Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Summary
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Release State | General Availability |
| Products | Power BI (Semantic models) Power BI (Dataflows) Fabric (Dataflow Gen2) Power Apps (Dataflows) Dynamics 365 Customer Insights Analysis Services |
| Authentication Types Supported | Organizational Account Account Key Shared Access Signature (SAS) Key Service principal |
| Function Reference Documentation | AzureStorage.DataLake AzureStorage.DataLakeContents |
Note
Some capabilities may be present in one product but not others due to deployment schedules and host-specific capabilities.
Prerequisites
An Azure subscription. Go to Get Azure free trial.
A storage account that has a hierarchical namespace. Follow the instructions at Create a storage account to create one. This article assumes that you've created a storage account named
myadlsg2.Ensure you're granted one of the following roles for the storage account: Blob Data Reader, Blob Data Contributor, or Blob Data Owner.
A sample data file named
Drivers.txtlocated in your storage account. You can download this sample from Azure Data Lake Git Repository, and then upload that file to your storage account.
Capabilities supported
- Import
- File System View
- CDM Folder View
Connect to Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 from Power Query Desktop
Select Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 in the get data experience. The get data experience in Power Query Desktop varies between apps. For more information about the Power Query Desktop get data experience for your app, go to Where to get data.
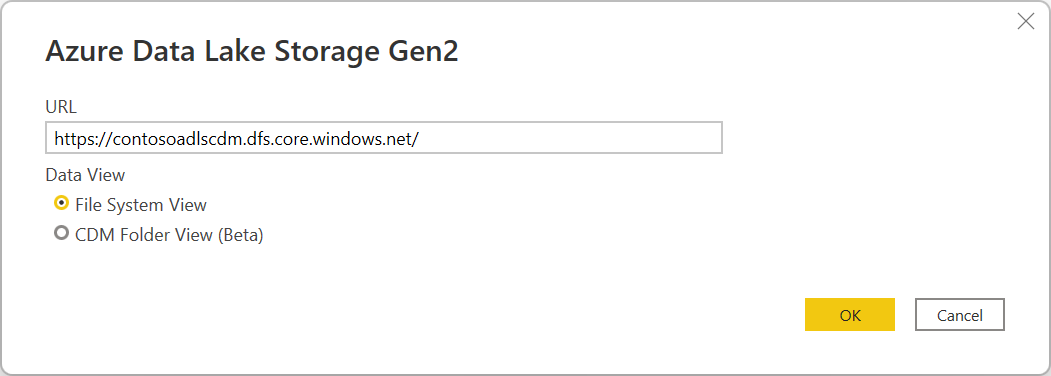
In the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 dialog box, provide the URL to your Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account, container, or subfolder using the container endpoint format. URLs for Data Lake Storage Gen2 have the following pattern:
https://<accountname>.dfs.core.windows.net/<container>/<subfolder>
You can also select whether you want to use the file system view or the Common Data Model folder view.
Select OK to continue.
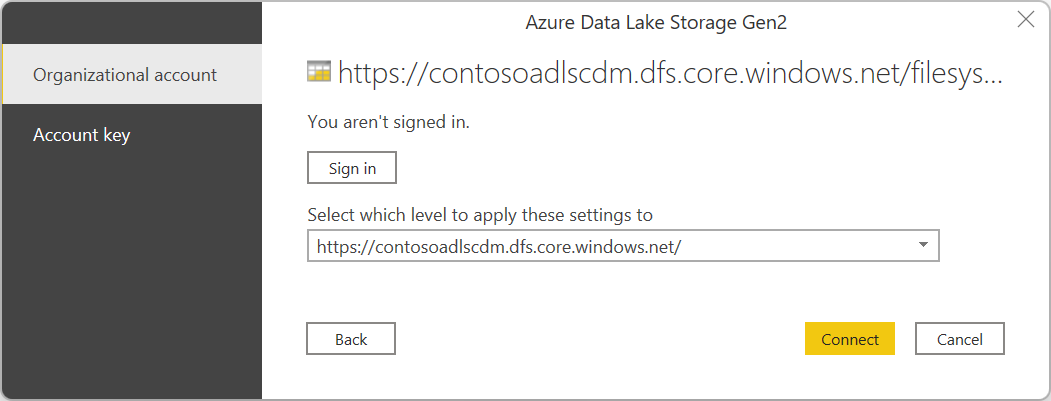
If this is the first time you're using this URL address, you'll be asked to select the authentication method.
If you select the Organizational account method, select Sign in to sign into your storage account. You'll be redirected to your organization's sign-in page. Follow the prompts to sign into the account. After you've successfully signed in, select Connect.
