Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This step-by-step guide demonstrates advanced techniques for Group Policy management using the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) and Microsoft Advanced Group Policy Management (AGPM). AGPM increases the capabilities of the GPMC, providing:
Standard roles for delegating permissions to manage Group Policy objects (GPOs) to multiple Group Policy administrators, as well as the ability to delegate access to GPOs in the production environment.
An archive to enable Group Policy administrators to create and modify GPOs offline before deploying them to a production environment.
The ability to roll back to any previous version of a GPO in the archive and to limit the number of versions stored in the archive.
Check-in/check-out capability for GPOs to ensure that Group Policy administrators do not inadvertently overwrite each other's work.
AGPM scenario overview
For this scenario, you will use a separate user account for each role in AGPM to demonstrate how Group Policy can be managed in an environment with multiple Group Policy administrators who have different levels of permissions. Specifically, you will perform the following tasks:
Using an account that is a member of the Domain Admins group, install AGPM Server and assign the AGPM Administrator role to an account or group.
Using accounts to which you will assign AGPM roles, install AGPM Client.
Using an account with the AGPM Administrator role, configure AGPM and delegate access to GPOs by assigning roles to other accounts.
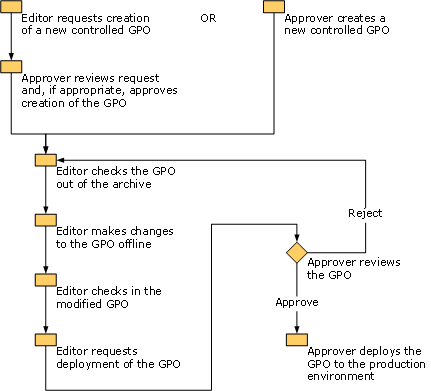
Using an account with the Editor role, request the creation of a GPO, which you then approve using an account with the Approver role. With the Editor account, check the GPO out of the archive, edit the GPO, check the GPO into the archive, and request deployment.
Using an account with the Approver role, review the GPO and deploy it to your production environment.
Using an account with the Editor role, create a GPO template and use it as a starting point to create a new GPO.
Using an account with the Approver role, delete and restore a GPO.
Requirements
Computers on which you want to install AGPM must meet the following requirements, and you must create accounts for use in this scenario.
Note
If you have AGPM 2.5 installed and are upgrading from Windows Server® 2003 to Windows Server 2008 or Windows Vista® with no service packs installed to Windows Vista with Service Pack 1, you must upgrade the operating system before you can upgrade to AGPM 3.0.
AGPM Server requirements
AGPM Server 3.0 requires Windows Server 2008 or Windows Vista with Service Pack 1 and the GPMC from Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) installed. Both 32-bit and 64-bit versions are supported.
Before you install AGPM Server, you must be a member of the Domain Admins group and the following Windows features must be present unless otherwise noted:
GPMC
- Windows Server 2008: The GPMC is automatically installed by AGPM if not present.
.NET Framework 3.5
The following Windows features are required by AGPM Server and will be automatically installed if not present:
WCF Activation; Non-HTTP Activation
Windows Process Activation Service
Process Model
.NET Environment
Configuration APIs
AGPM Client requirements
AGPM Client 3.0 requires Windows Server 2008 or Windows Vista with Service Pack 1 and the GPMC from Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) installed. Both 32-bit and 64-bit versions are supported. AGPM Client can be installed on a computer running AGPM Server.
The following Windows features are required by AGPM Client and will be automatically installed if not present unless otherwise noted:
GPMC
- Windows Server 2008: The GPMC is automatically installed by AGPM if not present.
.NET Framework 3.0
Scenario requirements
Before you begin this scenario, create four user accounts. During the scenario, you will assign one of the following AGPM roles to each of these accounts: AGPM Administrator (Full Control), Approver, Editor, and Reviewer. These accounts must be able to send and receive e-mail messages. Assign Link GPOs permission to the accounts with the AGPM Administrator, Approver, and (optionally) Editor roles.
Note
Link GPOs permission is assigned to members of Domain Administrators and Enterprise Administrators by default. To assign Link GPOs permission to additional users or groups (such as accounts with the roles of AGPM Administrator or Approver), select the node for the domain and then select the Delegation tab, select Link GPOs, select Add, and select users or groups to which to assign the permission.
Steps for installing and configuring AGPM
You must complete the following steps to install and configure AGPM.
