Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Content Security Policy (CSP) is currently supported in model-driven, canvas, and code apps. This article explains how to configure CSP for model-driven and canvas apps. For code apps CSP, see the code apps documentation. Admins can control whether the CSP header is sent and, to an extent, what it contains. The settings are at the environment level, which means they're applied to all apps in the environment once turned on.
Note
The content security policy only applies to environments using Dataverse.
Each component of the CSP header value controls the assets that can be downloaded. The Mozilla Developer Network (MDN) provides more detailed descriptions. The default values are as follows:
| Directive | Default value | Customizable |
|---|---|---|
| script-src | * 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval' blob: |
No |
| worker-src | 'self' blob: |
No |
| style-src | * 'unsafe-inline' blob: |
No |
| font-src | * data: |
No |
| frame-ancestors | 'self' https://*.powerapps.com |
Yes |
This configuration results in a default CSP of script-src * 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval' blob: ; worker-src 'self' blob:; style-src * 'unsafe-inline' blob:; font-src * data:; frame-ancestors 'self' https://*.powerapps.com;.
Strict mode
The Strict CSP toggle creates a CSP that mostly doesn't include wildcards or unsafe directives, such as unsafe-inline. When you turn on Strict CSP, the preceding directives become the following directives detailed in this section. The <platform> notation means that platform domains are provided as required by the product. The domains in this section might change over time as the product grows.
| Directive | Default value (model-driven) | Default value (canvas) | Customizable |
|---|---|---|---|
| script-src | 'self' blob: <platform>' |
'self' <platform>' |
Yes |
| worker-src | 'self' blob: |
'self' blob: |
No |
| style-src | 'self' 'unsafe-inline' blob: <platform> |
'self' 'unsafe-inline' <platform> |
Yes |
| font-src | 'self' data: <platform> |
'self' data: <platform> |
Yes |
| frame-ancestors | 'self' https://*.powerapps.com |
'self' https://*.powerapps.com |
Yes |
| img-src | 'self' blob: data: <platform> |
'self' data: <platform> |
Yes |
| connect-src | 'self' blob: data: wss: <platform> |
'self' blob: <platform> |
Yes |
| frame-src | 'self' blob: <platform> |
'self' <platform> |
Yes |
| base-uri | 'none' |
N/A | No |
| form-action | <platform> |
N/A | Yes |
| default-src | 'self' |
'self' |
No |
Prerequisites
For Dynamics 365 customer engagement apps and other model-driven apps, CSP is only available in online environments and in organizations with Dynamics 365 customer engagement (on-premises), version 9.1 or later version.
Configure CSP
You can toggle and configure CSP through the Power Platform admin center. It's important to enable a dev/test environment first since enabling CSP could start blocking scenarios if the policy is violated. The admin center also supports a report-only mode to allow for easier ramp-up in production.
Take these steps to configure CSP:
- Sign in to the Power Platform admin center.
- In the navigation pane, select Manage. In the Manage pane, select Environments.
- On the Environments page, select an environment.
- In the command bar, select Settings.
- Expand Product, and then select Privacy + Security.
The following image shows the default state of the settings:

Reporting
The Enable reporting toggle controls whether model-driven and canvas apps send violation reports. To enable it, specify an endpoint. The app sends violation reports to this endpoint regardless of whether CSP is enforced or not. If CSP isn't enforced, the app uses report-only mode. For more information, see reporting documentation.

Enforcement
Enforcement of CSP is controlled independently for model-driven and canvas apps to provide granular control over policies. Use the model-driven/canvas pivot to modify the intended app type.
The Enforce content security policy toggle turns on the default policy for enforcement for the given app type. Turning on this toggle changes the behavior of apps in this environment to adhere to the policy. Therefore, follow this suggested enablement flow:
- Enforce the policy on a dev or test environment.
- Enable report-only mode in production.
- Enforce the policy in production once no violations are reported.
Configure directives
The Configure directives section allows you to control individual directives within the policy. Currently, you can only customize the frame-ancestors directive.

If you leave the default directive toggled on, you use the default value specified in the table. If you turn off the toggle, you can specify custom values for the directive and append them to the default value. The following example sets custom values for frame-ancestors. The directive is set to frame-ancestors: 'self' https://*.powerapps.com https://www.foo.com https://www.bar.com in this example. This setting means the app can be hosted in the same origin, https://*.powerapps.com, https://www.foo.com, and https://www.bar.com, but not in other origins. Use the Add button to add entries to the list and the Delete icon to remove them.

