Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The append operation creates a single table by adding the contents of one or more tables to another, and aggregates the column headers from the tables to create the schema for the new table.
Note
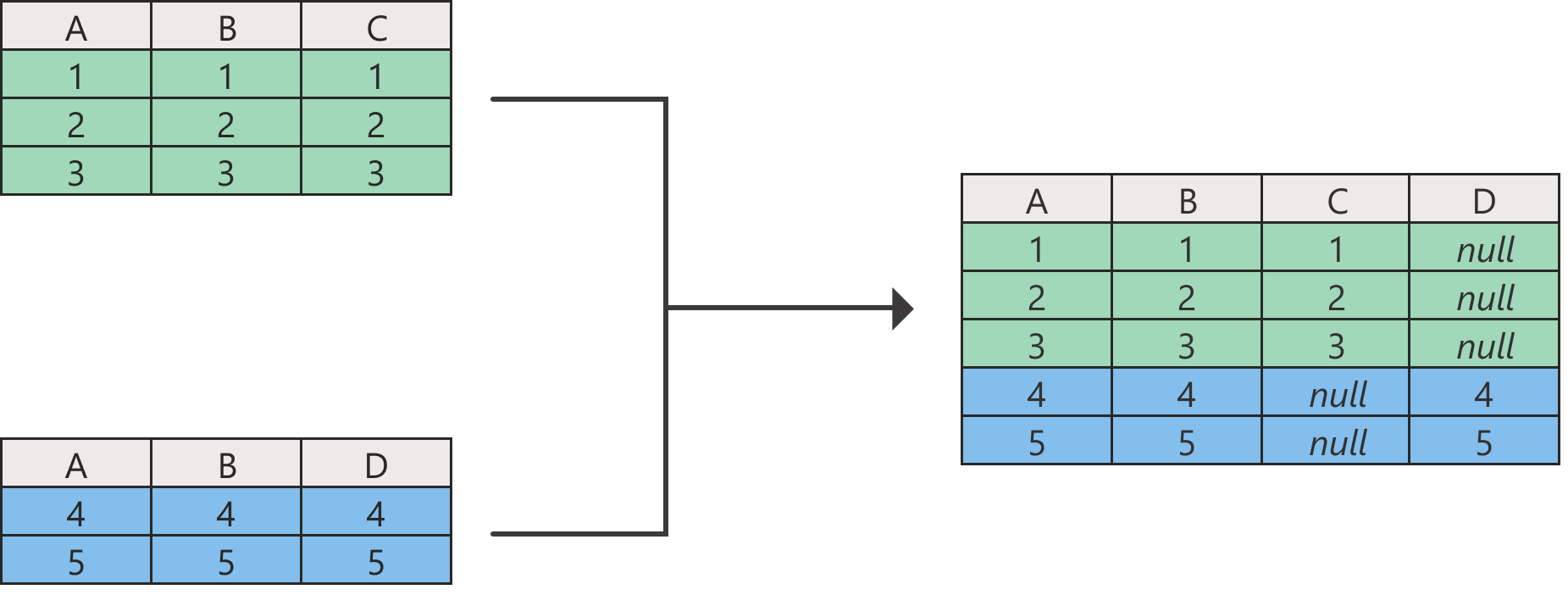
When tables that don't have the same column headers are appended, all column headers from all tables are appended to the resulting table. If one of the appended tables doesn't have a column header from other tables, the resulting table shows null values in the respective column, as shown in the previous image in columns C and D.
You can find the Append queries command on the Home tab in the Combine group. On the drop-down menu, there are two options:
Append queries - appends other tables to your current query.
For example: You have two tables, A and B. You select Append queries in table A, and request to append table B. Your table A query will now have an appended table that contains aggregated data from A and B. Your table B query is unchanged.
Append queries as new - appends other tables to a new query.
For example: You have two tables, A and B. You select Append queries as new in table A, and request to append table B. You now have a new query called Append1 that contains an aggregated table from A and B. Both your table A and table B queries are unchanged.
