Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This article provides guidance on creating and using different data types in Microsoft Dataverse formula columns, such as decimal, whole number, floating point, and choice columns. It outlines steps starting with selecting fx Formula as the data type and entering a numeric value-returning formula in the formula bar.
Start by creating a column for a table
Sign in to Power Apps at https://make.powerapps.com.
Select Tables, and then select the table where you want to add a formula column. If the item isn’t in the side panel pane, select …More and then select the item you want.
Select the Columns area, select New column, and then select the data type and enter the Power Fx formula. Depending on the formula you enter, you can create any of the following:
Create a decimal formula column
Create a formula column that returns a decimal number.
- Select Data type as fx Formula.
- Enter a formula that returns a numeric value in the Formula bar.
This example creates a formula column called Total Amount. The Price Per Unit column is of decimal data type.
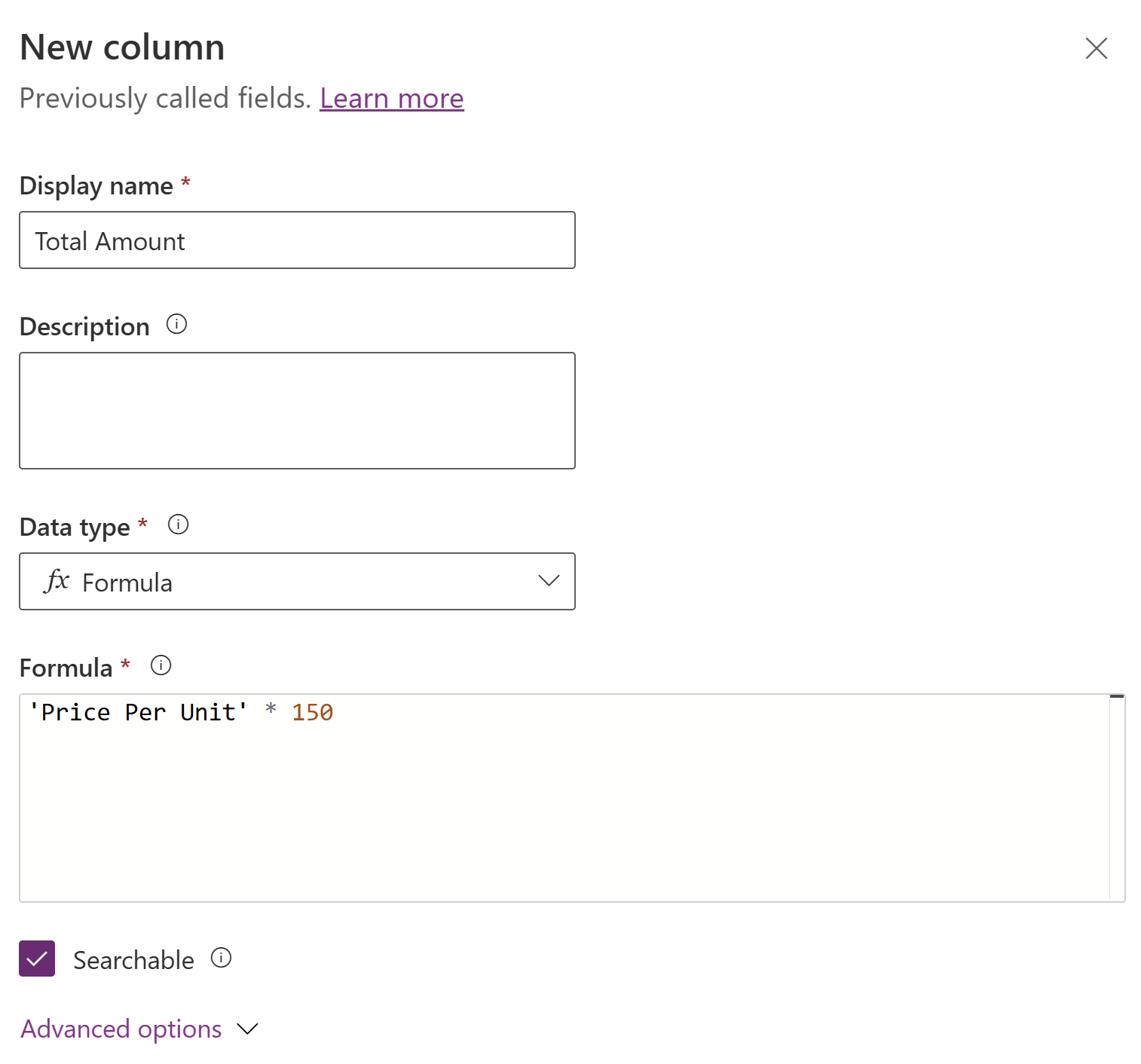
- Expand Advanced options, and then set the required number of decimal places.
