Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
The Microsoft Purview Data Map provides the foundation for data discovery and data governance. It captures metadata about data present in analytics, software-as-a-service (SaaS), and operational systems in hybrid, on-premises, and multicloud environments. The data map stays up to date with its built-in scanning and classification system.
All Microsoft Purview accounts have a data map that starts at one capacity unit, and can elastically grow. They scale up and down based on request load and metadata stored within the data map.
Data map capacity unit
The Data Map has two components: metadata storage and operation throughput, represented as a capacity unit (CU). All Microsoft Purview accounts, by default, start with one capacity unit and elastically grow based on usage. Each data Map capacity unit includes a throughput of 25 operations/sec and 10 GB of metadata storage limit.
Operations
Operations are the throughput measure of the Microsoft Purview Data Map. They include any Create, Read, Write, Update, and Delete operations on metadata stored in the Data Map. Some examples of operations are:
- Create an asset in Data Map
- Add a relationship to an asset such as owner, steward, parent, lineage, and so on
- Edit an asset to add business metadata such as description, glossary term, and so on
- Keyword search returning results to search result page
Storage
Storage is the second component of Data Map and includes the storage of technical, business, operational, and semantic metadata.
The technical metadata includes schema, data type, columns, and so on, that the Microsoft Purview scanning process discovers. The business metadata includes automated metadata, such as metadata promoted from Microsoft Power BI datasets or descriptions from SQL tables, and manual tagging of descriptions, glossary terms, and so on. Examples of semantic metadata include the collection mapping to data sources or classifications. The operational metadata includes data factory copy and data flow activity run statuses, and run times.
Working with Data Map
Elastic Data Map with autoscale – start with a Data Map as low as one capacity unit that can autoscale based on load. For most organizations, this feature leads to increased savings and a lower price point for starting data governance projects. This feature impacts pricing.
Enhanced scanning and ingestion – track and control the population of the data assets, classification, and lineage across both the scanning and ingestion processes. This feature impacts pricing.
Scenario
Claudia is a Microsoft Azure admin at Contoso who wants to create a new Microsoft Purview account from the Azure portal. She doesn't know the required size of Purview Data Map to support the future state of the platform. However, she knows that Data Map is billed using capacity units, which storage and operations throughput affect. She wants to create the smallest Data Map to keep the cost low and grow the Data Map size elastically based on consumption.
Claudia can create a Microsoft Purview account with the default Data Map size of one capacity unit that can automatically scale up and down. The autoscaling feature also allows for capacity to be tuned based on intermittent or planned data bursts during specific periods. Claudia follows the next steps in the creation experience to set up network configuration and completes the creation.
In the Azure portal, in the metrics tab for the Microsoft Purview account, Claudia can see the consumption of the Data Map storage and operations throughput. She can further set up an alert when the storage or operations throughput reaches a certain limit to monitor the consumption and billing of the new Microsoft Purview account.
Data Map billing
You pay for one capacity unit (25 ops/sec and 10 GB). Extra billing is based on the consumption of each extra capacity unit rolled up to the hour. Data Map operations scale in increments of 25 operations/sec, and metadata storage scales in increments of 10 GB. Data Map can automatically scale up and down within the elasticity window (check current limits). However, to get the next level of elasticity window, you need to create a support ticket.
Data Map capacity units come with a cap on operations throughput and storage. If storage exceeds the current capacity unit, you pay for the next capacity unit even if you don't use the operations throughput. The following table shows the Data Map capacity unit ranges. Contact support if the Data Map capacity unit goes beyond 100 capacity units.
| Data Map Capacity Unit | Operations/Sec throughput | Storage capacity in GB |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 25 | 10 |
| 2 | 50 | 20 |
| 3 | 75 | 30 |
| 4 | 100 | 40 |
| 5 | 125 | 50 |
| 6 | 150 | 60 |
| 7 | 175 | 70 |
| 8 | 200 | 80 |
| 9 | 225 | 90 |
| 10 | 250 | 100 |
| 100 | 2500 | 1000 |
Billing examples
Data Map's operation throughput for the given hour is less than or equal to 25 Ops/Sec and storage size is 1 GB. You pay for one capacity unit.
Data Map's operation throughput for the given hour is less than or equal to 25 Ops/Sec and storage size is 15 GB. You pay for two capacity units.