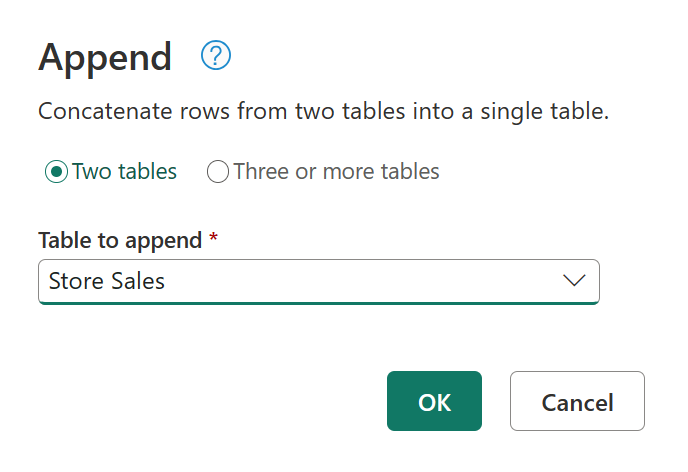
The append operation requires at least two tables. The Append dialog box has two modes:
- Two tables: Combine two table queries together. This mode is the default mode.
- Three or more tables: Allow an arbitrary number of table queries to be combined.
Note
The tables are appended in the order in which they're selected, starting with the Primary table for the Two tables mode and from the primary table in the Tables to append list for the Three or more tables mode.
Append two tables
For the example in this article, you use the following two tables with sample data:
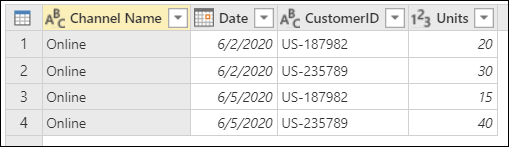
Online Sales: Sales made through an online channel.
Store Sales: Sales made through the company's physical locations.
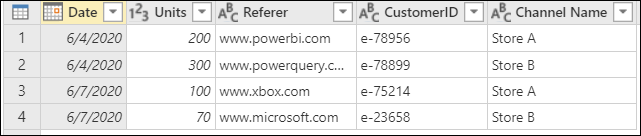
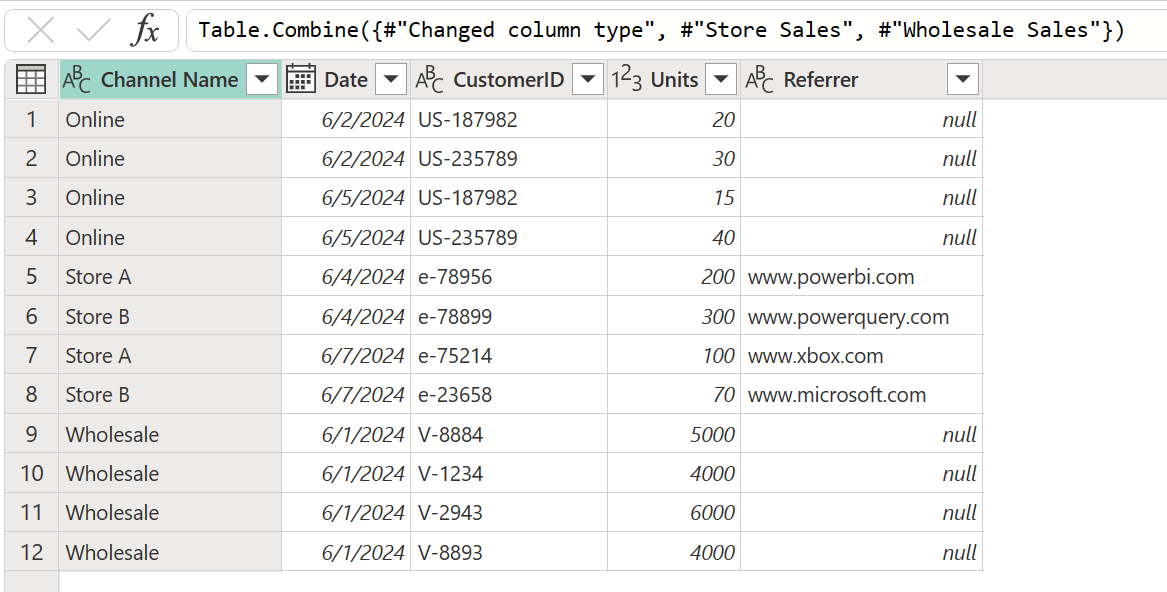
To append these tables, first select the Online Sales table. On the Home tab, select Append queries, which creates a new step in the Online Sales query. The Online Sales table is the primary table. The table to append to the primary table is Store Sales.