Step 3: Configure an AGPM Server connection
Step 4: Configure e-mail notification
Step 1: Install AGPM Server
In this step, you install AGPM Server on the member server or domain controller that will run the AGPM Service, and you configure the archive. All AGPM operations are managed through this Windows service and are executed with the service's credentials. The archive managed by an AGPM Server can be hosted on that server or on another server in the same forest.
To install AGPM Server on the computer that will host the AGPM Service
Log on with an account that is a member of the Domain Admins group.
Start the Microsoft Desktop Optimization Pack CD and follow the instructions on screen to select Advanced Group Policy Management - Server.
In the Welcome dialog box, select Next.
In the Microsoft Software License Terms dialog box, accept the terms and select Next.
In the Application Path dialog box, select a location in which to install AGPM Server. The computer on which AGPM Server is installed will host the AGPM Service and manage the archive. Select Next.
In the Archive Path dialog box, select a location for the archive relative to the AGPM Server. The archive path can point to a folder on the AGPM Server or elsewhere, but you should select a location with sufficient space to store all GPOs and history data managed by this AGPM Server. Select Next.
In the AGPM Service Account dialog box, select a service account under which the AGPM Service will run and then select Next.
In the Archive Owner dialog box, select an account or group to which to initially assign the AGPM Administrator (Full Control) role. This AGPM Administrator can assign AGPM roles and permissions to other Group Policy administrators (including the role of AGPM Administrator). For this scenario, select the account to serve in the AGPM Administrator role. Select Next.
In the Port Configuration dialog box, type a port on which the AGPM Service should listen. Do not clear the Add port exception to firewall check box unless you manually configure port exceptions or use rules to configure port exceptions. Select Next.
In the Languages dialog box, select one or more display languages to install for AGPM Server.
Select Install, and then select Finish to exit the Setup Wizard.
Caution
Don't modify settings for the AGPM Service through Administrative Tools and Services in the operating system. Doing so can prevent the AGPM Service from starting. For information on how to modify settings for the service, see Help for Advanced Group Policy Management.
Step 2: Install AGPM Client
Each Group Policy administrator—anyone who creates, edits, deploys, reviews, or deletes GPOs—must have AGPM Client installed on computers that they use to manage GPOs. For this scenario, you install AGPM Client on at least one computer. You do not need to install AGPM Client on the computers of end users who do not perform Group Policy administration.
To install AGPM Client on the computer of a Group Policy administrator
Start the Microsoft Desktop Optimization Pack CD and follow the instructions on screen to select Advanced Group Policy Management - Client.
In the Welcome dialog box, select Next.
In the Microsoft Software License Terms dialog box, accept the terms and select Next.
In the Application Path dialog box, select a location in which to install AGPM Client. Select Next.
In the AGPM Server dialog box, type the fully-qualified computer name for the AGPM Server and the port to which to connect. The default port for the AGPM Service is 4600. Do not clear the Allow Microsoft Management Console through the firewall check box unless you manually configure port exceptions or use rules to configure port exceptions. Select Next.
In the Languages dialog box, select one or more display languages to install for AGPM Client.
Select Install, and then select Finish to exit the Setup Wizard.
Step 3: Configure an AGPM Server connection
AGPM stores all versions of each controlled Group Policy object (GPO)—a GPO for which AGPM provides change control—in a central archive, so Group Policy administrators can view and modify GPOs offline without immediately impacting the deployed version of each GPO.
In this step, you configure an AGPM Server connection and ensure that all Group Policy administrators connect to the same AGPM Server. (For information about configuring multiple AGPM Servers, see Help for Advanced Group Policy Management.)
To configure an AGPM Server connection for all Group Policy administrators
On a computer on which you have installed AGPM Client, log on with the user account that you selected as the Archive Owner. This user has the role of AGPM Administrator (Full Control).
Select Start, point to Administrative Tools, and select Group Policy Management to open the GPMC.
Edit a GPO that is applied to all Group Policy administrators.
In the Group Policy Management Editor window, double-select User Configuration, Policies, Administrative Templates, Windows Components, and AGPM.
In the details pane, double-select AGPM: Specify default AGPM Server (all domains).
In the Properties window, select Enabled and type the fully-qualified computer name and port (for example, server.contoso.com:4600) for the server hosting the archive. By default, the AGPM Service uses port 4600.
Select OK, and then close the Group Policy Management Editor window. When Group Policy is updated, the AGPM Server connection is configured for each Group Policy administrator.
Step 4: Configure e-mail notification
As an AGPM Administrator (Full Control), you designate the e-mail addresses of Approvers and AGPM Administrators to whom an e-mail message containing a request is sent when an Editor attempts to create, deploy, or delete a GPO. You also determine the alias from which these messages are sent.
