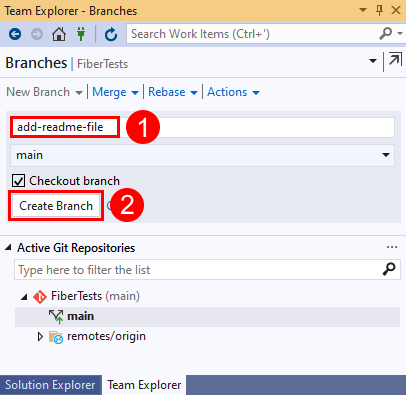
Create a new Git branch
TFS 2018
Visual Studio 2019 | Visual Studio 2022
The first commit in a new Git repo is the start of the main branch. As you work in the main branch, you make commits to record your work in that branch. Branching in Git occurs when you create a new line of development that diverges from a prior branch. You might choose to create a new branch to develop and test a new feature before adding it to your main branch. The recommended Git workflow is to use a new branch for every feature or bugfix. When you switch between branches, Git almost instantly switches the version of your repo files to match the branch you selected. Your commits are always saved to the current branch, and are isolated from commits in other branches.
For an overview of the Git workflow, see Azure Repos Git tutorial.
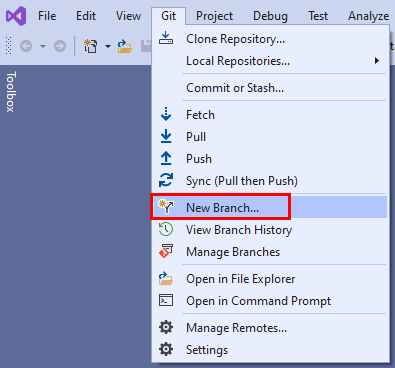
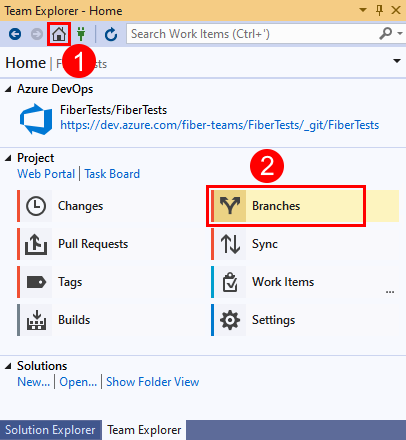
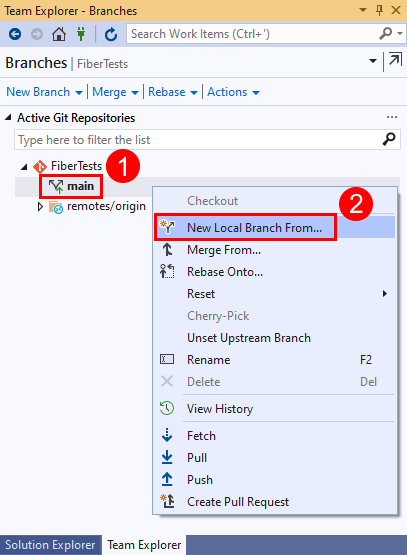
Create a new branch
Note
Branch names can't contain ASCII control characters, such as spaces, tildes, and colons. It's common practice to use lowercase characters and to separate words with a hyphen. Forward slashes can be used to group branches. Branch name length shouldn't exceed 250 ASCII characters. To avoid ambiguity between branch names and commit hashes, don't use branch names that consist of 40 hexadecimal characters. For more information on branch naming, see git-check-ref-format and Git cross-platform compatibility.
- Browser
- Visual Studio 2022
- Visual Studio 2019 - Git menu
- Visual Studio 2019 - Team Explorer
- Git Command Line
View your repo's branches by selecting Branches while viewing your repo on the web.
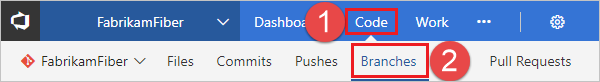
Select New branch in the upper-right corner of the page.
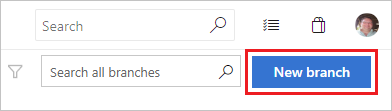
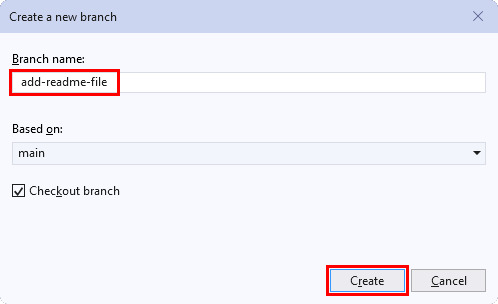
In the Create a branch dialog box, enter a name for your new branch, select a branch to base the work off of, and associate any work items.
Select Create branch.
Tip
After you've created a remote branch, you can fetch it into your local Git repo. At the command prompt, run:
git fetch
git switch <remote branch name>