Power Query performs the append operation based on the names of the column headers found on both tables, and not based on their relative position in the headers sections of their respective tables. The final table has all columns from all tables appended.
If one table doesn't have columns found in another table, null values appear in the corresponding column, as shown in the Referrer column of the final query.
Append three or more tables
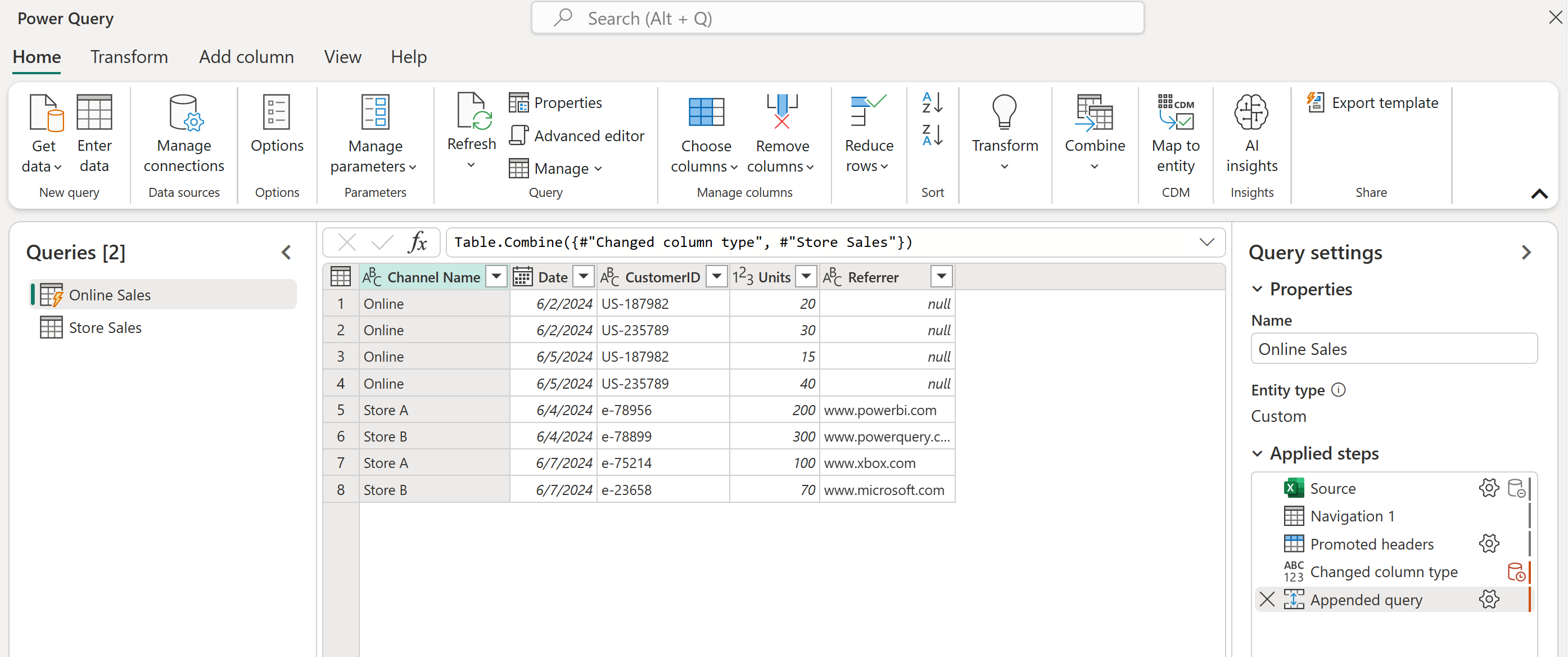
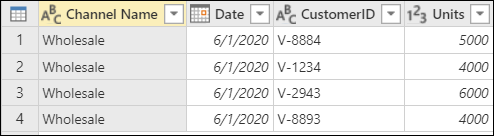
In this example, you want to append not only the Online Sales and Store Sales tables, but also a new table named Wholesale Sales.