Data Map's operation throughput for the given hour is 50 Ops/Sec and storage size is 15 GB. You pay for two capacity units.
Data Map's operation throughput for the given hour is 50 Ops/Sec and storage size is 25 GB. You pay for three capacity units.
Data Map's operation throughput for the given hour is 250 Ops/Sec and storage size is 15 GB. You pay for 10 capacity units.
Detailed billing example
The Data Map billing example shows a Data Map with growing metadata storage and variable operations per second over a six-hour window from 12 PM to 6 PM. The red line in the graph is operations per second consumption, and the blue dotted line is metadata storage consumption over this six-hour window:
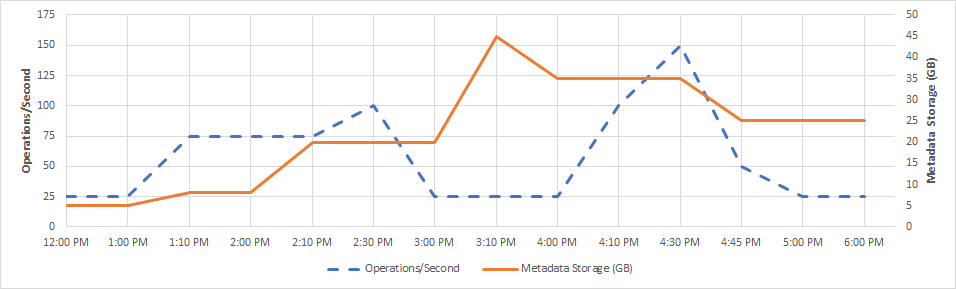
Each Data Map capacity unit supports 25 operations per second and 10 GB of metadata storage. The Data Map is billed hourly. The billing process considers the maximum Data Map capacity units needed within the hour, with a minimum of one capacity unit. At times, you might need more operations per second within the hour, and more operations increase the number of capacity units needed within that hour. At other times, your operations per second usage could be low, but you might still need a large volume of metadata storage. The metadata storage determines how many capacity units you need within the hour.
The table shows the maximum number of operations per second and metadata storage used per hour for this billing example:
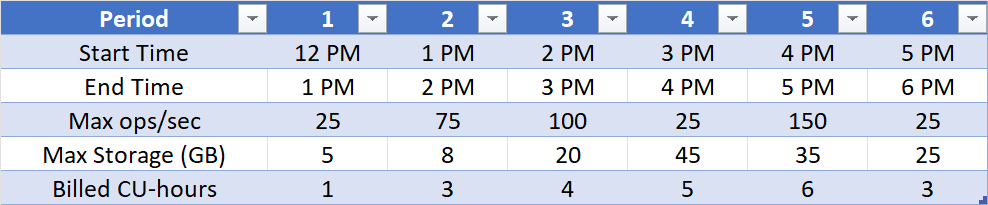
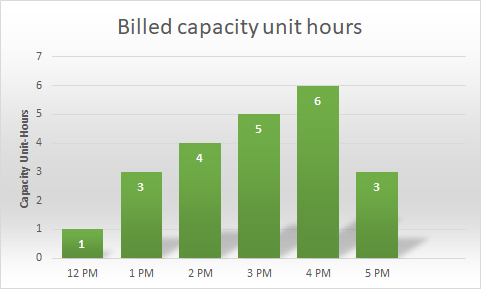
Based on the Data Map operations per second and metadata storage consumption in this period, this Data Map is billed for 22 capacity-unit hours over this six-hour period (1 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 3):
Important
Data Map can automatically scale up and down within the elasticity window (check current limits). To get the next level of the elasticity window, create a support ticket.
Increase operations throughput limit
The default limit for maximum operations per second is 10 capacity units. If you're working with a large Microsoft Purview environment and need higher throughput, you can request a larger capacity of elasticity window by creating a quota request. Select Data map capacity unit as the quota type. Provide as much relevant information as you can about your environment and the extra capacity you want.
Important
There's no default limit for metadata storage. As you add more metadata to Data Map, it elastically increases.
