Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
TMDL view lets you script, modify, and apply changes to semantic model objects with a modern code editor using Tabular Model Definition Language (TMDL) in Power BI Desktop, improving development efficiency and providing complete visibility and control over semantic model metadata.
TMDL view offers an alternative experience to semantic modeling using code, instead of a graphical user interface such as Model view.
TMDL view offers the following advantages:
- Enhanced development efficiency with a rich code editor that includes search-and-replace, keyboard shortcuts, multi-line edits and more.
- Increase reusability by easily scripting, sharing, and reusing TMDL scripts among semantic model developers. For example, use a centralized SharePoint site to easily share reusable semantic model objects such as calendar tables, or time intelligence calculation groups.
- Gain more control and transparency, showing all semantic model objects and properties, and allowing changes to items not available in the Power BI Desktop user interface, such as IsAvailableInMDX or DetailRowsDefinition.
Enable preview feature
To use TMDL view, you must enable the preview feature. In Power BI Desktop select File > Options and settings > Options > Preview features and select the box next to TMDL View.
Script to TMDL
In Power BI Desktop, select the TMDL view icon located along the left side of the window, as shown in the following image.

When TMDL view opens the code editor is initially empty. You can script any semantic model object such as a table, measure, or column by selecting the objects from the Data pane and dragging them onto the code editor:

When using TMDL view and dragging the object from the Data pane, Power BI scripts the entire object metadata into the current tab as TMDL, or opens a new tab if the current tab isn't empty, as a createOrReplace TMDL script of the selected objects, as shown in the following image:

Alternatively, you can right-click an object in the Data view and select Script TMDL to new tab or to the clipboard, shown in the following image:

Tip
Multi selection is supported by pressing the CTRL key before scripting the objects into the TMDL view code editor.
Code editor
Once you've scripted a semantic model object or pasted TMDL script into the code editor, you can use the comprehensive code experience features offered by the TMDL view code editor. The code experience features enable you to either explore the model metadata, or make modifications that can later be applied to the semantic model.
Semantic highlighting
Semantic highlighting is built into the code editor, which improves readability by applying different colors to parts of your code based on meaning. Such color coding makes it easier to understand the structure and functionality of your TMDL code, as shown in the following image.

You can also expand or collapse sections of your TMDL script, as shown in the following image:

Autocomplete
Autocomplete is built into the code editor, and offers intelligent suggestions while you type. Autocomplete can speed up your workflow, reduce the chance of errors, and help you understand your code options by dynamically suggesting possible values or properties by taking into consideration the cursor position.

You can also trigger the autocomplete feature in any location by pressing Ctrl+Space.
Tooltips
The context tooltip shows on mouse hover, providing information about each TMDL object or property.

Code actions
When the cursor is on a squiggle or selected text, the TMDL view displays a light bulb icon indicating available Code Actions, such as generating lineage tags or correcting property name misspellings.


Code formatting
Format your TMDL code by pressing Shift + Alt + F or by clicking the Format option in the ribbon.
You can also format selected text using the "Format Selection" option in the context menu.

Error diagnostics
The code editor's built-in error diagnostics help you identify and fix issues by highlighting TMDL language errors in the code editor, with detailed messages that provide guidance on resolving them. Additionally, an error summary is available in the Problems pane, allowing easy navigation to the error location in the code editor, as shown in the following image.

Apply changes to the semantic model
When you're ready, you can select the Apply button to execute the TMDL script against the semantic model, and have your TMDL code changes applied.

When successful, a notification is displayed and your modeling change are applied to the semantic model.

In the event of a failure, an error notification is displayed to show that your modeling changes weren't applied to the semantic model. You can view more information about the error by selecting the Show details link in the notification, which then expands the Output pane and displays error details.

