Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Xamarin.Forms CheckBox is a type of button that can either be checked or empty. When a checkbox is checked, it's considered to be on. When a checkbox is empty, it's considered to be off.
CheckBox defines a bool property named IsChecked, which indicates whether the CheckBox is checked. This property is also backed by a BindableProperty object, which means that it can be styled, and be the target of data bindings.
Note
The IsChecked bindable property has a default binding mode of BindingMode.TwoWay.
CheckBox defines a CheckedChanged event that's fired when the IsChecked property changes, either through user manipulation or when an application sets the IsChecked property. The CheckedChangedEventArgs object that accompanies the CheckedChanged event has a single property named Value, of type bool. When the event is fired, the value of the Value property is set to the new value of the IsChecked property.
Create a CheckBox
The following example shows how to instantiate a CheckBox in XAML:
<CheckBox />
This XAML results in the appearance shown in the following screenshots:

By default, the CheckBox is empty. The CheckBox can be checked by user manipulation, or by setting the IsChecked property to true:
<CheckBox IsChecked="true" />
This XAML results in the appearance shown in the following screenshots:

Alternatively, a CheckBox can be created in code:
CheckBox checkBox = new CheckBox { IsChecked = true };
Respond to a CheckBox changing state
When the IsChecked property changes, either through user manipulation or when an application sets the IsChecked property, the CheckedChanged event fires. An event handler for this event can be registered to respond to the change:
<CheckBox CheckedChanged="OnCheckBoxCheckedChanged" />
The code-behind file contains the handler for the CheckedChanged event:
void OnCheckBoxCheckedChanged(object sender, CheckedChangedEventArgs e)
{
// Perform required operation after examining e.Value
}
The sender argument is the CheckBox responsible for this event. You can use this to access the CheckBox object, or to distinguish between multiple CheckBox objects sharing the same CheckedChanged event handler.
Alternatively, an event handler for the CheckedChanged event can be registered in code:
CheckBox checkBox = new CheckBox { ... };
checkBox.CheckedChanged += (sender, e) =>
{
// Perform required operation after examining e.Value
};
Data bind a CheckBox
The CheckedChanged event handler can be eliminated by using data binding and triggers to respond to a CheckBox being checked or empty:
<CheckBox x:Name="checkBox" />
<Label Text="Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, elit rutrum, enim hendrerit augue vitae praesent sed non, lorem aenean quis praesent pede.">
<Label.Triggers>
<DataTrigger TargetType="Label"
Binding="{Binding Source={x:Reference checkBox}, Path=IsChecked}"
Value="true">
<Setter Property="FontAttributes"
Value="Italic, Bold" />
<Setter Property="FontSize"
Value="Large" />
</DataTrigger>
</Label.Triggers>
</Label>
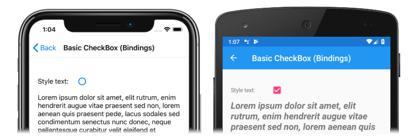
In this example, the Label uses a binding expression in a data trigger to monitor the IsChecked property of the CheckBox. When this property becomes true, the FontAttributes and FontSize properties of the Label change. When the IsChecked property returns to false, the FontAttributes and FontSize properties of the Label are reset to their initial state.
In the following screenshots, the iOS screenshot shows the Label formatting when the CheckBox is empty, while the Android screenshot shows the Label formatting when the CheckBox is checked:
For more information about triggers, see Xamarin.Forms Triggers.
Disable a Checkbox
Sometimes an application enters a state where a CheckBox being checked is not a valid operation. In such cases, the CheckBox can be disabled by setting its IsEnabled property to false.
CheckBox appearance
In addition to the properties that CheckBox inherits from the View class, CheckBox also defines a Color property that sets its color to a Color:
<CheckBox Color="Red" />
The following screenshots show a series of checked CheckBox objects, where each object has its Color property set to a different Color:

CheckBox visual states
CheckBox has an IsChecked VisualState that can be used to initiate a visual change to the CheckBox when it becomes checked.
The following XAML example shows how to define a visual state for the IsChecked state:
<CheckBox ...>
<VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
<VisualStateGroup x:Name="CommonStates">
<VisualState x:Name="Normal">
<VisualState.Setters>
<Setter Property="Color"
Value="Red" />
</VisualState.Setters>
</VisualState>
<VisualState x:Name="IsChecked">
<VisualState.Setters>
<Setter Property="Color"
Value="Green" />
</VisualState.Setters>
</VisualState>
</VisualStateGroup>
</VisualStateManager.VisualStateGroups>
</CheckBox>
In this example, the IsChecked VisualState specifies that when the CheckBox is checked, its Color property will be set to green. The Normal VisualState specifies that when the CheckBox is in a normal state, its Color property will be set to red. Therefore, the overall effect is that the CheckBox is red when it's empty, and green when it's checked.
For more information about visual states, see Xamarin.Forms Visual State Manager.