When you increase the operations throughput limit, you also increase the minimum number of capacity units. For example, if you increase the throughput limit to 20, you pay for a minimum of 2 capacity units. The following table shows the possible throughput options. The number you enter in the quota request is the minimum number of capacity units on the account.
| Minimum capacity units | Operations throughput limit |
|---|---|
| 1 | 10 (Default) |
| 2 | 20 |
| 3 | 30 |
| 4 | 40 |
| 5 | 50 |
| 6 | 60 |
| 7 | 70 |
| 8 | 80 |
| 9 | 90 |
| 10 | 100 |
Monitoring Data Map
The metrics data map capacity units and the data map storage size can be monitored in order to understand the data estate size and the billing.
Go to the Azure portal, and navigate to the Microsoft Purview accounts page and select your Purview account
Select Overview and scroll down to observe the Monitoring section for Data Map Capacity Units and Data Map Storage Size metrics over different time periods
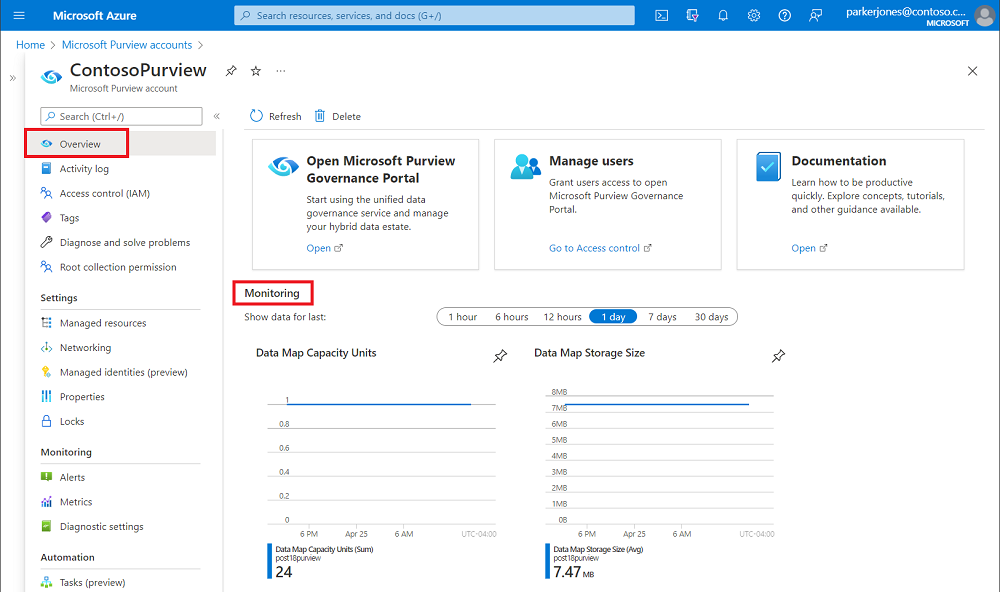
For other settings, navigate to the Monitoring --> Metrics to observe the Data Map Capacity Units and Data Map Storage Size.
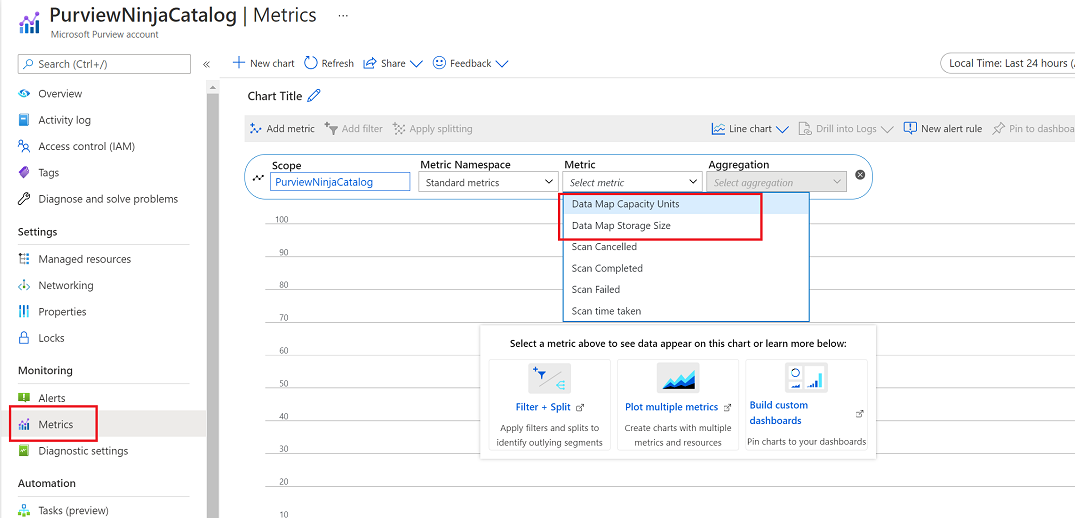
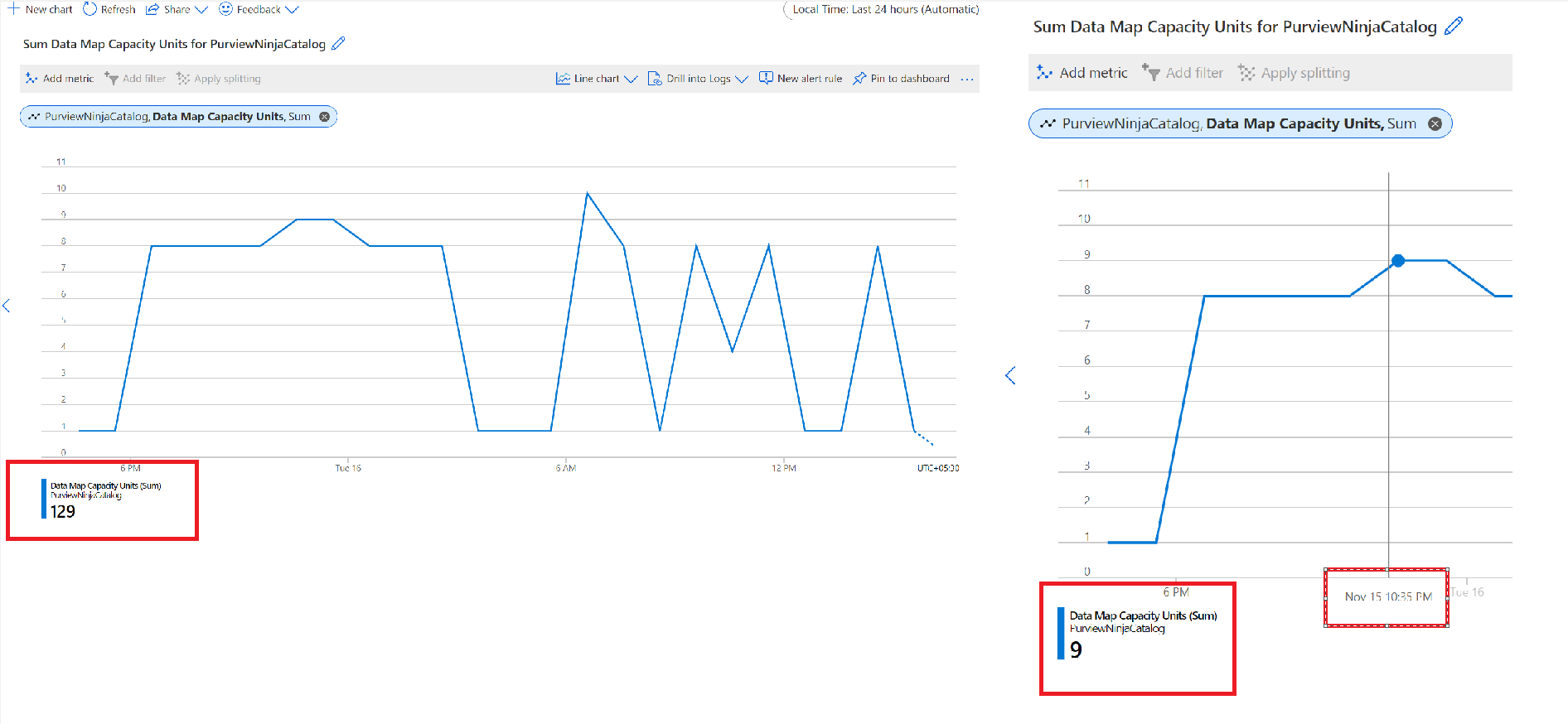
Select the Data Map Capacity Units to view the capacity unit usage over the last 24 hours. Observe that hovering the mouse over the line graph indicates the Data Map capacity units consumed at that particular time on the particular day.