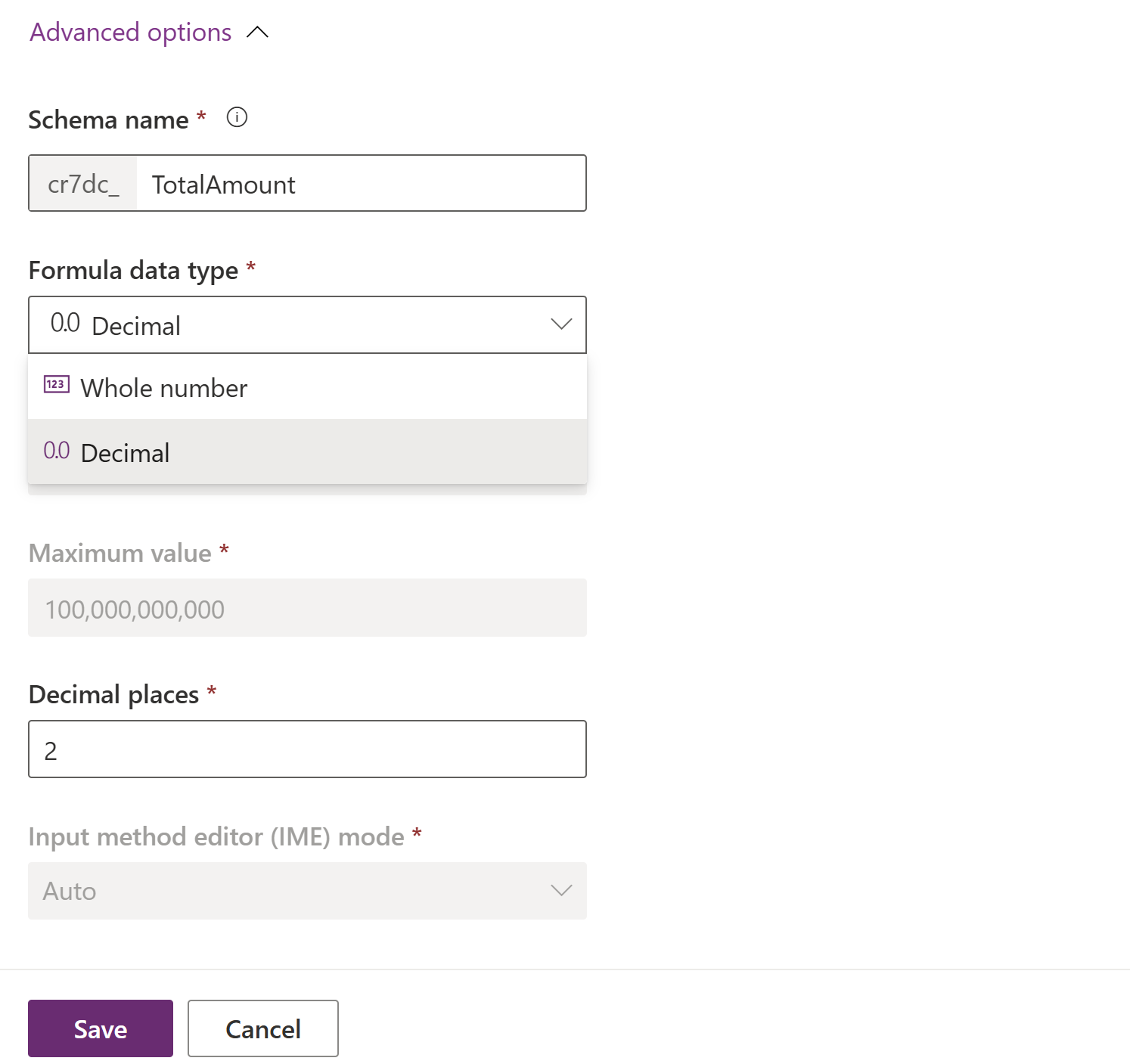
- Select Save. By default, Formula data type is set to Decimal and a decimal formula field is created.