Common configurations
For Microsoft Teams integration using the Dynamics 365 app, add the following to frame-ancestors:
https://teams.microsoft.com/https://teams.cloud.microsoft/https://msteamstabintegration.dynamics.com/
For the Dynamics 365 App for Outlook, add the following to frame-ancestors:
- Your Outlook Web App homepage origin
https://outlook.office.comhttps://outlook.office365.com
For embedding Power Apps in Power BI reports, add the following to frame-ancestors:
https://app.powerbi.comhttps://ms-pbi.pbi.microsoft.com
Important considerations
Turning off the default directive and saving with an empty list turns off the directive completely and doesn't send it as part of the CSP response header.
CSP configuration examples
Here are a couple examples of CSP configurations.
Example 1 - reporting turned off

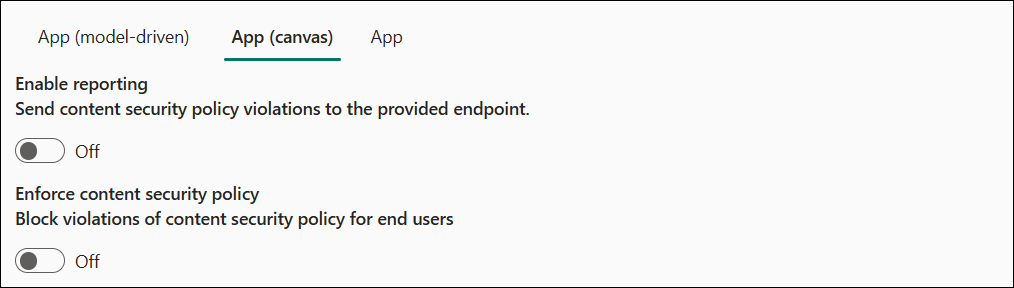
In the example:
- Reporting is turned off.
- Model-driven enforcement is enabled.
frame-ancestorsis customized tohttps://www.contoso.comandhttps://www.fabrikam.com.
- Canvas enforcement is disabled.
The effective headers are:
- Model-driven apps:
Content-Security-Policy: script-src * 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval' blob: data:; worker-src 'self' blob: data:; style-src * 'unsafe-inline' :blob; font-src * data:; frame-ancestors https://www.contoso.com https://www.fabrikam.com; - Canvas apps: CSP header isn't sent.
Example 2 - reporting turned on
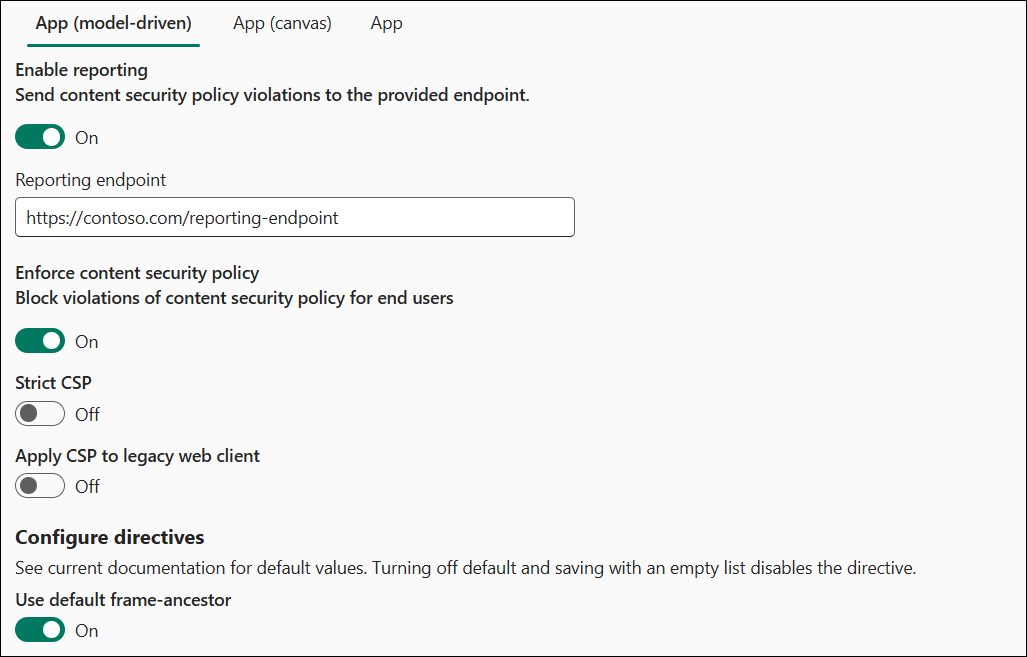
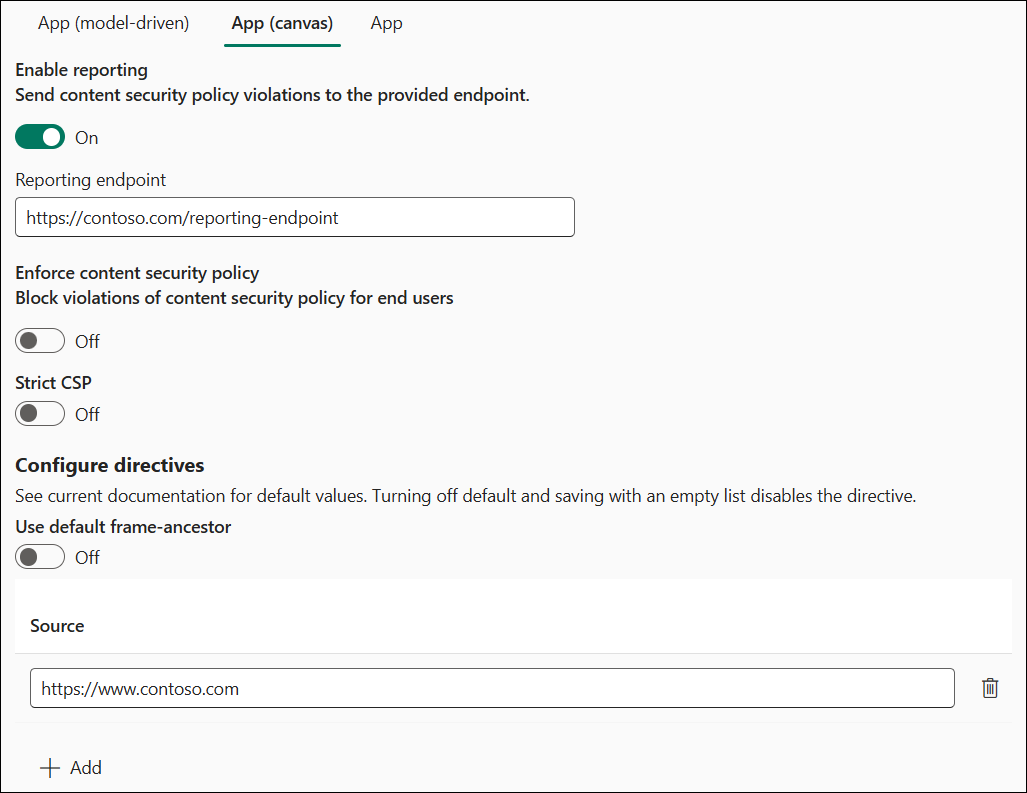
In the example:
- Reporting is turned on.
- Reporting endpoint is set to
https://contoso.com/reporting-endpoint
- Reporting endpoint is set to
- Model-driven enforcement is enabled.
