Use environment variables for Azure Key Vault secrets
Environment variables allow for referencing secrets stored in Azure Key Vault. These secrets are then made available for use within Power Automate flows and custom connectors. Notice that the secrets aren't available for use in other customizations or generally via the API.
The actual secrets are stored in Azure Key Vault and the environment variable references the key vault secret location. Using Azure Key Vault secrets with environment variables require that you configure Azure Key Vault so that Power Platform can read the specific secrets you want to reference.
Environment variables referencing secrets aren't currently available from the dynamic content selector for use in flows.
Configure Azure Key Vault
To use Azure Key Vault secrets with Power Platform, the Azure subscription that has the vault must have the PowerPlatform resource provider registered and the user who creates the environment variable must have appropriate permissions to the Azure Key Vault resource.
Note
- We have recently changed the security role that we use to assert access permissions within Azure Key Vault. Previous instructions included assigning the Key Vault Reader role. If you have set up your key vault previously with the Key Vault Reader role, make sure that you add the Key Vault Secrets User role to ensure that your users and Dataverse will have sufficient permissions to retrieve the secrets.
- We recognize that our service is using the Azure role-based access control APIs to assess security role assignment even if you still have your key vault configured to use the vault access policy permission model. To simplify your configuration, we recommended that you switch your vault permission model to Azure role-based access control. You can do this in the Access configuration tab.
Register the
Microsoft.PowerPlatformresource provider in your Azure subscription. Follow these steps to verify and configure: Resource providers and resource types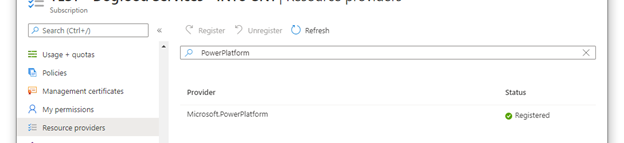
Create an Azure Key Vault vault. Consider using a separate vault for every Power Platform environment to minimize the threat in case of a breach. Consider configuring your key vault to use Azure role-based access control for the Permission model. More information: Best practices for using Azure Key Vault, Quickstart - Create an Azure Key Vault with the Azure portal
Users who create or use environment variables of type secret must have permission to retrieve the secret contents. To grant a new user the ability to use the secret, select the Access control (IAM) area, select Add, and then select Add role assignment from the dropdown. More information: Provide access to Key Vault keys, certificates, and secrets with an Azure role-based access control
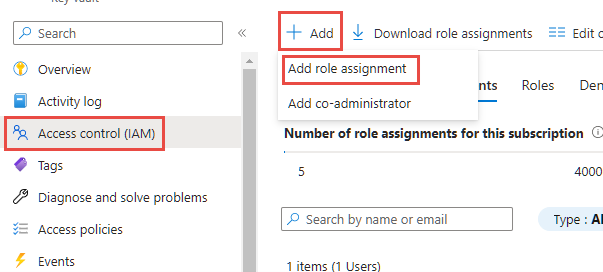
On the Add role assignment wizard, leave the default assignment type as Job function roles and continue to the Role tab. Locate the Key Vault Secrets User role and select it. Continue to the members tab and select the Select members link and locate the user in the side panel. When you have the user selected and shown on the members section, continue to the review and assign tab and complete the wizard.
Azure Key Vault must have the Key Vault Secrets User role granted to the Dataverse service principal. If it doesn't exist for this vault, add a new access policy using the same method you previously used for the end user permission, only using the Dataverse application identity instead of the user. If you have multiple Dataverse service principals in your tenant, then we recommend that you select them all and save the role assignment. Once the role is assigned, review each Dataverse item listed in the role assignments list and select the Dataverse name to view the details. If the Application ID isn't 00000007-0000-0000-c000-000000000000**, then select the identity, and then select Remove to remove it from the list.
If you have enabled Azure Key Vault Firewall, you have to allow Power Platform IP addresses access to your key vault. Power Platform isn't included in the "Trusted Services Only" option. Hence, refer to Power Platform URLs and IP address ranges article for the current IP addresses used in the service.
If you haven't done so already, add a secret to your new vault. More information: Azure Quickstart - Set and retrieve a secret from Key Vault using Azure portal
Create a new environment variable for the Key Vault secret
Once Azure Key Vault is configured and you have a secret registered in your vault, you can now reference it within Power Apps using an environment variable.
