Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
SQL Server on Linux
SQL Server's backup and restore feature is the recommended way to migrate a database from SQL Server on Windows to SQL Server on Linux. In this tutorial, you walk through the steps required to move a database to Linux with backup and restore techniques.
- Create a backup file on Windows with SSMS
- Install a bash shell on Windows
- Move the backup file to Linux from the bash shell
- Restore the backup file on Linux with Transact-SQL
- Run a query to verify the migration
You can also create a SQL Server Always On Availability Group to migrate a SQL Server database from Windows to Linux. See sql-server-linux-availability-group-cross-platform.
Prerequisites
The following prerequisites are required to complete this tutorial:
On a Windows machine:
- SQL Server installed.
- SQL Server Management Studio installed.
- Target database to migrate.
On a Linux machine:
- SQL Server (Red Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, or Ubuntu) with command-line tools.
Note
Starting in SQL Server 2025 (17.x), SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) isn't supported.
Create a backup on Windows
There are several ways to create a backup file of a database on Windows. The following steps use SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS).
Start SQL Server Management Studio on your Windows machine.
In the connection dialog, enter localhost.
In Object Explorer, expand Databases.
Right-click your target database, select Tasks, and then select Back Up....
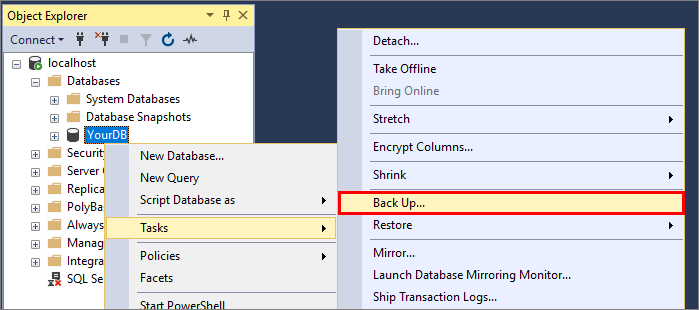
In the Backup Up Database dialog, verify that Backup type option is Full, and the Back up to option is Disk. Note name and location of the file. For example, a database named
YourDBon SQL Server 2019 (15.x) has a default backup path ofC:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Backup\YourDB.bak.Select OK to back up your database.
Another option is to run a Transact-SQL query to create the backup file. The following Transact-SQL command performs the same actions as the previous steps for a database called YourDB:
BACKUP DATABASE [YourDB]
TO DISK = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Backup\YourDB.bak'
WITH NOFORMAT, NOINIT, NAME = N'YourDB-Full Database Backup', SKIP, NOREWIND, NOUNLOAD, STATS = 10;
GO
Install a bash shell on Windows
To restore the database, you must first transfer the backup file from the Windows machine to the target Linux machine. In this tutorial, we move the file to Linux from a bash shell (terminal window) running on Windows.
Install a bash shell on your Windows machine that supports the scp (secure copy) and ssh (remote sign in) commands. Two examples include:
Open a bash session on Windows.
Copy the backup file to Linux
In your bash session, navigate to the directory containing your backup file. For example:
cd 'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\Backup\'Use the scp command to transfer the file to the target Linux machine. The following example transfers
YourDB.bakto the home directory ofuser1on the Linux server with an IP address of 192.168.2.9:scp YourDB.bak user1@192.168.2.9:./Here's the expected output:
The authenticity of host 192.168.2.9(192.168.2.9)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256: aB1cD2eF-3gH4iJ5kL6-mN7oP8qR= Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '192.168.2.9' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. Password: YourDB.bak 100% 8960KB 7.4MB/s 00:01
Tip
There are alternatives to using scp for file transfer. One is to use Samba to configure an SMB network share between Windows and Linux. For a walkthrough on Ubuntu, see Samba as a file server. Once established, you can access it as a network file share from Windows, such as \\machinenameorip\share.
Move the backup file before restoring
At this point, the backup file is on your Linux server in your user's home directory. Before restoring the database to SQL Server, you must place the backup in a subdirectory of /var/opt/mssql, as this directory is owned by the user mssql and group mssql. If you're looking to change the default backup location, see the Configure with mssql-conf article.