frame-ancestorsis kept as default
- Canvas enforcement is disabled.
frame-ancestorsis customized tohttps://www.contoso.com
The effective CSP values are:
- Model-driven apps:
Content-Security-Policy: script-src * 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval' blob:; worker-src 'self' blob:; style-src * 'unsafe-inline' blob:; font-src * data:; frame-ancestors 'self' https://*.powerapps.com; report-uri https://contoso.com/reporting-endpoint; - Canvas apps:
Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only: script-src * 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval'; worker-src 'self' blob:; style-src * 'unsafe-inline'; font-src * data:; frame-ancestors https://www.contoso.com; report-uri https://contoso.com/reporting-endpoint;
Modify organization settings directly
You can configure CSP without using the UI by modifying these organization settings directly:
IsContentSecurityPolicyEnabled controls whether the Content-Security-Policy header is sent in model-driven apps.
ContentSecurityPolicyConfiguration controls the value of the frame-ancestors portion (as seen earlier, it sets to
'self'ifContentSecurityPolicyConfigurationisn't set). Define this setting by using a JSON object with the following structure –{ "Frame-Ancestor": { "sources": [ { "source": "foo" }, { "source": "bar" } ] } }. This configuration translates intoscript-src * 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval'; worker-src 'self' blob:; style-src * 'unsafe-inline' blob:; font-src * data:; frame-ancestors 'foo' 'bar';- (From MDN) The HTTP Content-Security-Policy (CSP) frame-ancestors directive specifies valid parents that may embed a page using
<frame>,<iframe>,<object>,<embed>, or<applet>.