If you select the Account key method, enter your account key and then select Connect.
The Navigator dialog box shows all files under the URL you provided. Verify the information and then select either Transform Data to transform the data in Power Query or Load to load the data.
Connect to Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 from Power Query Online
Select the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 option in the get data experience. Different apps have different ways of getting to the Power Query Online get data experience. For more information about how to get to the Power Query Online get data experience from your app, go to Where to get data.
In Connect to data source, enter the URL to your Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account. Refer to Limitations to determine the URL to use.
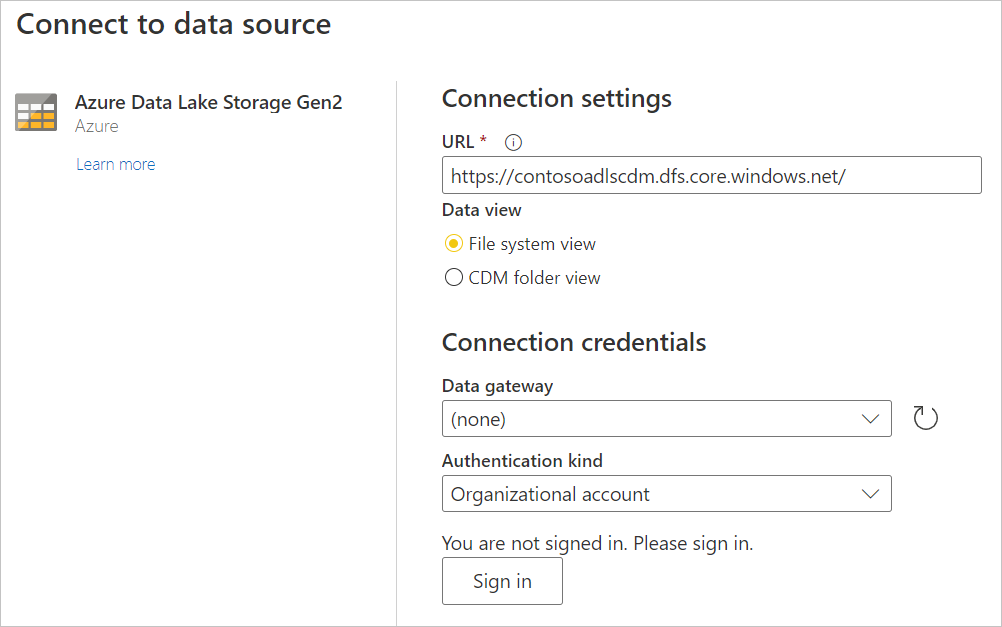
Select whether you want to use the file system view or the Common Data Model folder view.
If needed, select the on-premises data gateway in Data gateway.
Select Sign in to sign into the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 account. You'll be redirected to your organization's sign-in page. Follow the prompts to sign in to the account.
After you've successfully signed in, select Next.
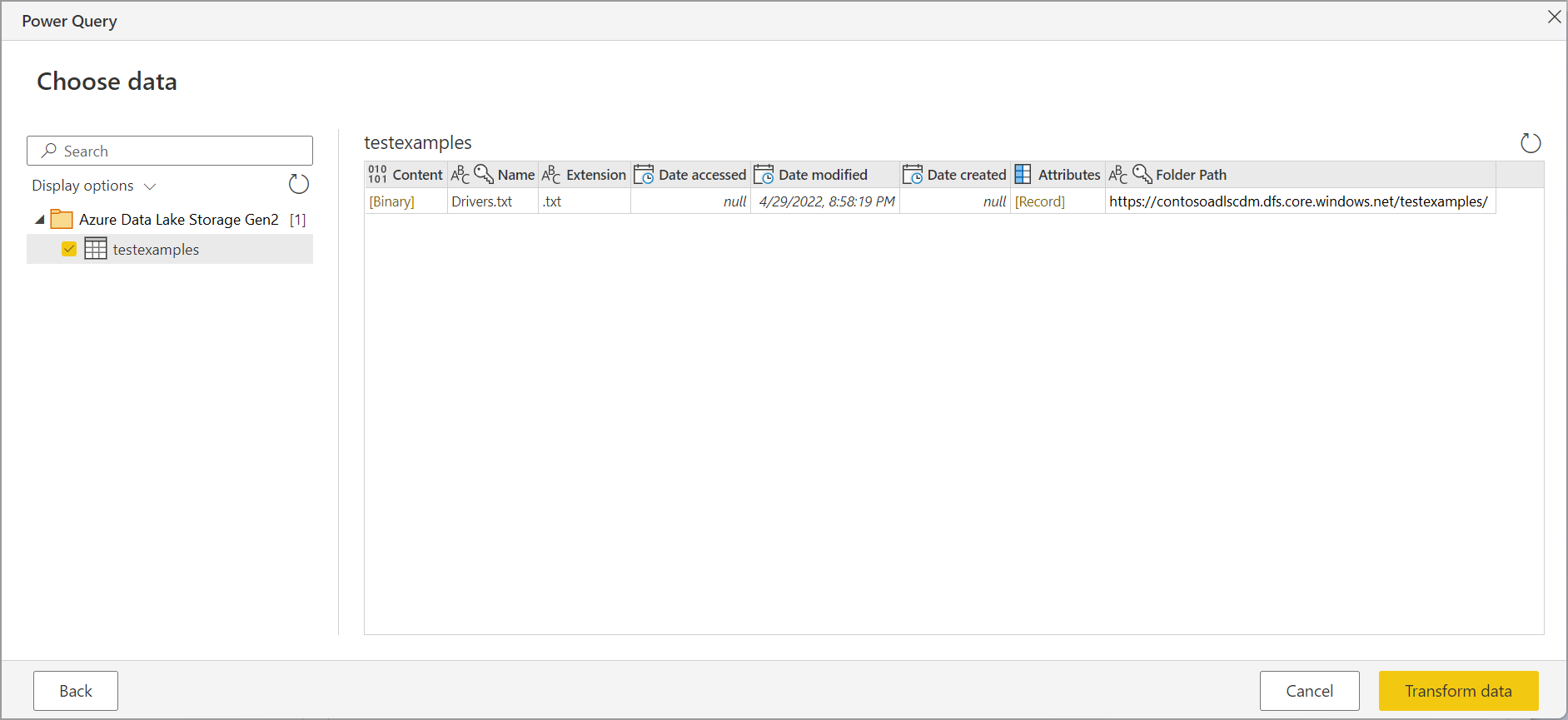
The Choose data page shows all files under the URL you provided. Verify the information and then select Transform Data to transform the data in Power Query.
Limitations
Subfolder or file not supported in Power Query Online and Power BI Desktop
Currently, in Power Query Online and in Power BI Desktop, the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 connector only supports paths with container, and not subfolder or file. For example, https://<accountname>.dfs.core.windows.net/<container> works, while https://<accountname>.dfs.core.windows.net/<container>/<filename> or https://<accountname>.dfs.core.windows.net/<container>/<subfolder> might fail.
Refresh authentication
Microsoft doesn't support dataflow or semantic model refresh using OAuth2 authentication when the Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2 (ADLS) account is in a different tenant. This limitation only applies to ADLS when the authentication method is OAuth2, that is, when you attempt to connect to a cross-tenant ADLS using an Microsoft Entra ID account. In this case, we recommend that you use a different authentication method that isn't OAuth2/Microsoft Entra ID, such as the Key authentication method.