In the same Windows bash session, connect remotely to your target Linux machine with ssh. The following example connects to the Linux machine
192.168.2.9as useruser1.ssh user1@192.168.2.9You're now running commands on the remote Linux server.
Enter super user mode.
sudo suCreate a new backup directory. The
-pparameter does nothing if the directory already exists.mkdir -p /var/opt/mssql/backupMove the backup file to that directory. In the following example, the backup file resides in the home directory of
user1. Change the command to match the location and file name of your backup file.mv /home/user1/YourDB.bak /var/opt/mssql/backup/Exit super user mode.
exit
Restore your database on Linux
To restore the database backup, you can use the RESTORE DATABASE Transact-SQL (TQL) command.
The following steps use the sqlcmd tool. If you haven't installed SQL Server tools, see Install the sqlcmd and bcp SQL Server command-line tools on Linux.
In the same terminal, launch sqlcmd. The following example connects to the local SQL Server instance with the
saaccount. Enter the password when prompted, or specify the password by adding the-Pparameter.sqlcmd -S localhost -U saAt the
>1prompt, enter the followingRESTORE DATABASEcommand, pressing ENTER after each line (you can't copy and paste the entire multi-line command at once). Replace all occurrences ofYourDBwith the name of your database.RESTORE DATABASE YourDB FROM DISK = '/var/opt/mssql/backup/YourDB.bak' WITH MOVE 'YourDB' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB.mdf', MOVE 'YourDB_Log' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB_Log.ldf'; GOYou should get a message the database is successfully restored.
RESTORE DATABASEmight return an error like the following example:File 'YourDB_Product' cannot be restored to 'Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB_Product.ndf'. Use WITH MOVE to identify a valid location for the file. Msg 5133, Level 16, State 1, Server servername, Line 1 Directory lookup for the file "Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB_Product.ndf" failed with the operating system error 2(The system cannot find the file specified.).In this case, the database contains secondary files. If these files aren't specified in the
MOVEclause ofRESTORE DATABASE, the restore procedure tries to create them in the same path as the original server.You can list all files included in the backup:
RESTORE FILELISTONLY FROM DISK = '/var/opt/mssql/backup/YourDB.bak'; GOYou should get a list like the following example (listing only the two first columns):
LogicalName PhysicalName .............. ------------------- ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- --------------- YourDB Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB.mdf .............. YourDB_Product Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB_Product.ndf .............. YourDB_Customer Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB_Customer.ndf .............. YourDB_log Z:\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL15.GLOBAL\MSSQL\Data\YourDB\YourDB_Log.ldf ..............You can use this list to create
MOVEclauses for the extra files. In this example, theRESTORE DATABASEis:RESTORE DATABASE YourDB FROM DISK = '/var/opt/mssql/backup/YourDB.bak' WITH MOVE 'YourDB' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB.mdf', MOVE 'YourDB_Product' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB_Product.ndf', MOVE 'YourDB_Customer' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB_Customer.ndf', MOVE 'YourDB_Log' TO '/var/opt/mssql/data/YourDB_Log.ldf'; GOVerify the restoration by listing all of the databases on the server. The restored database should be listed.
SELECT name FROM sys.databases; GORun other queries on your migrated database. The following command switches context to the
YourDBdatabase and selects rows from one of its tables.USE YourDB; SELECT * FROM YourTable; GOWhen you're done using sqlcmd, type
exit.When you're done working in the remote ssh session, type
exitagain.
Next step
In this tutorial, you learned how to back up a database on Windows and move it to a Linux server running SQL Server. You learned how to:
- Use SSMS and Transact-SQL to create a backup file on Windows
- Install a Bash shell on Windows
- Use scp to move backup files from Windows to Linux
- Use ssh to remotely connect to your Linux machine
- Relocate the backup file to prepare for restore
- Use sqlcmd to run Transact-SQL commands
- Restore the database backup with the
RESTORE DATABASEcommand - Run the query to verify the migration
Next, explore other migration scenarios for SQL Server on Linux.