Note
TMDL view modifies only the semantic model metadata, without refreshing data or affecting the report. If your changes require a data refresh, such as altering a PowerQuery expression or calculated column expression, you must manually refresh the table or model for the changes to take effect. Additionally, renaming a field in TMDL view may break visuals within the report that use that field.
Preview changes to the semantic model
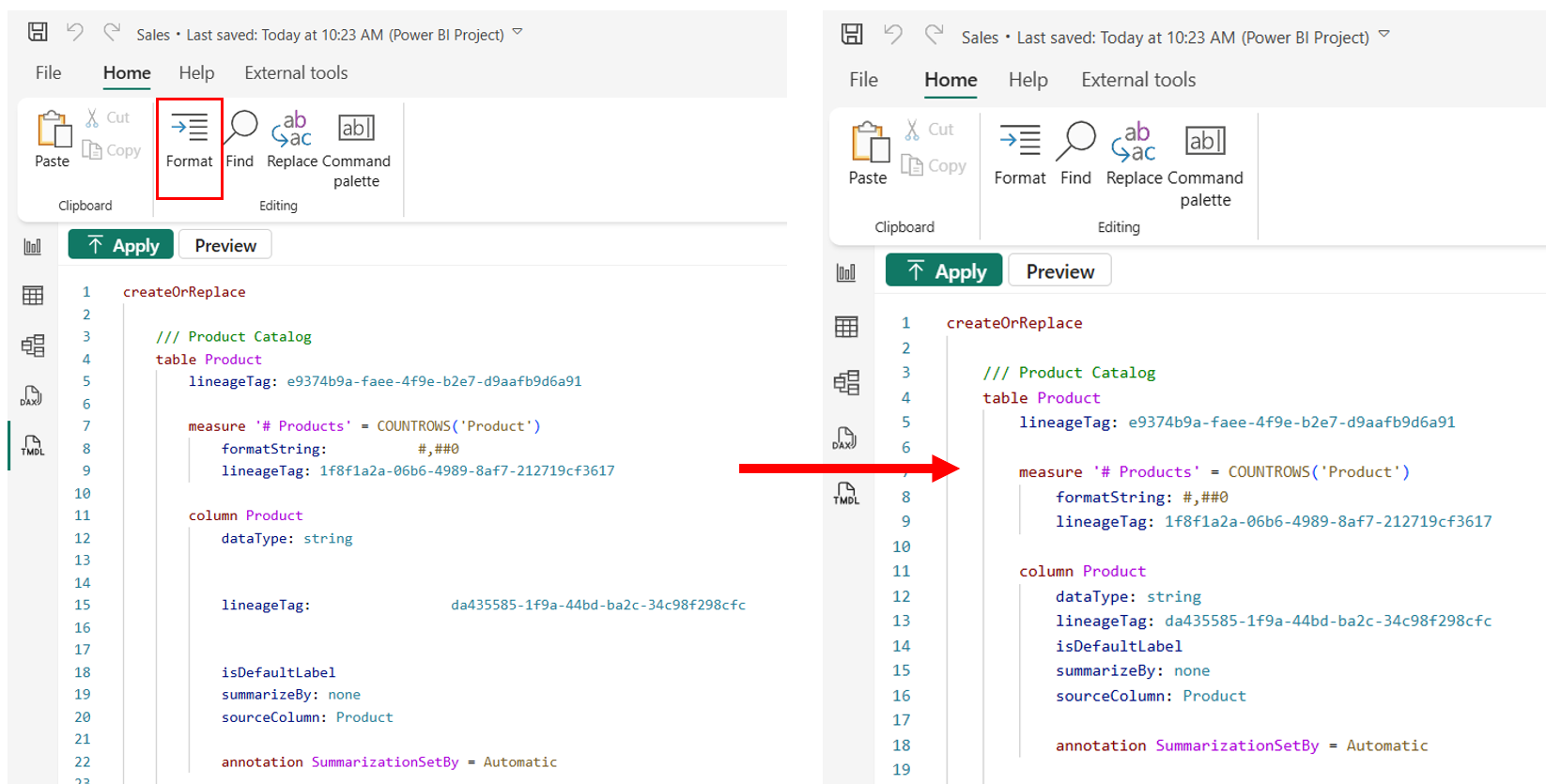
TMDL view enables you to preview script changes by showing a preview of the semantic model before and after script execution, shown as a TMDL code diff. Previewing script changes is particularly useful when copying scripts from other sources, letting you to assess their impact before running them against your semantic model.
Selecting the Preview button displays a TMDL diff of the semantic model before and after executing the TMDL script in the opened tab.

A side-by-side window appears in the right pane, as shown in the following image.
Red and green boxes highlight the changes, with red boxes indicated removed or changed lines, and green indicating new lines.

Note
The comparison isn't directly against the TMDL script currently displayed, but rather a comprehensive semantic model comparison before and after executing the script. So, some properties may be ordered differently than what is shown in the tab, adhering to the default TMDL property/object ordering.
The preview is read-only, but you can keep editing your script. To refresh the preview after changes, select the Update Preview button, as shown in the banner in the following image.

There's a toolbar in the top right corner of the preview screen that enables navigation of all code diffs, enabling you to toggle between inline or side-by-side diff, viewing or hiding unchanged regions, and closing the preview view.

There are a few considerations to keep in mind when previewing changes to the semantic model:
- TMDL view resets view configurations to default on each preview execution.
- A preview runs only with a valid TMDL change. Invalid TMDL scripts won't execute a preview and an error is displayed in the Output pane.
TMDL script tabs
In TMDL view you can have multiple script tabs at once, any of which can be renamed or removed.

The contents of the TMDL view tabs are saved in the report file when you save the Power BI Desktop report, so you can continue where you left off the next time you open the Power BI Desktop report file. When saving to a Power BI Project (PBIP), each script tab is saved as a .tmdl file in the \TMDLScripts folder, as shown in the following image.

Tip
You can open and edit TMDL scripts in Visual Studio Code, and they will properly reload after restarting Power BI Desktop.
The Problems and Output panes display errors and messages specific to the script tab that's currently selected and displayed. Switching to a different TMDL script tab refreshes both of those panes with information specific to the selected and currently shown tab.
You can select the Clear button to empty the Output pane messages.