To configure e-mail notification for AGPM
In the details pane, select the Domain Delegation tab.
In the From e-mail address field, type the e-mail alias for AGPM from which notifications should be sent.
In the To e-mail address field, type the e-mail address for the user account to which you intend to assign the Approver role.
In the SMTP server field, type a valid SMTP mail server.
In the User name and Password fields, type the credentials of a user with access to the SMTP service. Select Apply.
Step 5: Delegate access
As an AGPM Administrator (Full Control), you delegate domain-level access to GPOs, assigning roles to the account of each Group Policy administrator.
Note
You can also delegate access at the GPO level rather than the domain level. For details, see Help for Advanced Group Policy Management.
Important
You should restrict membership in the Group Policy Creator Owners group, so it cannot be used to circumvent AGPM management of access to GPOs. (In the Group Policy Management Console, select Group Policy Objects in the forest and domain in which you want to manage GPOs, select Delegation, and then configure the settings to meet the needs of your organization.)
To delegate access to all GPOs throughout a domain
On the Domain Delegation tab, select the Add button, select the user account of the Group Policy administrator to serve as Approver, and then select OK.
In the Add Group or User dialog box, select the Approver role to assign that role to the account, and then select OK. (This role includes the Reviewer role.)
Select the Add button, select the user account of the Group Policy administrator to serve as Editor, and then select OK.
In the Add Group or User dialog box, select the Editor role to assign that role to the account, and then select OK. (This role includes the Reviewer role.)
Select the Add button, select the user account of the Group Policy administrator to serve as Reviewer, and then select OK.
In the Add Group or User dialog box, select the Reviewer role to assign only that role to the account.
Steps for managing GPOs
You must complete the following steps to create, edit, review, and deploy GPOs using AGPM. Additionally, you will create a template, delete a GPO, and restore a deleted GPO.
Step 3: Review and deploy a GPO
Step 4: Use a template to create a GPO
Step 5: Delete and restore a GPO
Step 1: Create a GPO
In an environment with multiple Group Policy administrators, those with the Editor role have the ability to request the creation of new GPOs, but such a request must be approved by someone with the Approver role because the creation of a new GPO impacts the production environment.
In this step, you use an account with the Editor role to request the creation of a new GPO. Using an account with the Approver role, you approve this request and complete the creation of a GPO.
To request the creation of a new GPO managed through AGPM
On a computer on which you have installed AGPM Client, log on with a user account that has been assigned the Editor role in AGPM.
In the Group Policy Management Console tree, select Change Control in the forest and domain in which you want to manage GPOs.
Right-select the Change Control node, and then select New Controlled GPO.
In the New Controlled GPO dialog box:
To receive a copy of the request, type your e-mail address in the Cc field.
Type MyGPO as the name for the new GPO.
Type a comment for the new GPO.
Select Create live so the new GPO will be deployed to the production environment immediately upon approval. Select Submit.
When the AGPM Progress window indicates that overall progress is complete, select Close. The new GPO is displayed on the Pending tab.
To approve the pending request to create a GPO
On a computer on which you have installed AGPM Client, log on with a user account that has been assigned the role of Approver in AGPM.
Open the e-mail inbox for the account, and note that you have received an e-mail message from the AGPM alias with the Editor's request to create a GPO.
In the Group Policy Management Console tree, select Change Control in the forest and domain in which you want to manage GPOs.
On the Contents tab, select the Pending tab to display the pending GPOs.
Right-select MyGPO, and then select Approve.
Select Yes to confirm approval of the creation of the GPO. The GPO is moved to the Controlled tab.
Step 2: Edit a GPO
You can use GPOs to configure computer or user settings and deploy them to many computers or users. In this step, you use an account with the Editor role to check out a GPO from the archive, edit the GPO offline, check the edited GPO into the archive, and request deployment of the GPO to the production environment. For this scenario, you configure a setting in the GPO to require that the password be at least eight characters in length.
To check the GPO out from the archive for editing
On a computer on which you have installed AGPM Client, log on with a user account that has been assigned the role of Editor in AGPM.
In the Group Policy Management Console tree, select Change Control in the forest and domain in which you want to manage GPOs.
On the Contents tab in the details pane, select the Controlled tab to display the controlled GPOs.
Right-select MyGPO, and then select Check Out.
Type a comment to be displayed in the history of the GPO while it is checked out, and then select OK.
When the AGPM Progress window indicates that overall progress is complete, select Close. On the Controlled tab, the state of the GPO is identified as Checked Out.