Create a whole number formula column
Create a formula column that returns a whole number.
- Select Data type as fx Formula.
- Enter a formula that returns a numeric value in the Formula bar.
This example creates a formula column called Number of Units. Total Price and Price Per Unit columns are of decimal data type.
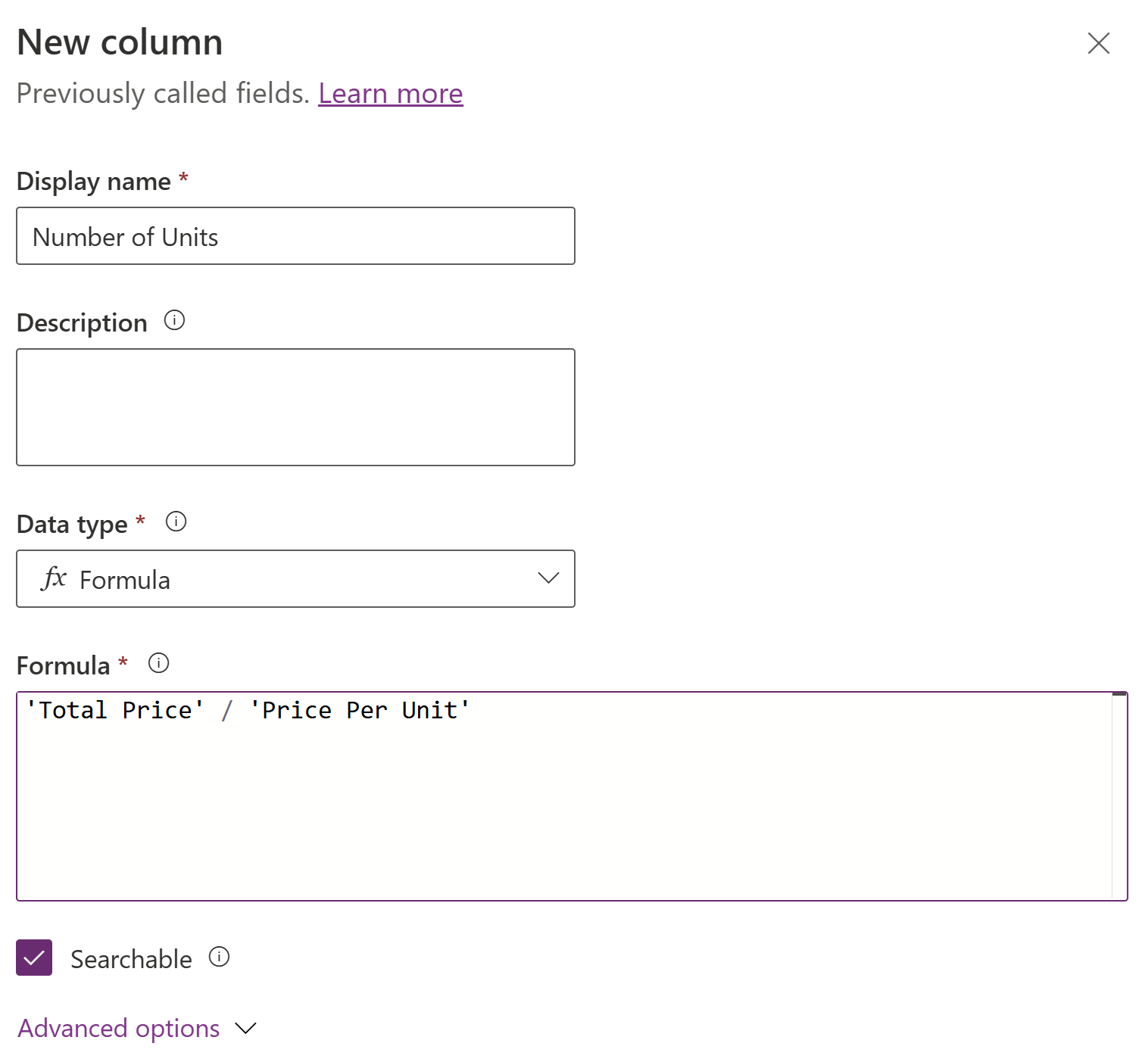
- Expand Advanced options, and select Whole number as the Formula data type and set the required format for whole number column.
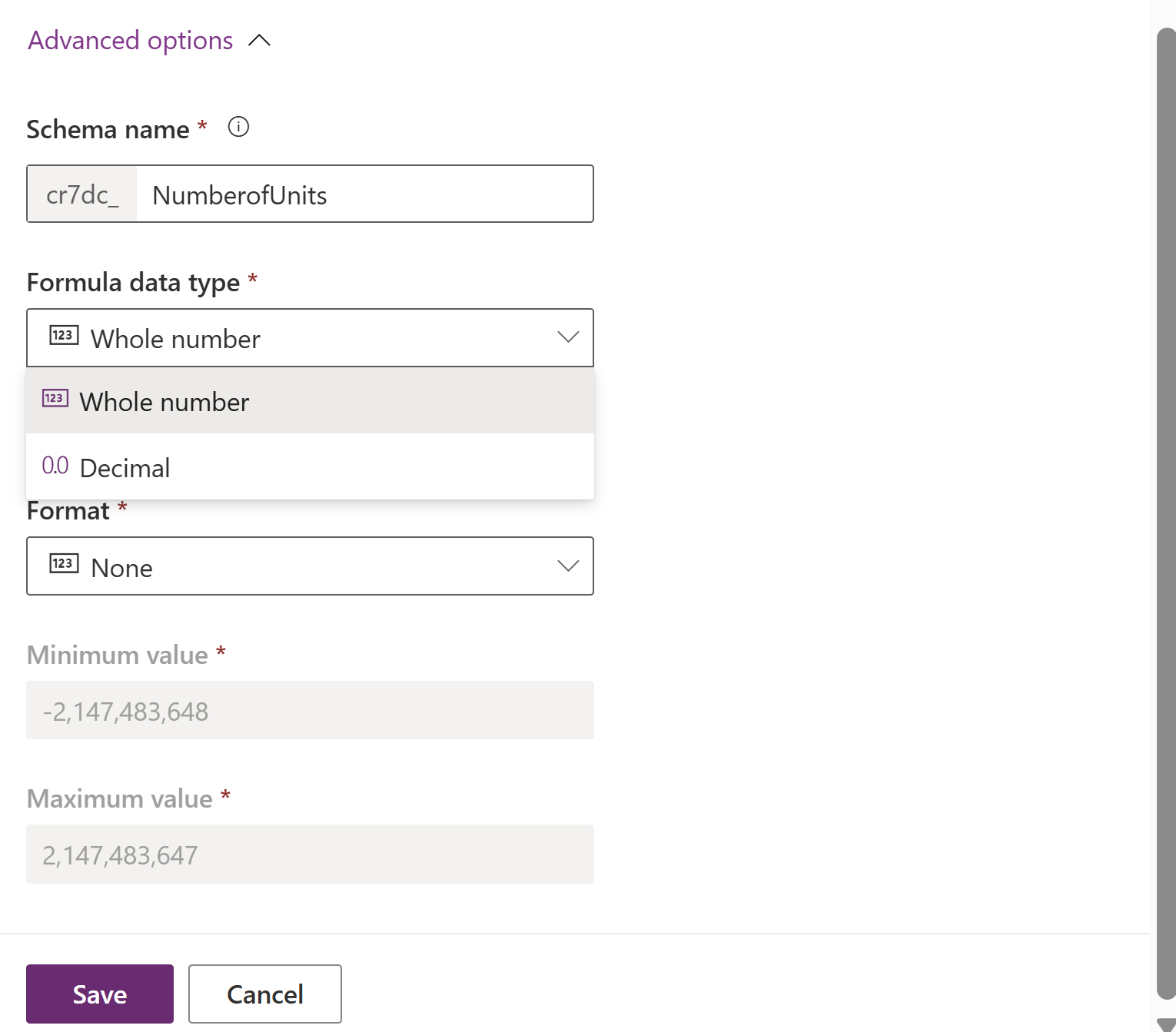
- Select Save.
Create a floating point number formula column
Create a formula column that returns float.
- Select Data type as fx Formula.
- Enter a formula that returns a floating point number in the Formula bar.
Enter a formula that returns a floating point number in the Formula bar. This example creates a formula column called Total Price. Weight is a simple float column and Price Per Gm is a simple decimal column.

- Expand Advanced options, and set the required number of decimal places.
- Select Save.
Guidelines for creating floating point number formula columns
- If an operand involved in an arithmetic operation is of float type, then the result of the formula is of float type. For example:
1 + 2 + Float(1)as it uses a float type operand -Float(1).
- A numeric function returns a float value when the first parameter provided to the function is of float type. Otherwise, the function returns a decimal value. For example:
Sum(1, 2, Float(1))is of decimal type andSum(Float(1), 1, 2)is of float type.
Float,Sqrt,Ln,Power,Expfunctions and the^operator return a float value.
Create a choice formula column
To create a choice formula column, either global choice or local choice of a simple choice column can be used as result.
Using global choice
Create a global choice. This example creates a global choice called Task Priority.

Create a formula column that returns a choice using a global choice.
- Select Data type as fx Formula.
- Enter a formula that returns a choice value in the Formula bar.
This example creates a formula column Priority using global choice Task Priority.

- Select Save. Notice that the column created is of data type Choice fx.
Using local choice from a simple choice column
Create a simple choice column. This example creates a Task Priority simple choice column for the account table.

Create a formula column that returns choice using a local choice of a simple choice column.
- Select Data type as fx Formula.
- Enter a formula that returns a choice value in the Formula bar.
This example creates a formula column Priority on Account entity using local choice of a choice column Task Priority for the account table.

- Select Save.
Guidelines for working with choices in formula columns
Local choices of related table's simple choice column can't be used as a result type in formula columns.
Options from the same option set should be used for all result arguments in choice formula columns.
A choice used by a formula column can't be updated.
Options of a choice can't be passed as an argument to string functions. Value function can be used to return the numeric value of an option.
Formula column's dependent local choice column or global choice can't be deleted.
For using a related table local choices (optionset) column's options in the formula column definition, first use choice and then use options of that local choice.
For example, a choice column named Color on the Contact table.
 The choice column has options Red, Yellow, and Green.
The choice column has options Red, Yellow, and Green.
 For a formula column on the account table using the Color choice column, the formula appears like this:
For a formula column on the account table using the Color choice column, the formula appears like this:Recommended -
If(ParentAccount.Color == 'Color (Accounts)'.Red, 1, 2)Not Recommended -
If( 'Color (Accounts)'.Red == ParentAccount.Color, 1, 2)