public static void ProcessUpsert(CrmServiceClient service, String Filename)
{
Console.WriteLine("Executing upsert operation.....");
XmlTextReader tr = new XmlTextReader(Filename);
XmlDocument xdoc = new XmlDocument();
xdoc.Load(tr);
XmlNodeList xnlNodes = xdoc.DocumentElement.SelectNodes("/products/product");
foreach (XmlNode xndNode in xnlNodes)
{
String productCode = xndNode.SelectSingleNode("Code").InnerText;
String productName = xndNode.SelectSingleNode("Name").InnerText;
String productCategory = xndNode.SelectSingleNode("Category").InnerText;
String productMake = xndNode.SelectSingleNode("Make").InnerText;
//use alternate key for product
Entity productToCreate = new Entity("sample_product", "sample_productcode", productCode);
productToCreate["sample_name"] = productName;
productToCreate["sample_category"] = productCategory;
productToCreate["sample_make"] = productMake;
var request = new UpsertRequest()
{
Target = productToCreate
};
try
{
// Execute UpsertRequest and obtain UpsertResponse.
var response = (UpsertResponse)service.Execute(request);
if (response.RecordCreated)
Console.WriteLine("New record {0} is created!", productName);
else
Console.WriteLine("Existing record {0} is updated!", productName);
}
// Catch any service fault exceptions that Dataverse throws.
catch (FaultException<Microsoft.Xrm.Sdk.OrganizationServiceFault>)
{
throw;
}
}
}
See also
Use change tracking to synchronize data with external systems
Define alternate keys for a table
Use an alternate key to reference a record