Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
In this tutorial, you use Visual Studio to create and run a C# console app, and explore some features of the Visual Studio integrated development environment (IDE). This tutorial is part 1 of a two-part tutorial series.
In this tutorial, you complete the following tasks:
- Create a Visual Studio project.
- Create a C# console app.
- Debug your app.
- Close your app.
- Inspect your complete code.
In part 2 of this tutorial, you extend this app to add more projects, learn debugging tricks, and reference non-Microsoft packages.
Prerequisites
You must have Visual Studio installed.
If you don't have Visual Studio, go to Visual Studio downloads to install it for free.
Create a project
To start, create a C# application project. The project type comes with all the template files you need.
Create the app
In this section, you complete the following tasks:
- Explore some basic integer math in C#.
- Add code to create a basic calculator app.
- Debug the app to find and fix errors.
- Refine the code to make it more efficient.
Explore integer math
Start with some basic integer math in C#.
Add code to create a calculator
Continue by adding a more complex set of calculator code to your project.
Add decimal functionality
Now, tweak the code to add more functionality.
The current calculator app only accepts and returns whole numbers. For example, if you run the app and divide the number 42 by the number 119, your result is zero, which isn't exact.
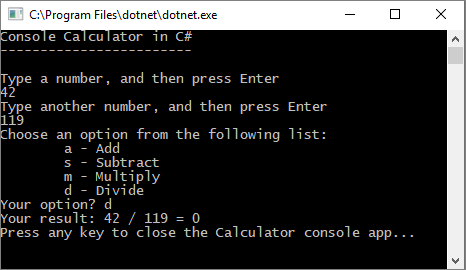
To fix the code to improve precision by handling decimals:
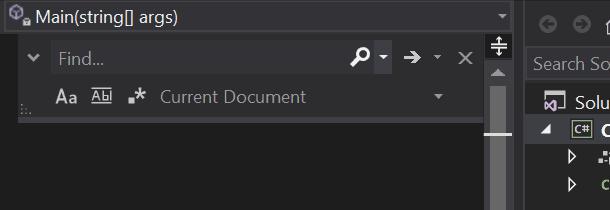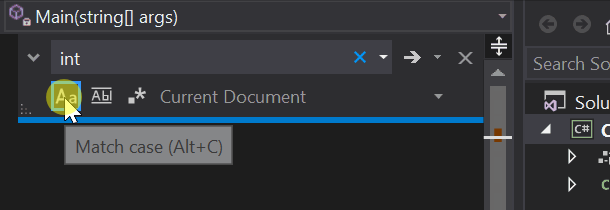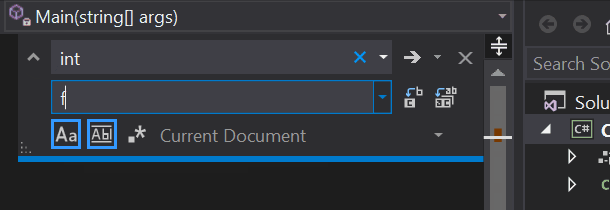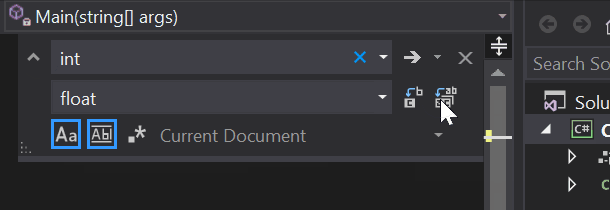
From Program.cs in the Visual Studio editor, press Ctrl+H to open the Find and Replace control.
Type int in the control, and type float in the Replace field.
Select the icons for Match case and Match whole word in the control, or press Alt+C and Alt+W.
Select the Replace all icon or press Alt+A to run the search and replace.
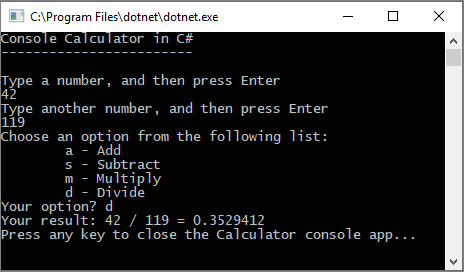
Run your calculator app again, and divide the number 42 by the number 119.