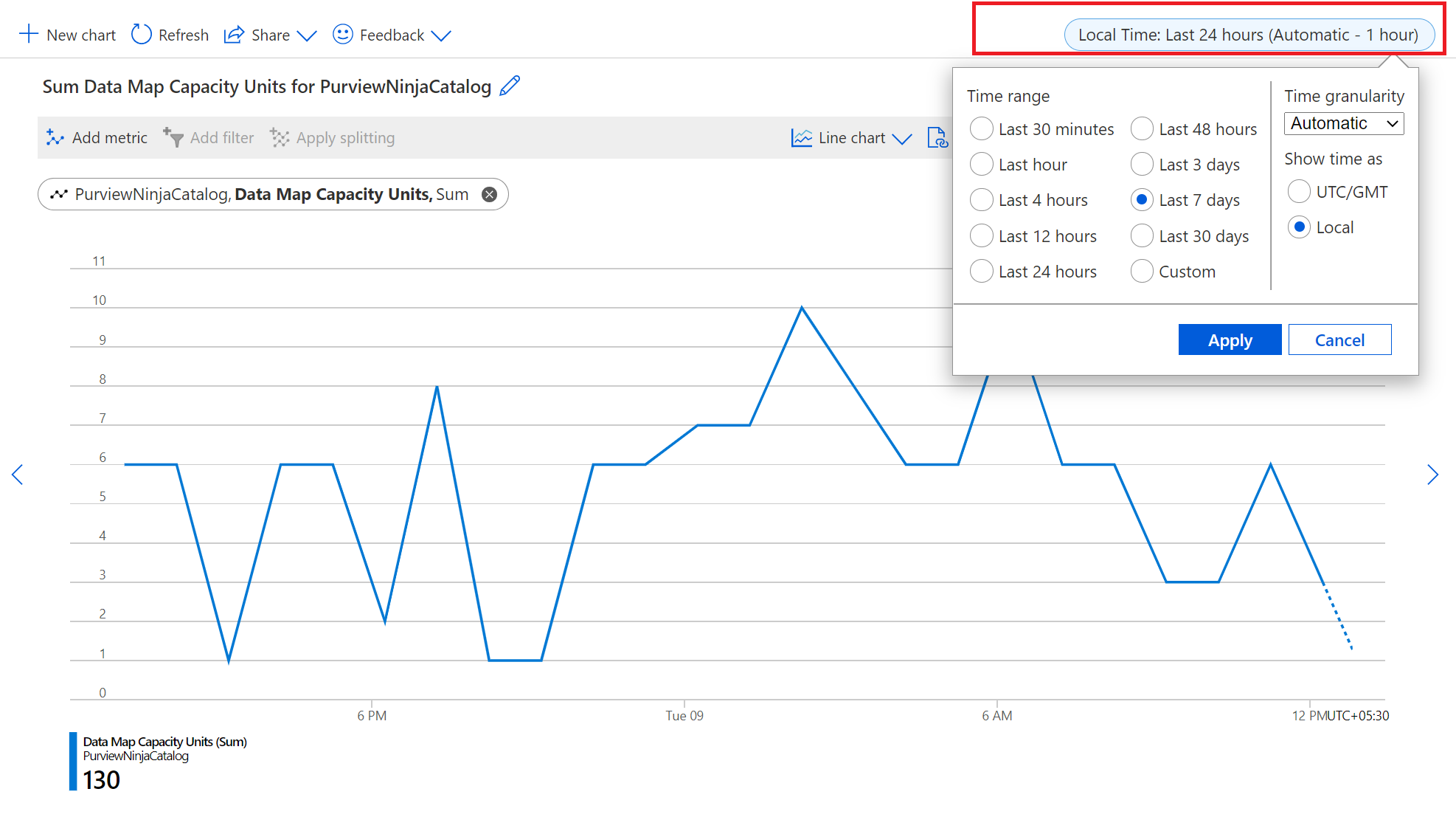
Select the Local Time: Last 24 hours (Automatic - 1 hour) at the top right of the screen to modify time range displayed for the graph.