Note
- User access validation for the secret is performed in the background. If the user doesn’t have at least read permission, this validation error is displayed: "This variable didn't save properly. User is not authorized to read secrets from 'Azure Key Vault path'."
- Currently, Azure Key Vault is the only secret store that is supported with environment variables.
- The Azure Key Vault must be in the same tenant as your Power Platform subscription.
Sign on to Power Apps, and in the Solutions area, open the unmanaged solution you're using for development.
Select New > More > Environment variable.
Enter a Display name and optionally, a Description for the environment variable.
Select the Data Type as Secret and Secret Store as Azure Key Vault.
Choose from the following options:
- Select New Azure Key Vault value reference. After the information is added in the next step and saved, an environment variable value record is created.
- Expand Show default value, to display the fields to create a Default Azure Key Vault secret. After the information is added in the next step and saved, the default value demarcation is added to the environment variable definition record.
Enter the following information:
Azure Subscription ID: The Azure subscription ID associated with the key vault.
Resource Group Name: The Azure resource group where the key vault that contains the secret is located.
Azure Key Vault Name: The name of the key vault that contains the secret.
Secret Name: The name of the secret located in Azure Key Vault.
Tip
The subscription ID, resource group name, and key vault name can be found on the Azure portal Overview page of the key vault. The secret name can be found on the key vault page in the Azure portal by selecting Secrets under Settings.
Select Save.
Create a Power Automate flow to test the environment variable secret
A simple scenario to demonstrate how to use a secret obtained from Azure Key Vault is to create a Power Automate flow to use the secret to authenticate against a web service.
Note
The URI for the web service in this example is not a functioning web service.
Sign into Power Apps, select Solutions, and then open the unmanaged solution you want. If the item isn’t in the side panel pane, select …More and then select the item you want.
Select New > Automation > Cloud flow > Instant.
Enter a name for the flow, select Manually trigger a flow, and then select Create.
Select New step, select the Microsoft Dataverse connector, and then on the Actions tab select Perform an unbound action.
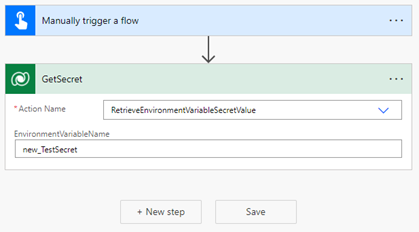
Select the action named RetrieveEnvironmentVariableSecretValue from the dropdown list.
Provide the environment variable unique name (not the display name) added in the previous section, for this example new_TestSecret is used.
Select ... > Rename to rename the action so that it can be more easily referenced in the next action. In this screenshot, it's renamed to GetSecret.
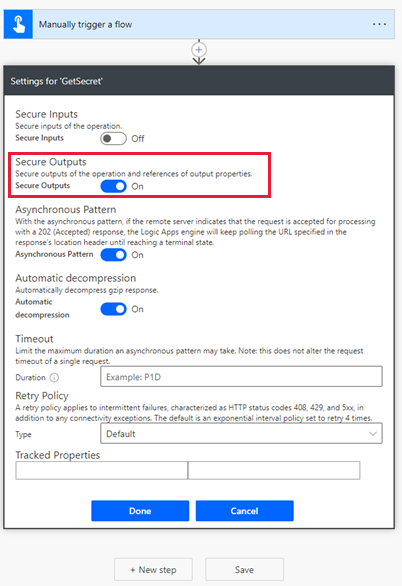
Select ... > Settings to display the GetSecret action settings.
Enable the Secure Outputs option in the settings, and then select Done. This is to prevent the output of the action getting exposed in the flow run history.
Select New step, search, and select the HTTP connector.
Select the Method as GET and enter the URI for the web service. In this example, the fictitious web service httpbin.org is used.
Select Show advanced options, select the Authentication as Basic, and then enter the Username.
