Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
This guide will discuss the differences between a system app and a user app, and how to install a Xamarin.Android application as a system application. This guide applies to authors of custom Android ROM images. It will not explain how to create a custom ROM.
System App
Authors of custom Android ROM images or manufacturers of Android devices may wish to include a Xamarin.Android application as a system app when distributing a ROM or a device. A system app is an app that is considered to be important to the functioning of the device or provide functionality that the custom ROM author always wants to be available.
System apps are installed in the folder /system/app/ (a read-only directory on the file system) and cannot be deleted or moved by the user unless that user has root access. In contrast, an application that is installed by the user (typically from Google Play or by sideloading the app) is known as a user app. User apps can be deleted by the user and in many cases can be moved to a different location on the device (such as some kind of external storage).
System apps behave exactly like user apps, but have the following notable exceptions:
System apps are upgradable just like a normal user app. However, because a copy of the app always exists in /system/app/, it is always possible to roll back the application to the original version.
System apps may be granted certain system-only permissions that are not available to a user app. An example of a system-only permission is
BLUETOOTH_PRIVILEGED, which allows applications to pair with Bluetooth devices without any user interaction.
It is possible to distribute a Xamarin.Android app as a system application. In addition to providing an APK to the custom ROM, there are two shared libraries, libmonodroid.so and libmonosgen-2.0.so that must be manually copied from the APK to the filesytem of the ROM image. This guide will explain the steps involved.
Restrictions
This guide applies to authors of custom Android ROM images. It will not explain how to create a custom ROM.
This guide assumes familiarity with packaging a release APK for a Xamarin.Android and an understanding of CPU Architectures for Android applications.
Install a Xamarin.Android App as a System App
The following steps describe how to install a Xamarin.Android app as a system app.
Package a release APK of the Xamarin.Android app – This is described in more detail by the Publishing an Application guide.
Extract shared libraries from the APK – Using any ZIP utility program, open up the APK file and examine the contents of the /lib/ folder. This folder will have a subdirectory for each application binary interface (ABI)that is supported by the application; the contents of this folder will include all of the shared libraries that are required by the app on that particular ABI:
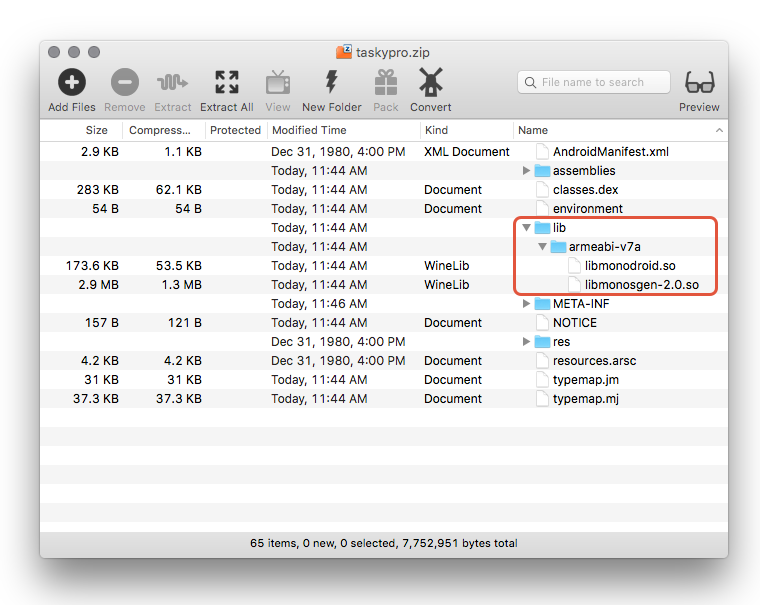
In the previous screenshot, there is only one supported ABI (armeabi-v7a) holding the two .so files that are required by the app. Note that it is only necessary to extract the ABI files that are appropriate for the device or the target architecture of the device ROM, i.e. do not copy .so files from the x86 folder to an armeabi-v7a device or ROM.
Copy .so files to /system/lib – Copy the .so files that were extracted from the APK in the previous step to the /system/lib/ folder on the custom ROM.
Copy the APK file to /system/app – The final step is to copy the APK file to the /system/app folder on the ROM.
Summary
This guide discussed the difference between a system app and a user app, and explained how to install a Xamarin.Android application as a system app.