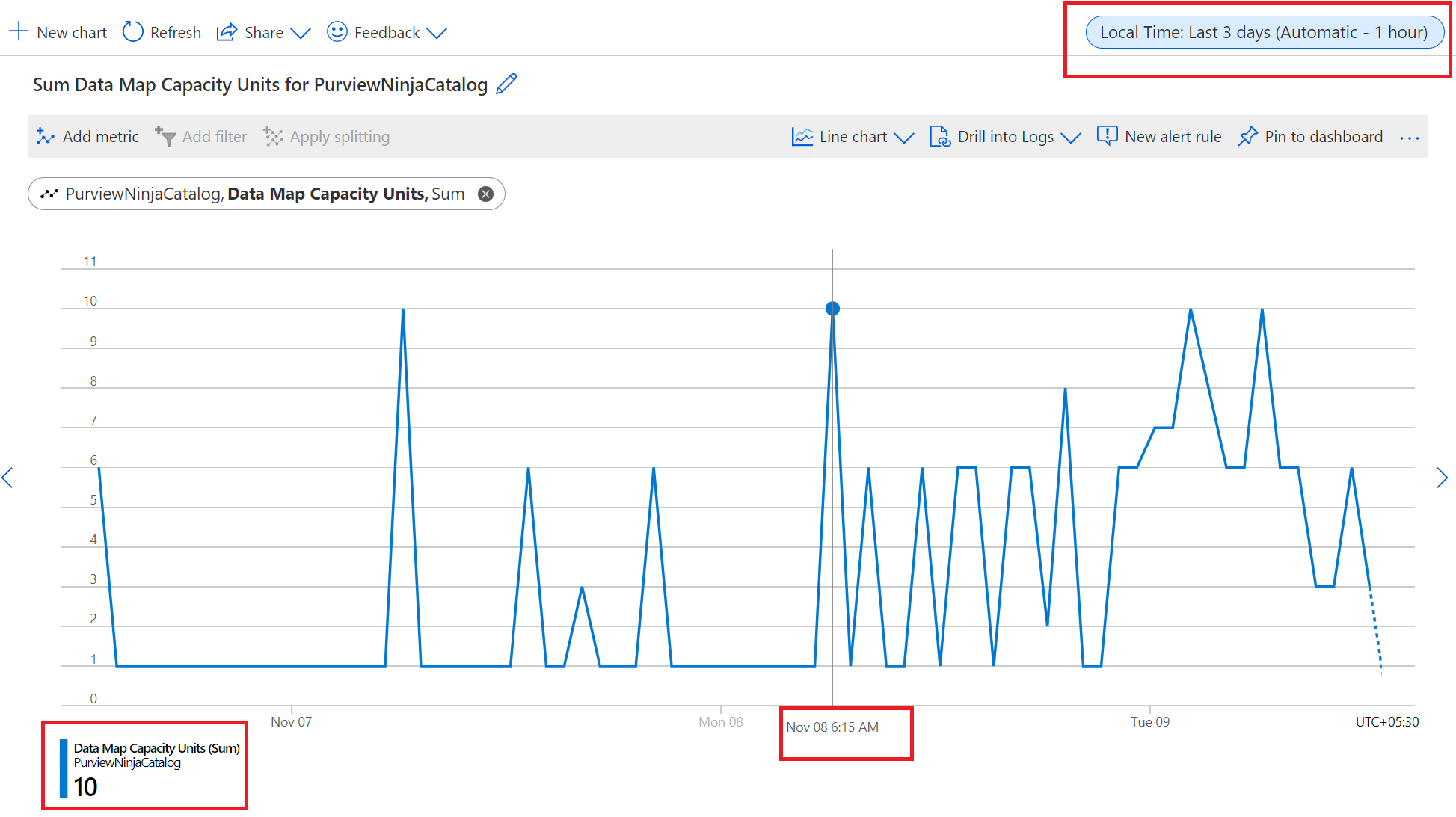
Customize the graph type by selecting the option:
Select the New chart to add the graph for the Data Map Storage Size chart.
Summary
Data Map provides a low-cost barrier for customers to start their data governance journey. Data Map can grow elastically with a pay-as-you-go model starting from as small as one capacity unit. You don't need to worry about choosing the correct Data Map size for your data estate at creation time.