To edit the GPO offline and configure the minimum password length
On the Controlled tab, right-select MyGPO, and then select Edit to open the Group Policy Management Editor window and make changes to an offline copy of the GPO. For this scenario, configure the minimum password length:
Under Computer Configuration, double-select Policies, Windows Settings, Security Settings, Account Policies, and Password Policy.
In the details pane, double-select Minimum password length.
In the properties window, select the Define this policy setting check box, set the number of characters to 8, and then select OK.
Close the Group Policy Management Editor window.
To check the GPO into the archive
On the Controlled tab, right-select MyGPO and then select Check In.
Type a comment, and then select OK.
When the AGPM Progress window indicates that overall progress is complete, select Close. On the Controlled tab, the state of the GPO is identified as Checked In.
To request the deployment of the GPO to the production environment
On the Controlled tab, right-select MyGPO and then select Deploy.
Because this account is not an Approver or AGPM Administrator, you must submit a request for deployment. To receive a copy of the request, type your e-mail address in the Cc field. Type a comment to be displayed in the history of the GPO, and then select Submit.
When the AGPM Progress window indicates that overall progress is complete, select Close. MyGPO is displayed on the list of GPOs on the Pending tab.
Step 3: Review and deploy a GPO
In this step, you act as an Approver, creating reports and analyzing the settings and changes to settings in the GPO to determine whether you should approve them. After evaluating the GPO, you deploy it to the production environment and link it to a domain or an organizational unit (OU) so that it takes effect when Group Policy is refreshed for computers in that domain or OU.
To review settings in the GPO
On a computer on which you have installed AGPM Client, log on with a user account that has been assigned the role of Approver in AGPM. (Any Group Policy administrator with the Reviewer role, which is included in all of the other roles, can review the settings in a GPO.)
Open the e-mail inbox for the account and note that you have received an e-mail message from the AGPM alias with an Editor's request to deploy a GPO.
In the Group Policy Management Console tree, select Change Control in the forest and domain in which you want to manage GPOs.
On the Contents tab in the details pane, select the Pending tab.
Double-select MyGPO to display its history.
Review the settings in the most recent version of MyGPO:
In the History window, right-select the GPO version with the most recent timestamp, select Settings, and then select HTML Report to display a summary of the GPO's settings.
In the Web browser, select show all to display all of the settings in the GPO. Close the browser.
Compare the most recent version of MyGPO to the first version checked in to the archive:
In the History window, select the GPO version with the most recent time stamp. Press CTRL and select the oldest GPO version for which the Computer Version is not \*.
Select the Differences button. The Account Policies/Password Policy section is highlighted in green and preceded by [+], indicating that this setting is configured only in the latter version of the GPO.
Select Account Policies/Password Policy. The Minimum password length setting is also highlighted in green and preceded by [+], indicating that it is configured only in the latter version of the GPO.
Close the Web browser.
To deploy the GPO to the production environment
On the Pending tab, right-select MyGPO and then select Approve.
Type a comment to include in the history of the GPO.
Select Yes. When the AGPM Progress window indicates that overall progress is complete, select Close. The GPO is deployed to the production environment.
To link the GPO to a domain or organizational unit
In the GPMC, right-select the domain or an OU to which to apply the GPO that you configured, and then select Link an Existing GPO.
In the Select GPO dialog box, select MyGPO, and then select OK.
Step 4: Use a template to create a GPO
In this step, you use an account with the Editor role to create a template—an uneditable, static version of a GPO for use as a starting point for creating new GPOs—and then create a new GPO based upon that template. Templates are useful for quickly creating multiple GPOs that include many of the same settings.
To create a template based on an existing GPO
On a computer on which you have installed AGPM Client, log on with a user account that has been assigned the role of Editor in AGPM.
In the Group Policy Management Console tree, select Change Control in the forest and domain in which you want to manage GPOs.
On the Contents tab in the details pane, select the Controlled tab.
Right-select MyGPO, and then select Save as Template to create a template incorporating all settings currently in MyGPO.
Type MyTemplate as the name for the template and a comment, and then select OK.
When the AGPM Progress window indicates that overall progress is complete, select Close. The new template appears on the Templates tab.
To request the creation of a new GPO managed through AGPM
Select the Controlled tab.
Right-select the Change Control node, and then select New Controlled GPO.
In the New Controlled GPO dialog box:
To receive a copy of the request, type your e-mail address in the Cc field.
Type MyOtherGPO as the name for the new GPO.
Type a comment for the new GPO.