Select the Password field, and then on the Dynamic content tab under the flow step name above (GetSecret in this example) select RetrieveEnvironmentVariableSecretValueResponse EnvironmentVariableSecretValue, which is then added as an expression
outputs('GetSecretTest')?['body/EnvironmentVariableSecretValue']orbody('GetSecretTest')['EnvironmentVariableSecretValue'].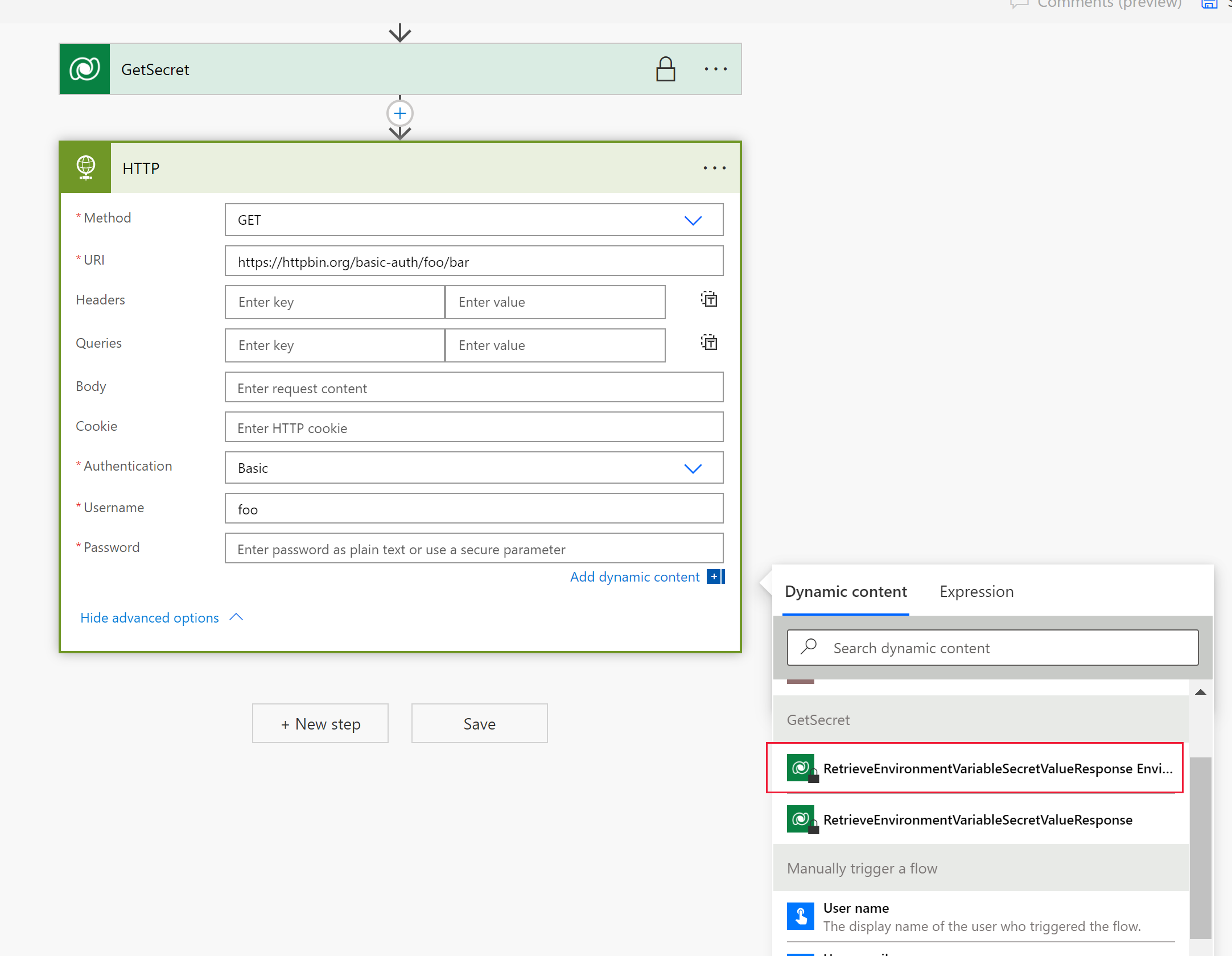
Select ... > Settings to display the HTTP action settings.
Enable the Secure Inputs and Secure Outputs options in the settings, and then select Done. Enabling these options prevents the input and outputs of the action getting exposed in the flow run history.
Select Save to create the flow.