Proxy and firewall requirements
When you create a dataflow using a gateway, you might need to change some of your proxy settings or firewall ports to successfully connect to your Azure data lake. If a dataflow fails with a gateway-bound refresh, it might be due to a firewall or proxy issue on the gateway to the Azure storage endpoints.
If you're using a proxy with your gateway, you might need to configure the Microsoft.Mashup.Container.NetFX45.exe.config file in the on-premises data gateway. More information: Configure proxy settings for the on-premises data gateway.
To enable connectivity from your network to the Azure data lake, you might need to enable list specific IP addresses on the gateway machine. For example, if your network has any firewall rules in place that might block these attempts, you'll need to unblock the outbound network connections for your Azure data lake. To enable list the required outbound addresses, use the AzureDataLake service tag. More information: Virtual network service tags
Dataflows also support the "Bring Your Own" data lake option, which means you create your own data lake, manage your permissions, and you explicitly connect it to your dataflow. In this case, when you're connecting to your development or production environment using an Organizational account, you must enable one of the following roles for the storage account: Blob Data Reader, Blob Data Contributor, or Blob Data Owner.
Power Query Online and Azure Storage are in the same region
Direct access to an Azure Storage account with the firewall enabled and in the same region as Power Query Online isn't supported. This limitation arises because Power Query services, when deployed in the same region as the Azure storage account, use private Azure IP addresses for communication. For further details, refer to the Azure documentation on storage network security.
To work around this limitation and enable access to Azure Storage from Power Query Online in the same region, use one of the following methods:
- Utilize an On-premises data gateway, which serves as a bridge between Power Query Online and Azure Storage.
- Use a Virtual Network (VNet) data gateway.