The app now returns a decimal number instead of zero.
Now the app can produce decimal results. Make a few more tweaks to the code so the app can calculate decimals too.
Use the Find and Replace control to change each instance of the
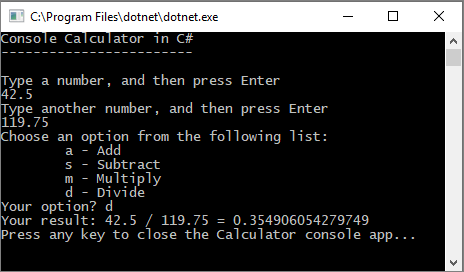
floatvariable todouble, and to change each instance of theConvert.ToInt32method toConvert.ToDouble.Run your calculator app, and divide the number 42.5 by the number 119.75.
The app now accepts decimal values, and returns a longer decimal numeral as its result.
In the Revise the code section, you reduce the number of decimal places in the results.
Debug the app
You improved your basic calculator app, but your app doesn't yet handle exceptions, such as user input errors. For example, if users try to divide by zero, or enter an unexpected character, the app might stop working, return an error, or return an unexpected non-numeric result.
Let's walk through a few common user input errors, locate them in the debugger if they appear there, and fix them in the code.
Tip
For more information about the debugger and how it works, see First look at the Visual Studio debugger.
Fix the divide by zero error
If you try to divide a number by zero, the console app might freeze, and then shows you what's wrong in the code editor.
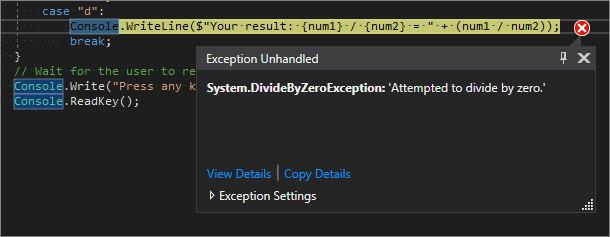
Note
Sometimes the app doesn't freeze, and the debugger doesn't show a divide-by-zero error. Instead, the app might return an unexpected non-numeric result, such as an infinity symbol. The following code fix still applies.
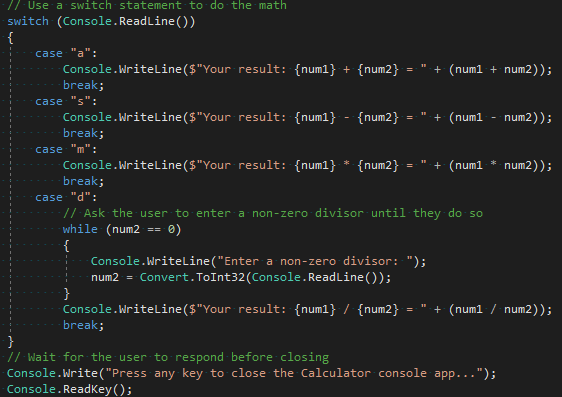
Let's change the code to handle this error. In Program.cs, replace the code for case "d": with the following code:
// Ask the user to enter a non-zero divisor until they do so.
while (num2 == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("Enter a non-zero divisor: ");
num2 = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine());
}
Console.WriteLine($"Your result: {num1} / {num2} = " + (num1 / num2));
break;
After you replace the code, the section with the switch statement should look similar to the following screenshot:
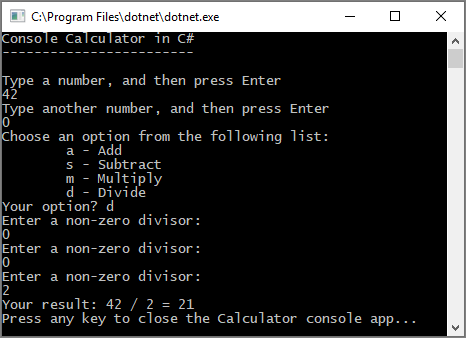
Now, when you divide any number by zero, the app asks for another number, and keeps asking until you provide a nonzero number.
Fix the format error
If you enter an alphabetic character when the app expects a numeric character, the app freezes. Visual Studio shows you what's wrong in the code editor.
To prevent this exception, you can refactor the code you previously entered.
Close the app
If you haven't already done so, close the Calculator app.