- (From MDN) The HTTP Content-Security-Policy (CSP) frame-ancestors directive specifies valid parents that may embed a page using
IsContentSecurityPolicyEnabledForCanvas controls whether the Content-Security-Policy header is sent in canvas apps.
ContentSecurityPolicyConfigurationForCanvas controls the policy for canvas using the same process described in
ContentSecurityPolicyConfiguration.ContentSecurityPolicyReportUri controls whether reporting should be used. This setting is used by both model-driven and canvas apps. A valid string sends violation reports to the specified endpoint, using report-only mode if
IsContentSecurityPolicyEnabled/IsContentSecurityPolicyEnabledForCanvasis turned off. An empty string disables reporting. For more information, see reporting documentation.
Configuring CSP without UI
Especially for environments not in the Power Platform admin center such as on-premises configurations, admins may want to configure CSP using scripts to directly modify settings.
Enable CSP without UI
Take these steps to enable CSP without UI:
- Open browser dev tools while using the model-driven app as a user with organization entity update privileges (System Administrator is a good option).
- Paste and execute the following script into the console.
- To enable CSP, pass the default configuration -
enableFrameAncestors(["'self'"]) - As an example of enabling other origins to embed the app -
enableFrameAncestors(["*.powerapps.com", "'self'", "abcxyz"])
async function enableFrameAncestors(sources) {
const baseUrl = Xrm.Utility.getGlobalContext().getClientUrl();
if (!Array.isArray(sources) || sources.some(s => typeof s !== 'string')) {
throw new Error('sources must be a string array');
}
const orgResponse = await fetch(`${baseUrl}/api/data/v9.1/organizations`);
if (!orgResponse.ok) throw new Error('Failed to retrieve org info');
const orgs = await orgResponse.json();
const { organizationid, contentsecuritypolicyconfiguration, iscontentsecuritypolicyenabled } = orgs.value[0];
console.log(`Organization Id: ${organizationid}`);
console.log(`CSP Enabled?: ${iscontentsecuritypolicyenabled}`);
console.log(`CSP Config: ${contentsecuritypolicyconfiguration}`);
const orgProperty = prop => `${baseUrl}/api/data/v9.1/organizations(${organizationid})/${prop}`;
console.log('Updating CSP configuration...')
const config = {
'Frame-Ancestor': {
sources: sources.map(source => ({ source })),
},
};
const cspConfigResponse = await fetch(orgProperty('contentsecuritypolicyconfiguration'), {
method: 'PUT',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({
value: JSON.stringify(config),
}),
});
if (!cspConfigResponse.ok) {
throw new Error('Failed to update csp configuration');
}
console.log('Successfully updated CSP configuration!')
if (iscontentsecuritypolicyenabled) {
console.log('CSP is already enabled! Skipping update.')
return;
}
console.log('Enabling CSP...')
const cspEnableResponse = await fetch(orgProperty('iscontentsecuritypolicyenabled'), {
method: 'PUT',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({
value: true,
}),
});
if (!cspEnableResponse.ok) {
throw new Error('Failed to enable csp');
}
console.log('Successfully enabled CSP!')
}
Disable CSP without UI
Take these steps to disable CSP without UI:
- Open browser dev tools while using the model-driven app as a user with organization entity update privileges (System Administrator is a good option).
- Paste and execute the following script into the console.
- To disable CSP, paste into the console:
disableCSP()
async function disableCSP() {
const baseUrl = Xrm.Utility.getGlobalContext().getClientUrl();
const orgResponse = await fetch(`${baseUrl}/api/data/v9.1/organizations`);
if (!orgResponse.ok) throw new Error('Failed to retrieve org info');
const orgs = await orgResponse.json();
const { organizationid, iscontentsecuritypolicyenabled } = orgs.value[0];
console.log(`Organization Id: ${organizationid}`);
console.log(`CSP Enabled?: ${iscontentsecuritypolicyenabled}`);
const orgProperty = prop => `${baseUrl}/api/data/v9.1/organizations(${organizationid})/${prop}`;
if (!iscontentsecuritypolicyenabled) {
console.log('CSP is already disabled! Skipping update.')
return;
}
console.log('Disabling CSP...')
const cspEnableResponse = await fetch(orgProperty('iscontentsecuritypolicyenabled'), {
method: 'PUT',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({
value: false,
}),
});
if (!cspEnableResponse.ok) {
throw new Error('Failed to disable csp');
}
console.log('Successfully disabled CSP!')
}