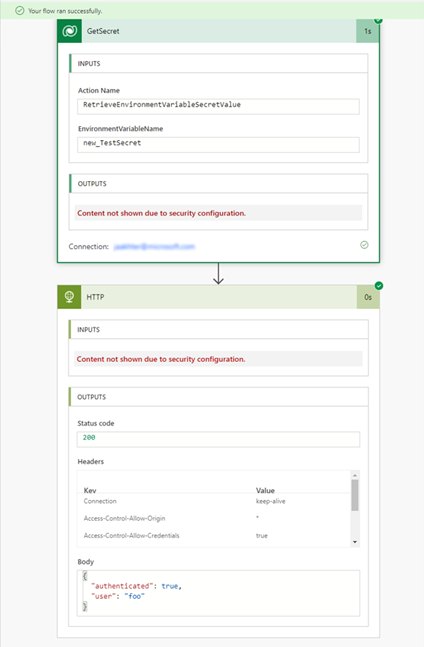
Manually run the flow to test it.
Using the run history of the flow, the outputs can be verified.
Use environment variable secrets in Microsoft Copilot Studio
Environment variable secrets in Microsoft Copilot Studio work a bit differently. You need to run through the steps in the sections in Configure Azure Key Vault and Create a new environment variable for the Key Vault secret to use secrets with environment variables.
Give Copilot Studio access to Azure Key Vault
Follow these steps:
Go back to your Azure Key Vault.
Copilot Studio needs access to the key vault. To grant Copilot Studio the ability to use the secret, select Access control (IAM) on the left navigation, select Add, and then select Add role assignment.

Select the Key Vault Secrets User role, and then select Next.
Select Select Members, search for Power Virtual Agents Service, select it, and then choose Select.
Select Review + assign on the bottom of the screen. Review the information and select Review + assign again if all is correct.
Add a tag to allow a copilot to access the secret in Azure Key Vault
By completing the previous steps in this section, Copilot Studio now has access to the Azure Key Vault, but you can't use it yet. To complete the task, follow these steps:
Go to Microsoft Copilot Studio and open the copilot you want to use for the environment variable secret or create a new one.
Open a topic or create a new one.
Select the + icon to add a node, and then select Send a message.
Select the Insert variable {x} option in the Send a message node.
Select the Environment tab. Select the environment variable secret you created in the Create a new environment variable for the Key Vault secret step.
Select Save to save your topic.
In the test pane, test your topic by using one of the start phrases of the topic where you just added the Send a message node with the environment variable secret. You should run into an error that looks like this:

This means you need to go back to Azure Key Vault and edit the secret. Leave Copilot Studio open, because you come back here later.
Go to Azure Key Vault. In the left navigation, select Secrets under Objects. Select the secret you want to make available in Copilot Studio by selecting the name.
Select the version of the secret.
Select 0 tags next to Tags. Add a Tag Name and a Tag Value. The error message in Copilot Studio should give you the exact values of those two properties. Under Tag Name you need to add AllowedBots and in Tag Value you need to add the value that was displayed in the error message. This value is formatted as
{envId}/{schemaName}. In the case when there are multiple copilots that need to be allowed, separate the values with a comma. When done, select OK.Select Apply to apply the tag to the secret.
Go back to Copilot Studio. Select Refresh in the Test your copilot pane.
In the test pane, test your topic again by using one of the start phrases of the topic.
The value of your secret should be shown in the test panel.
Add a tag to allow all copilots in an environment access to the secret in Azure Key Vault
Alternatively, you can allow all copilots in an environment access to the secret in Azure Key Vault. To complete the task, follow these steps:
- Go to Azure Key Vault. In the left navigation, select Secrets under Objects. Select the secret you want to make available in Copilot Studio by selecting the name.
- Select the version of the secret.
- Select 0 tags next to Tags. Add a Tag Name and a Tag Value. Under Tag Name add AllowedEnvironments and in Tag Value add the environment ID of the environment you want to allow. When done, select OK
- Select Apply to apply the tag to the secret.
Limitation
Environment variables referencing Azure Key Vault secrets are currently limited for use with Power Automate flows, Copilot Studio copilots, and custom connectors.
See also
Use data source environment variables in canvas apps
Use environment variables in Power Automate solution cloud flows
Environment variables overview.