Messages are kept only for each Power BI Desktop session, so restarting Power BI Desktop clears all output messages for all script tabs.
Compatibility level upgrade prompt
The compatibility level of a Power BI semantic model determines the features that are accessible. TMDL view allows you to add any Analysis Services object or property, even if it's not available at the current compatibility level. When applying a change that necessitates a compatibility level upgrade, TMDL view provides a prompt indicating which object or objects require the upgrade.

Object renaming with TMDL view
To rename an object within the TMDL view, it is necessary to script its parent. For instance, renaming a column requires scripting the table, while renaming a table necessitates scripting the entire semantic model. Learn more about tabular object model hierarchy in the following document: Tabular object model hierarchy.
With the TMDL view, bulk renaming can be performed efficiently using simple find and replace patterns. For instance, you can rename all table columns to lowercase by following these steps.
Open the TMDL view, script the table you intend to modify.
Press CTRL+F to open the find and replace dialog, ensure that the Regular Expression option is enabled.

Enter the following patterns in the find and replace fields and select Replace All.
| Action | Pattern/Replacement |
|---|---|
| Find | (^\s+column\s+)(.+) |
| Replace | $1\L$2 |

Run your TMDL script to rename all table columns to lowercase instantly:
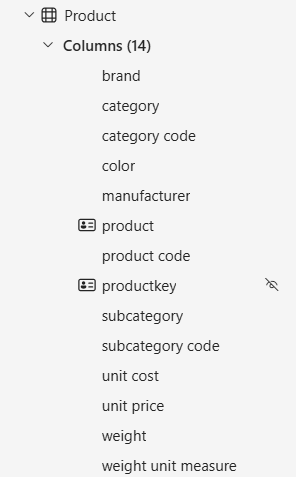
Notice that column name will differ from the sourceColumn property.

Synchronization between the semantic model table and Power Query query relies on sourceColumn, keeping names independent. When you open the Power Query editor, it will display the column names that match the sourceColumn, rather than the model's column name. Additionally, renaming a column in the user interface will not automatically add a rename step to the query until sourceColumn and column name are identical.

TMDL view and Power BI project
When you save your work as a Power BI project (PBIP), you gain access to your semantic model definition metadata as TMDL files, providing a useful source control and co-development experience, while also allowing you to make changes to the semantic model outside of Power BI Desktop. However, if you modify the TMDL files within the PBIP, you must restart Power BI Desktop to reload those changes. In contrast, the TMDL view follows a scripting mental model, enabling you to efficiently apply changes directly to the semantic model being edited in Power BI Desktop using TMDL, regardless of whether the file format is PBIX or PBIP.
You can seamlessly integrate both experiences. For instance, you can update the TMDL definition in PBIP for quick changes without launching Power BI Desktop, and utilize the TMDL view when Power BI Desktop is already open to efficiently implement a series of changes to the semantic model using TMDL. Both approaches offer a rich and consistent TMDL coding experience.
Common use cases for TMDL view
Scenario: I need to reuse or share a semantic model table with its complete definition, including columns, Power Query expression, and sort by configuration, and others in another semantic model.
Solution: Open the semantic model with the table, script it using the TMDL view. Copy the script to the other Power BI Desktop window, open the TMDL view tab, and apply the script.
Scenario: I've named all my tables with the prefixes "dim_" or "fact_". I'd like to remove these prefixes without manually updating each of the over 100 tables.
Solution: Open the TMDL view, script the semantic model, search for the prefix (regular expressions are supported) and replace it with an empty text.
Scenario: I need to create a perspective in my semantic model to use the personalized visuals feature. However, I can't create or edit it using the graphical interface of Power BI Desktop.
Solution: Open the TMDL view, create a new empty tab (or use the script from an existing perspective), then create or edit the perspective using TMDL. This method also applies to other semantic model metadata that lack a graphical interface, such as translations, detail row expressions and others.
createOrReplace
perspective SalesView
perspectiveTable Sales
perspectiveMeasure 'Sales Amount'
perspectiveMeasure 'Sales Qty'
perspectiveColumn Quantity
perspectiveColumn 'Amount'
Scenario: I need to modify the Power Query expression of my table without triggering a refresh.
Solution: Script the table, modify the Power Query expression, and apply the changes. TMDL view doesn't require refreshing your data.
Scenario: I need switch the storage mode of my table from DirectQuery to Import, and vice-versa
Solution: Script the table, update the partition mode, and apply changes.
Scenario: I need to back up my semantic model definition before making significant changes and easily roll back to a previous definition, if needed.
Solution: Script the semantic model or specific parts you want to back up, make your changes in other views, and if needed, return to the TMDL view to restore the previous metadata by running the saved script.
Considerations and limitations
TMDL view is currently in preview, so keep the following limitations in mind:
- You can use the TMDL view to edit any object or property within a semantic model. However, incomplete or incorrect modifications may lead to unexpected behavior. For more guidance on these operations, refer to the Model Authoring article.
- The Command palette displays some commands that aren't currently supported.
- Setting up the initial Git integration from the workspace won't include TMDL View scripts saved in published semantic model. Learn more in the Fabric Git integration article.
- You can't script model explorer groups such as Measures, Columns, so on.
Related content
The following articles describe more about TMDL and its uses.