Select Create live, so the new GPO will be deployed to the production environment immediately upon approval.
For From GPO template, select MyTemplate. Select Submit.
When the AGPM Progress window indicates that overall progress is complete, select Close. The new GPO is displayed on the Pending tab.
Use an account that has been assigned the role of Approver to approve the pending request to create the GPO as you did in Step 1: Create a GPO. MyTemplate incorporates all of the settings that you configured in MyGPO. Because MyOtherGPO was created using MyTemplate, it initially contains all of the settings that MyGPO contained at the time that MyTemplate was created. You can confirm this by generating a difference report to compare MyOtherGPO to MyTemplate.
To check the GPO out from the archive for editing
On a computer on which you have installed AGPM Client, log on with a user account that has been assigned the role of Editor in AGPM.
Right-select MyOtherGPO, and then select Check Out.
Type a comment to be displayed in the history of the GPO while it is checked out, and then select OK.
When the AGPM Progress window indicates that overall progress is complete, select Close. On the Controlled tab, the state of the GPO is identified as Checked Out.
To edit the GPO offline and configure the account lockout duration
On the Controlled tab, right-select MyOtherGPO, and then select Edit to open the Group Policy Management Editor window and make changes to an offline copy of the GPO. For this scenario, configure the minimum password length:
Under Computer Configuration, double-select Policies, Windows Settings, Security Settings, Account Policies, and Account Lockout Policy.
In the details pane, double-select Account lockout duration.
In the properties window, check Define this policy setting, set the duration to 30 minutes, and then select OK.
Close the Group Policy Management Editor window.
Check MyOtherGPO into the archive and request deployment as you did for MyGPO in Step 2: Edit a GPO. You can compare MyOtherGPO to MyGPO or to MyTemplate using difference reports. Any account that includes the Reviewer role (AGPM Administrator [Full Control], Approver, Editor, or Reviewer) can generate reports.
To compare a GPO to another GPO and to a template
To compare MyGPO and MyOtherGPO:
On the Controlled tab, select MyGPO. Press CTRL and then select MyOtherGPO.
Right-select MyOtherGPO, point to Differences, and select HTML Report.
To compare MyOtherGPO and MyTemplate:
On the Controlled tab, select MyOtherGPO.
Right-select MyOtherGPO, point to Differences, and select Template.
Select MyTemplate and HTML Report, and then select OK.
Step 5: Delete and restore a GPO
In this step, you act as an Approver to delete a GPO.
To delete a GPO
On a computer on which you have installed AGPM Client, log on with a user account that has been assigned the role of Approver.
In the Group Policy Management Console tree, select Change Control in the forest and domain in which you want to manage GPOs.
On the Contents tab, select the Controlled tab to display the controlled GPOs.
Right-select MyGPO, and then select Delete. Select Delete GPO from archive and production to delete both the version in the archive as well as the deployed version of the GPO in the production environment.
Type a comment to be displayed in the audit trail for the GPO, and then select OK.
When the AGPM Progress window indicates that overall progress is complete, select Close. The GPO is removed from the Controlled tab and is displayed on the Recycle Bin tab, where it can be restored or destroyed.
Occasionally you may discover after deleting a GPO that it is still needed. In this step, you act as an Approver to restore a GPO that has been deleted.
To restore a deleted GPO
On the Contents tab, select the Recycle Bin tab to display deleted GPOs.
Right-select MyGPO, and then select Restore.
Type a comment to be displayed in the history of the GPO, and then select OK.
When the AGPM Progress window indicates that overall progress is complete, select Close. The GPO is removed from the Recycle Bin tab and is displayed on the Controlled tab.
Note
Restoring a GPO to the archive does not automatically redeploy it to the production environment. To return the GPO to the production environment, deploy the GPO as in Step 3: Review and deploy a GPO.
After editing and deploying a GPO, you may discover that recent changes to the GPO are causing a problem. In this step, you act as an Approver to roll back to a previous version of the GPO. You can roll back to any version in the history of the GPO. You can use comments and labels to identify known good versions and when specific changes were made.
To roll back to a previous version of a GPO
On the Contents tab, select the Controlled tab to display the controlled GPOs.
Double-select MyGPO to display its history.
Right-select the version to be deployed, select Deploy, and then select Yes.
When the Progress window indicates that overall progress is complete, select Close. In the History window, select Close.
Note
To verify that the version that has been redeployed is the version intended, examine a difference report for the two versions. In the History window for the GPO, select the two versions, right-select them, point to Difference, and then select either HTML Report or XML Report.