Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
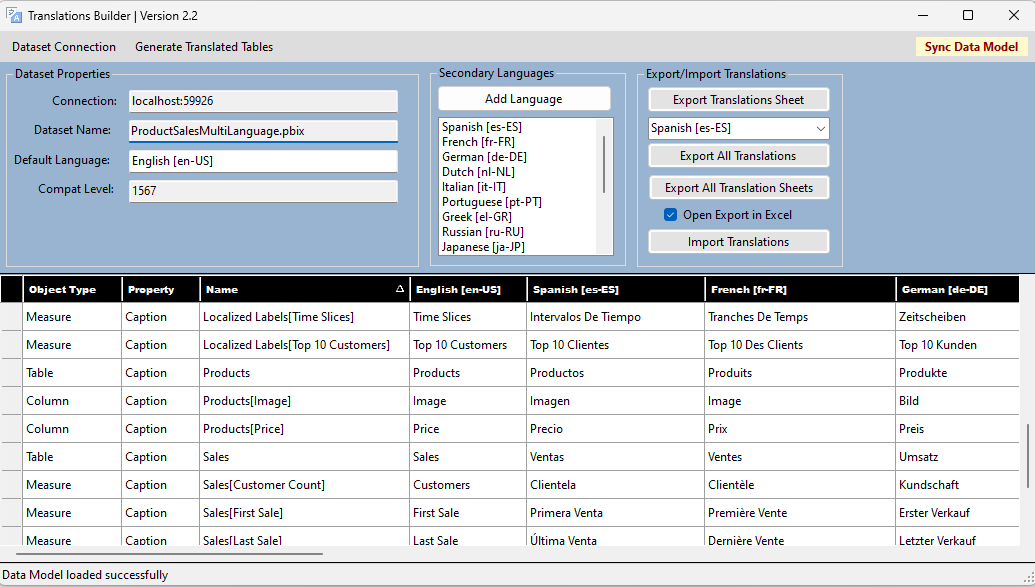
Content creators can use Translations Builder to add multiple-language support to .pbix project files in Power BI Desktop. The following screenshot shows what Translations Builder looks like when working with a simple .pbix project that supports a few secondary languages.
Translations Builder is an external tool developed for Power BI Desktop using C#, .NET 6, and Windows Forms. Translations Builder uses an API called Tabular Object Model (TOM) to update data models that are loaded into memory and run in a session of Power BI Desktop.
Translations Builder does most of its work by adding and updating the metadata translations associated with data model objects including tables, columns, and measures. There are also cases in which Translations Builder creates new tables in a data model to implement strategies to handle aspects of building multiple-language reports.
When you open a .pbix project in Power BI Desktop, the data model defined inside the .pbix file is loaded into memory in a local session of the Analysis Services engine. Translations Builder uses TOM to establish a direct connection to the data model of the current .pbix project.
Open Translations Builder
If you don't already have Power BI Desktop installed, see Get Power BI Desktop.
On the same computer where you run Power BI Desktop, download and install Translations Builder by using the Translations Builder Installation Guide.
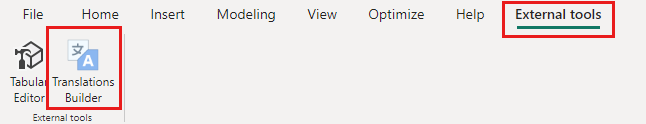
After you install Translations Builder, you can open it directly from Power BI Desktop in the External Tools ribbon. The Translations Builder project uses external tools integration support. For more information, see External tools in Power BI Desktop.
When you launch an external tool like Translations Builder, Power BI Desktop passes startup parameters to the application, including a connection string. Translations Builder uses the connection string to establish a connection back to the data model that's loaded in Power BI Desktop.
This approach allows Translations Builder to display data model information and to provide commands to automate adding metadata translations. For more information, see Translations Builder Developers Guide.
Translations Builder allows a content creator to view, add, and update metadata translations using a two-dimensional grid. This translations grid simplifies the user experience because it abstracts away the low-level details of reading and writing metadata translation associated with a dataset definition. You work with metadata translations in the translation grid similar to working with data in an Excel spreadsheet.