The new approach for this example is to select Append queries as new, and then in the Append dialog box, select the Three or more tables option button. In the Available table(s) list, select each table you want to append, and then select Add. After all the tables you want appear in the Tables to append list, select OK.
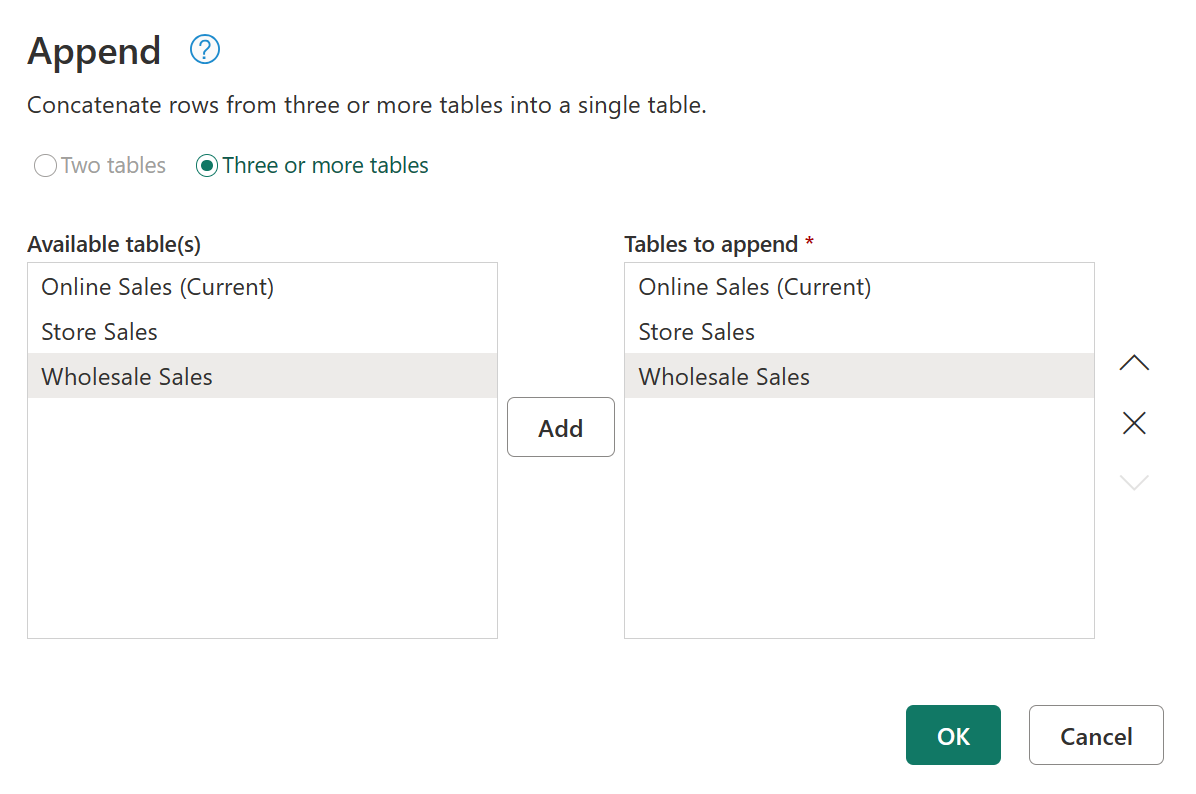
After you select OK, a new query is created with all your tables appended.