Close the Output pane in Visual Studio.
In Visual Studio, press Ctrl+S to save your app.
Add Git source control
Now that you have an application, you might want to add it to a Git repository. Visual Studio makes that process easy with Git tools you can use directly from the IDE.
Tip
Git is the most widely used modern version control system. Whether you're a professional developer or you're learning how to code, Git can be very useful. If you're new to Git, the https://git-scm.com/ website is a good place to start. You can find cheat sheets, a popular online book, and Git Basics videos.
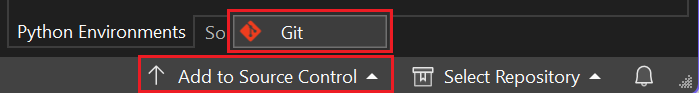
To associate your code with Git, start by creating a new Git repository where your code is located:
In the status bar at the bottom-right of Visual Studio, select Add to Source Control, and then select Git.
In the Create a Git repository dialog box, sign in to GitHub:
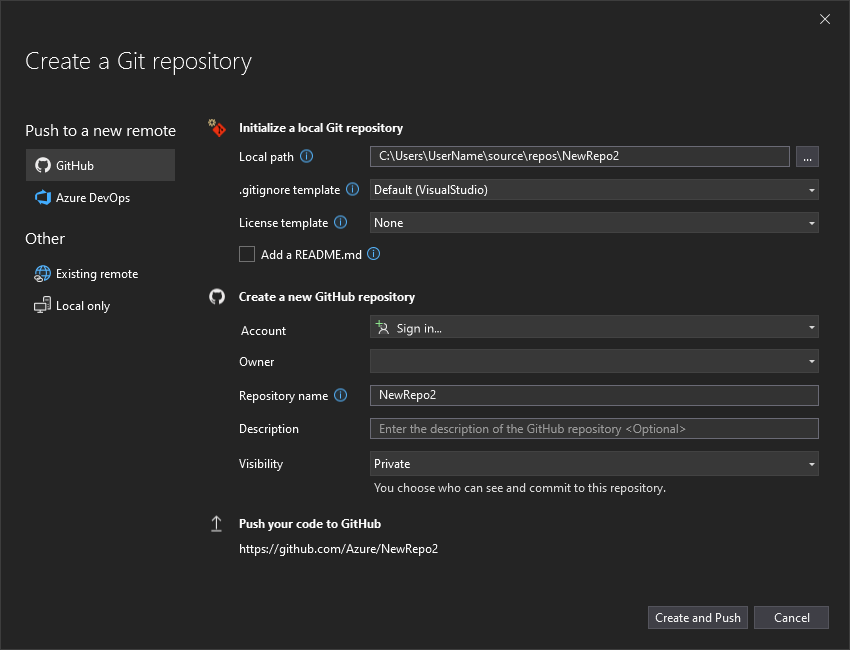
The repository name autopopulates based on your folder location. Your new repository is private by default, which means you're the only one who can access it.
Tip
Whether your repository is public or private, it's best to have a remote backup of your code stored securely on GitHub. Even if you aren't working with a team, a remote repository makes your code available to you from any computer.
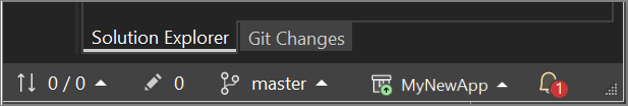
Select Create and Push. After you create your repository, you see status details in the status bar:
Use Git actions in Visual Studio
Here's a brief summary of Git actions available in the Visual Studio status bar:
The Up/Down arrows show how many outgoing/incoming commits are in your current branch. You can use this icon to pull any incoming commits or push any outgoing commits.
To view a specific commit, select the Up/Down arrow, and then select View Outgoing/Incoming.
The Pencil shows the number of uncommitted changes to your code. You can select this icon to view those changes in the Git Changes window.
The Git menu provides tools for repository actions on your files. You can use git fetch, pull, push, and sync for version control in Visual Studio.
For more information about how to use Git with your app, see About Git in Visual Studio.
Review: Code complete
In this tutorial, you made many changes to the Calculator app. The app now handles computing resources more efficiently, and handles most user input errors.
Here's the complete code, all in one place:
Next step
Continue with the second part of this tutorial: