JBoss EAP on RHEL (stand-alone VM)
- Solution Overview
- Template Solution Architecture
- Subscriptions and Costs
- Prerequisites
- Deployment Steps
- Deployment Time
- Validation Steps
- Troubleshooting
- Support
Solution Overview
JBoss Enterprise Application Platform (EAP) is an open source platform for highly transactional, web-scale Java applications. EAP combines the familiar and popular Jakarta EE specifications with the latest technologies, like MicroProfile, to modernize your applications from traditional Java EE into the new world of DevOps, cloud, containers, and microservices. EAP includes everything needed to build, run, deploy, and manage enterprise Java applications in a variety of environments, including on-premises, virtual environments, and in private, public, and hybrid clouds.
Red Hat Subscription Management (RHSM) is a customer-driven, end-to-end solution that provides tools for subscription status and management and integrates with Red Hat's system management tools. To obtain an RHSM account for JBoss EAP, go to: www.redhat.com.
Template Solution Architecture
This Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template creates all the Azure compute resources to run JBoss EAP 7.4 setup on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 8.6 VM as per the user choice. The following resources are created by this template:
- RHEL 8.6 Virtual Machine
- Virtual Network
- JBoss EAP 7.4 setup on a RHEL VM
- Sample Java application named JBoss-EAP on Azure deployed on JBoss EAP
- Storage Account
Note that the users will use Red Hat Enterprise Linux version 8.6 and JBoss EAP version for deployment.
- JBoss EAP 7.4 on RHEL 8.6
Following is the Architecture:
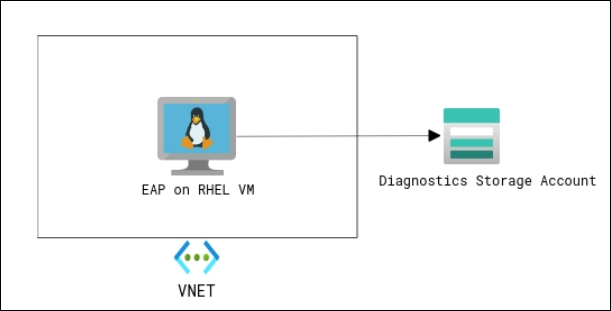
To learn more about the JBoss Enterprise Application Platform, visit: Documentation for JBoss EAP 7.4.
Subscriptions and Costs
This ARM template is designed with flexible operating system (OS) options:
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux OS as Pay-As-You-Go (PAYG) or Bring-Your-Own-Subscription (BYOS) via Red Hat Gold Image model.
- Red Hat JBoss EAP is available through BYOS only.
Using RHEL OS with PAYG Model
By default this template uses the on-demand Red Hat Enterprise Linux PAYG image from the Azure Gallery. When using this on-demand image, there is an additional hourly RHEL subscription charge for using this image on top of the normal compute, network and storage costs. At the same time, the instance will be registered to your Red Hat subscription, therefore consuming one of your entitlements. This will lead to "double billing". To avoid this, you would need to build your own RHEL image, which is defined in this Red Hat KB article for uploading RHEL image to Azure or use RHEL Gold Image from the Azure Private Gallery offering.
Read Red Hat Enterprise Linux pricing for details on the RHEL VM pricing with PAYG model. In order to use RHEL in PAYG model, you will need an Azure Subscription with the specified payment method (RHEL 8.6 is an Azure Marketplace product and requires a payment method to be specified in the Azure Subscription).
Using RHEL OS with BYOS Model
In order to use BYOS for RHEL OS Licensing, you need to have a valid Red Hat subscription with entitlements to use RHEL OS in Azure. Please complete the following prerequisites in order to use RHEL OS through BYOS model before you deploy this quickstart template.
Ensure you have RHEL OS and JBoss EAP entitlements attached to your Red Hat Subscription.
Authorize your Azure Subscription ID to use RHEL BYOS images. Please follow Red Hat Cloud Access program overview to complete this process. This includes multiple steps including:
2.1 Enable Microsoft Azure as provider in your Red Hat Cloud Access Dashboard.
2.2 Add your Azure Subscription IDs.
2.3 Enable new products for Cloud Access on Microsoft Azure.
2.4 Activate Red Hat Gold Images for your Azure Subscription. Refer to Getting access to Gold Images for more details.
2.5 Wait for Red Hat Gold Images to be available in your Azure subscription. These are typically available within 3 hours.
Accept the Marketplace Terms and Conditions in Azure for the RHEL BYOS Images. You can complete this by running Azure CLI commands, as instructed below. Refer to RHEL BYOS Gold Images in Azure documentation for more details.
3.1 Launch an Azure CLI session and make sure your CLI version is updated to version 2.8 or newer before running these commands. Check the CLI version by running the following command and if your CLI version requires updating.
az version3.2 Once your CLI session is ready, authenticate with your Azure account. Refer to Signing in with Azure CLI for assistance.
3.3 Verify the RHEL BYOS image is available in your subscription by running the following CLI command. If your RHEL BYOS is not listed, please refer to #2 and ensure that your Azure subscription is activated for RHEL BYOS images.
az vm image list --offer rhel-byos --all3.4 Run the following command to accept the Marketplace Terms for RHEL BYOS.
az vm image terms accept --publisher redhat --offer rhel-byos --plan rhel-lvm86- For RHEL 8.6 BYOS VMYour subscription is now ready to deploy RHEL 8.6 BYOS virtual machine.
Using JBoss EAP with BYOS Model
JBoss EAP is available on Azure through BYOS model only; you need to supply your RHSM credentials along with RHSM Pool ID showing valid EAP entitlements when deploying this template. If you do not have EAP entitlement, you must contact Red Hat for a subscription before you get started.
Prerequisites
Ensure you have an Azure subscription compliant with licensing requirements specified in 'Subscriptions and Costs' section.
To deploy the template, you will need:
Admin Username and password or SSH key data which is an SSH RSA public key for the VM
JBoss EAP Username and password
RHSM Username and password
RHSM Pool ID for JBoss EAP and/or RHEL OS
Deployment Steps
Build your environment with JBoss EAP 7.4 on a VM running RHEL 8.6 on Azure by clicking the Deploy to Azure button and fill in the following parameter values:
Subscription - Choose the appropriate subscription for deployment.
Resource Group - Create a new Resource Group or select an existing one.
Location - Choose the appropriate location for deployment.
Admin Username - User account name for logging into the RHEL VM.
Authentication Type - Type of authentication to use on the VM (password or SSH key).
Admin Password or SSH key - User account password or SSH key data which is an SSH RSA public key for logging into the RHEL VM.
JBoss EAP Username - Username for JBoss EAP Admin Console.
JBoss EAP Password - User account password for JBoss EAP Admin Console.
RHEL OS Subscription Type - Select the type of RHEL OS license from the dropdown options for deploying the VM. You will have either the option of PAYG (by default) or BYOS.
RHSM Username - Username for the Red Hat Subscription Manager account.
RHSM Password - User account password for your RHSM account.
RHSM Pool ID for JBoss EAP - RHSM Pool ID (ensure you have EAP entitlement)
RHSM Pool ID for RHEL - RHSM Pool ID (ensure you have RHEL entitlement). This is mandatory when selecting BYOS RHEL OS as Subscription Type. This should be left blank when selecting RHEL OS PAYG Subscription Type.
JAVA VERSION - Select the Java version to be installed.
VM Size - Select the appropriate size of the VM from the dropdown options.
Leave the rest of the parameter values (Artifacts and Location) as is, accept the Terms and Conditions, and click on Purchase.
Deployment Time
The deployment takes approximately 10 minutes to complete.
Validation Steps
Once the deployment is successful, go to the outputs section of the deployment to obtain the Private IP of the RHEL VM, app URL and the Admin Console URL. You can access the RHEL VM and the application by following one of the 5 options:
Create a Jump VM in a different Virtual Network and access the RHEL VM using Virtual Network Peering. (recommended method)
Create a Public IP to access the RHEL VM and JBoss EAP Admin Console.
Create a Jump VM in a different subnet (new subnet) in the same Virtual Network and access the RHEL VM via a Jump VM.
Using an Application Gateway.
Using an External Load Balancer (ELB).

Option 1 of 5. Create a Jump VM in a different Virtual Network and access the RHEL VM using Virtual Network Peering.
Create a Windows Virtual Machine - in a new Azure Resource Group, create a Windows VM. This should be in the same location as RHEL VM. Provide the required details and leave other configurations as default. This will create the Jump VM in a new Virtual Network.
Peer the Virtual Networks - this is how you associate the RHEL VM with the Jump VM. Once the Virtual Network peering is successful, both the VMs can communicate with each other.
Go to the Jump VM details page and copy the Public IP. Log into the Jump VM using this Public IP.
Copy the Private IP of RHEL VM from the output page and use it to log into the RHEL VM from the Jump VM.
Paste the app URL that you copied from the output page in a browser inside the Jump VM to view the JBoss EAP on Azure web page.

Access the JBoss EAP Admin Console - paste the Admin Console URL copied from the output page in a browser inside the Jump VM, enter the JBoss EAP username and password to log in.
Option 2 of 5. Create Public IP to access the RHEL VM and JBoss EAP Admin Console
The RHEL VM you created does not have a Public IP associated with it. You can create a Public IP for accessing the VM and associate the Public IP to the VM. All this can be done using Azure Portal or Powershell commands or CLI commands.
Obtain the Public IP of a VM - go to the VM details page and copy the Public IP. You can use this Public IP to access the VM and JBoss EAP Admin Console.
View the JBoss EAP on Azure web page - open a web browser and go to http://<PUBLIC_HOSTNAME>:8080/JBoss-EAP_on_Azure/ and you should see the application running.

Log into the JBoss EAP Admin Console - open a web browser and go to http://<PUBLIC_HOSTNAME>:9990. Enter the JBoss EAP username and password to log in.

Option 3 of 5. Create a Jump VM in a different subnet (new subnet) in the same Virtual Network and access the RHEL VM via Jump VM.
Add a new subnet in the existing Virtual Network which contains the RHEL VM.
Create a Windows Virtual Machine in Azure in the same Resource Group as the RHEL VM. Provide the required details and leave other configurations as default except for the Virtual Network and subnet. Make sure you select the existing Virtual Network in the Resource Group and select the subnet you just created in the step above. This will be your Jump VM.
Access Jump VM Public IP - once successfully deployed, go to the VM details page and copy the Public IP. Log into the Jump VM using this Public IP.
Log into RHEL VM - copy the Private IP of RHEL VM from the output page and use it to log into the RHEL VM from the Jump VM.
Access the JBoss EAP on Azure web page - in your Jump VM, open a browser and paste the app URL that you copied from the output page of the deployment.

Access the JBoss EAP Admin Console - paste the Admin Console URL that you copied from the output page in a browser inside the Jump VM to access the JBoss EAP Admin Console and enter the JBoss EAP username and password to log in.

Option 4 of 5. Using an Application Gateway
Create an Application Gateway - to access the ports of the RHEL VM, create an Application Gateway in a different subnet. This subnet must only contain the Application Gateway.
Set Frontends parameters - make sure you select Public IP or both and provide the required details. Under Backends section, select Add a backend pool option and add the RHEL VM to the backend pool of the Application Gateway.
Set access ports - under Configuration section add routing rules to access the ports 8080 and 9990 of the RHEL VM.
Copy Public IP of Application Gateway - once the Application Gateway is created with the required configurations, go to the overview page and copy the Public IP of the Application Gateway.
To view the JBoss EAP on Azure web page - open a web browser and go to http://<PUBLIC_IP_AppGateway>:8080/JBoss-EAP_on_Azure/ and you should see the application running.

To log into the JBoss EAP Admin Console - open a web browser and go to http://<PUBLIC_IP_AppGateway>:9990. Enter the JBoss EAP username and password to log in.

Option 5 of 5. Using an External Load Balancer.
Create a Load Balancer to access the ports of the RHEL VM. Provide the required details to deploy the external Load Balancer and leave other configurations as default. Leave the SKU as Basic for this configuration.
Add Load Balancer rules - once the Load balancer has been created successfully, create Load Balancer resources, add Load Balancer rules to access the ports 8080 and 9990 of the RHEL VM.
Add the RHEL VM to the backend pool of the Load Balancer - click on Backend pools under settings section and then select the backend pool you created in the step above. Select the Virtual Machine corresponding to the option Associated to and then add the RHEL VM.
To obtain the Public IP of the Load Balancer - go to the Load Balancer overview page and copy the Public IP of the Load Balancer.
To view the JBoss EAP on Azure web page - open a web browser and go to http://<PUBLIC_IP_LoadBalancer>:8080/JBoss-EAP_on_Azure/ and you should see the application running.

To log into the JBoss EAP Admin Console - open a web browser and go to http://<PUBLIC_IP_LoadBalancer>:9990. Enter the JBoss EAP username and password to log in.

Troubleshooting
This section includes common errors faced during deployments and details on how you can troubleshoot these errors.
Azure Platform
If the parameter criteria are not fulfilled (ex - the admin password criteria was not met) or if any mandatory parameters are not provided in the parameters section then the deployment will not start. The Terms & Conditions must be accepted before clicking on Purchase.
Once the deployment starts the resources being deployed will be visible on the deployment page. In the case of any deployment failure, after parameter validation process, a more detailed failure message is available.
If your deployment fails at the VM Custom Script Extension resource, a more detailed failure message is available in the VM log file. Please refer to the next section for further troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting EAP deployment extension
This quickstart template uses VM Custom Script Extension to deploy and configure JBoss EAP with a sample application. Your deployment can fail at this stage due to several reasons such as:
- Invalid RHSM or EAP entitlement
- Invalid JBoss EAP or RHEL OS entitlement Pool ID
Follow the steps below to troubleshoot this further:
Log into the provisioned VM through SSH as mentioned in the 'Validation section'.
Switch to root user
sudo su -Enter the VM admin password if prompted.
Change directory to logging directory
cd /var/lib/waagent/custom-script/download/0Review the logs in jbosseap.install.log log file.
more jbosseap.install.log
This log file will have details that include deployment failure reason and possible solutions. If your deployment failed due to RHSM account or entitlements, please refer to 'Subscriptions and Costs' section to complete the prerequisites and try again. Note that after your Azure subscription receives access to Red Hat Gold Images, you can locate them in the Azure portal. Go to Create a Resource > See all. At the top of the page, you'll see that You have private offers available bar, click on View private offers link to view your private offers.
Your Private Offer will be tagged with Private as seen below.
Please refer to Using the Azure Custom Script Extension Version 2 with Linux VMs for more details on troubleshooting VM custom script extensions.
Cleanup
If your deployment fails due to any reason (like the ones mentioned above), make sure you delete the whole resource group so that you are not charged for any of the resources deployed so far before failure occurred. In case of successful deployment, follow the same process of deleting the resource group created by the template and related resources (if created in other resource groups) to optimize Azure cost. Note that if you want to keep any resources in the resource group, you can delete other resources manually which does not have dependencies on the resources that you do not want to delete. Once your resources are deleted make sure you log into your RHSM account and remove the system you registered for the deployment of the template, so that you do not hit the "Maximum Enabled Entitlement Quantity" (if you have set any). You can remove the registered system under the Systems section in the Red Hat portal.
Support
For any support related questions, issues or customization requirements with the GitHub template please contact Spektra Systems.
If you are experiencing production deployment issues please contact Red Hat Support.
Tags: JBoss, Red Hat, EAP 7.4, RHEL 8.6, Azure, Azure VM, JavaEE, Microsoft.Resources/deployments, Microsoft.Storage/storageAccounts, Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks, Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces, Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines, Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/extensions, CustomScript


